Abstract
Purpose
Fedratinib is an oral and selective kinase inhibitor with activity against wild type and mutationally activated Janus kinase 2 and FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3, for the treatment of adult patients with intermediate-2 or high-risk primary or secondary myelofibrosis. This open-label mass balance study in healthy subjects investigated the excretion balance and systemic exposure of radioactivity after oral administration of [14C]-fedratinib; and the pharmacokinetics of fedratinib and its contribution to overall exposure of radioactivity.
Methods
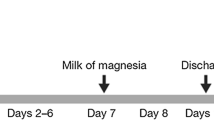
Six healthy males received a single oral dose of 200 mg [14C]-fedratinib base (2.775 MBq, 75 μCi) as a solution. Blood, urine and feces samples were collected for up to 35 day postdose. Urine and feces samples were collected until the 24-h excretion of radioactivity fell below 0.5% of administered dose (at least 14 day postdose). Expired air was collected up to 8-h postdose. Total radioactivity (blood, plasma, urine, feces, and expired air) and fedratinib concentrations (plasma) were measured.
Results
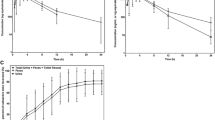
Approximately 77% (23% unchanged) of fedratinib derived radioactivity was excreted in feces and 5% (3% unchanged) was excreted in urine. Excretion via expired air was negligible. The time to maximum concentration for both total radioactivity and parent drug was similar, with unchanged drug representing the majority of the circulating radioactivity. The ratio of blood to plasma concentration of radioactivity ranged from 0.615 to 0.753 indicating limited distribution of fedratinib and/or its metabolites into red blood cells.
Conclusions
Fedratinib derived radioactivity was primarily excreted in feces following a single oral dose of radiolabeled fedratinib to healthy subjects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vainchenker W, Kralovics R (2017) Genetic basis and molecular pathophysiology of classical myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 129(6):667–679. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-10-695940
Tefferi A (2016) Primary myelofibrosis: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 91(12):1262–1271. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24592
Moulard O, Mehta J, Fryzek J, Olivares R, Iqbal U, Mesa RA (2014) Epidemiology of myelofibrosis, essential thrombocythemia, and polycythemia vera in the European Union. Eur J Haematol 92(4):289–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.12256
Celgene Corporation (2019) Inrebic (fedratinib) [package insert]. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/212327s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 11 Apr 2020
Ogasawara K, Zhou S, Krishna G, Palmisano M, Li Y (2019) Population pharmacokinetics of fedratinib in patients with myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera, and essential thrombocythemia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 84(4):891–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03929-9
Pardanani A, Gotlib JR, Jamieson C, Cortes JE, Talpaz M, Stone RM et al (2011) Safety and efficacy of TG101348, a selective JAK2 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis. J Clin Oncol 29(7):789–796. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.32.8021
Pardanani A, Tefferi A, Jamieson C, Gabrail NY, Lebedinsky C, Gao G et al (2015) A phase 2 randomized dose-ranging study of the JAK2-selective inhibitor fedratinib (SAR302503) in patients with myelofibrosis. Blood Cancer J 5:e335. https://doi.org/10.1038/bcj.2015.63
Zhang M, Xu C, Ma L, Shamiyeh E, Yin J, von Moltke LL et al (2015) Effect of food on the bioavailability and tolerability of the JAK2-selective inhibitor fedratinib (SAR302503): results from two phase I studies in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 4(4):315–321. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpdd.161
Zhang M, Xu CR, Shamiyeh E, Liu F, Yin JY, von Moltke LL et al (2014) A randomized, placebo-controlled study of the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerability of the oral JAK2 inhibitor fedratinib (SAR302503) in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 54(4):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcph.218
Ogasawara K, LoRusso PM, Olszanski AJ, Rixe O, Xu C, Yin J et al (2020) Assessment of effects of repeated oral doses of fedratinib on inhibition of cytochrome P450 activities in patients with solid tumors using a cocktail approach. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 86(1):87–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04102-3
Louton T, Kuhnz W, Dibbelt L, Knuppen R (1994) Weighted serum pools in comparison to the trapezoidal rule for estimating AUCs for ethinyl estradiol. The relationship of the variance of the determination to the interindividual variance. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 46(1):77–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00195920
Riad LE, Chan KK, Sawchuk RJ (1991) Determination of the relative formation and elimination clearance of two major carbamazepine metabolites in humans: a comparison between traditional and pooled sample analysis. Pharm Res 8(4):541–543. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1015875800846
Penner N, Klunk LJ, Prakash C (2009) Human radiolabeled mass balance studies: objectives, utilities and limitations. Biopharm Drug Dispos 30(4):185–203. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdd.661
Ogasawara K, Xu C, Kanamaluru V, Palmisano M, Krishna G (2020) Effects of repeated oral doses of ketoconazole on a sequential ascending single oral dose of fedratinib in healthy subjects. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 85(5):899–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04067-3
Roffey SJ, Obach RS, Gedge JI, Smith DA (2007) What is the objective of the mass balance study? A retrospective analysis of data in animal and human excretion studies employing radiolabeled drugs. Drug Metab Rev 39(1):17–43. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602530600952172
Ogasawara K, Smith WB, Xu C, Yin J, Palmisano M, Krishna G (2020) Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of fedratinib, an oral, selective Janus kinase 2 inhibitor, in subjects with renal or hepatic impairment. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 85(6):1109–1117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04084-2
Docci D, Bilancioni R, Pistocchi E, Mosconi G, Turci F, Salvi G et al (1985) Serum alpha-1-acid glycoprotein in chronic renal failure. Nephron 39(3):160–163. https://doi.org/10.1159/000183364
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all study participants, their families and clinical study team members.
Funding
The clinical pharmacology study was sponsored by Sanofi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K.O., S.S., M.P., and G.K. are employees and hold equity ownership in Bristol Myers Squibb. C.X., V.K., and L.R. are employees and hold equity ownership in Sanofi. N.S. is an employee of Covance, which was paid by Sanofi to conduct the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogasawara, K., Xu, C., Kanamaluru, V. et al. Excretion balance and pharmacokinetics following a single oral dose of [14C]-fedratinib in healthy subjects. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 86, 307–314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04121-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-020-04121-0