Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to measure the frequency of three CYP2B6 [CYP2B6*4 (rs2279343), CYP2B6*5 (rs3211371) and CYP2B6*9 (rs3745274)] alleles in patients with breast cancer receiving cyclophosphamide (CP) therapy and test whether these variants are predictors of CP-associated toxicity and efficacy.
Methods
A total of 145 female breast cancer patients admitted to the American University of Beirut Medical Center for breast cancer-related therapy were included. Chart review was performed for collection of toxicity data. A time-to-event analysis was performed with a subset of 38 patients.
Results
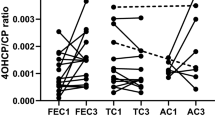
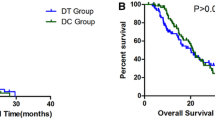
The minor allele frequencies of CYP2B6*9, CYP2B6*4 and CYP2B6*5 were 0.27, 0.29 and 0.07, respectively. CYP2B6 *5/*6, *6/*9 or *6/*6 haplotypes were associated with a significantly shorter time to recurrence of the disease. There were no significant associations with myelo-toxicity.
Conclusions
This is the first report on the pharmacogenetic profile of patients with breast cancer and the therapeutic and myelo-toxic behavior of CP in women from an Arab Middle Eastern country. Our results show that genotyping for these CYP2B6 alleles does not help in personalizing therapy from a toxicity perspective, and the association of shorter survival in these subjects with homozygous variants is interesting yet insufficient to justify routine genotyping prior to therapy, or to consider using a higher CP dose. Larger future studies or meta-analyses will be needed to further clarify the potential implication of these genetic polymorphisms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ (2007) Progress and promise: highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer. Ann Oncol 18:1133–1144
Pinto N, Ludeman SM, Dolan ME (2009) Drug focus: pharmacogenetic studies related to cyclophosphamide-based therapy. Pharmacogenomics 10:1897–1903
Ekhart C, Doodeman VD, Rodenhuis S, Smits PH, Beijnen JH, Huitema AD (2008) Influence of polymorphisms of drug metabolizing enzymes (CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, GSTA1, GSTP1, ALDH1A1 and ALDH3A1) on the pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide and 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide. Pharmacogenet Genomics 18:515–523
Roy P, Yu LJ, Crespi CL, Waxman DJ (1999) Development of a substrate-activity based approach to identify the major human liver P-450 catalysts of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide activation based on cDNA-expressed activities and liver microsomal P-450 profiles. Drug Metab Dispos 27:655–666
Wang H, Tompkins LM (2008) CYP2B6: new insights into a historically overlooked cytochrome P450 isozyme. Curr Drug Metab 9:598–610
Choi JY, Nowell SA, Blanco JG, Ambrosone CB (2006) The role of genetic variability in drug metabolism pathways in breast cancer prognosis. Pharmacogenomics 7:613–624
Petros WP, Broadwater G, Berry D, Jones RB, Vredenburgh JJ, Gilbert CJ, Gibbs JP, Colvin OM, Peters WP (2002) Association of high-dose cyclophosphamide, cisplatin, and carmustine pharmacokinetics with survival, toxicity, and dosing weight in patients with primary breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 8:698–705
Petros WP, Hopkins PJ, Spruill S, Broadwater G, Vredenburgh JJ, Colvin OM, Peters WP, Jones RB, Hall J, Marks JR (2005) Associations between drug metabolism genotype, chemotherapy pharmacokinetics, and overall survival in patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:6117–6125
Xie H, Griskevicius L, Stahle L, Hassan Z, Yasar U, Rane A, Broberg U, Kimby E, Hassan M (2006) Pharmacogenetics of cyclophosphamide in patients with hematological malignancies. Eur J Pharm Sci 27:54–61
Nakajima M, Komagata S, Fujiki Y, Kanada Y, Ebi H, Itoh K, Mukai H, Yokoi T, Minami H (2007) Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2B6 affect the pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of cyclophosphamide in Japanese cancer patients. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17:431–445
Bray J, Sludden J, Griffin MJ, Cole M, Verrill M, Jamieson D, Boddy AV (2010) Influence of pharmacogenetics on response and toxicity in breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Br J Cancer 102:1003–1009
Low SK, Kiyotani K, Mushiroda T, Daigo Y, Nakamura Y, Zembutsu H (2009) Association study of genetic polymorphism in ABCC4 with cyclophosphamide-induced adverse drug reactions in breast cancer patients. J Hum Genet 54:564–571
Gor PP, Su HI, Gray RJ, Gimotty PA, Horn M, Aplenc R, Vaughan WP, Tallman MS, Rebbek TR, DeMichele A (2010) Cyclophosphamide-metabolizing enzyme polymorphisms and survival outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Breast Cancer Res 12:R26
Yao S, Barlow WE, Albain KS, Choi JY, Zhao H, Livingston RB, Davis W, Rae JM, Yeh IT, Hutchins MF, Ravdin PM, Martino S, Lyss AP, Osborne CK, Abeloff M, Hortobagyi GN, Hayes DF, Ambrosone CB (2010) Gene polymorphisms in cyclophosphamide metabolism pathway, treatment-related toxicity, and disease-free survival in SWOG 8897 clinical trial for breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16:6169–6176
National Cancer Institute. Common terminology criteria for adverse events. http://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/About.html. Accessed 1 Jan 2010
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism-release: NCBI dbSNP build 130. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed. Accessed 1 Jan 2010
Al-Dayel F, Al-Rasheed M, Ibrahim M, Bu R, Bavi P, Abubaker J, Al-Jomah N, Mohamed GH, Moorji A, Uddin S, Siraj AK, Al-Kuraya K (2008) Polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes CYP1A1, GSTT and GSTP contribute to the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma risk in the Saudi Arabian population. Leuk Lymphoma 49:122–129
Darazy M, Balbaa M, Mugharbil A, Saeed H, Sidani H, Abdel-Razzak Z (2011) CYP1A1, CYP2E1, and GSTM1 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to colorectal and gastric cancer among Lebanese. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 15:423–429
Ren S, Yang JS, Kalhorn TF, Slattery JT (1997) Oxidation of cyclophosphamide to 4-hydroxycyclophosphamide and deschloroethylcyclophosphamide in human liver microsomes. Cancer Res 57:4229–4235
Ren S, Kalhorn TF, McDonald GB, Anasetti C, Appelbaum FR, Slattery JT (1998) Pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide and its metabolites in bone marrow transplantation patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 64:289–301
Chang TK, Yu L, Goldstein JA, Waxman DJ (1997) Identification of the polymorphically expressed CYP2C19 and the wild-type CYP2C9-ILE359 allele as low-Km catalysts of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide activation. Pharmacogenetics 7:211–221
Griskevicius L, Yasar U, Sandberg M, Hidestrand M, Eliasson E, Tybring G, Hassan M, Dahl M (2003) Bioactivation of cyclophosphamide: the role of polymorphic CYP2C enzymes. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 59:103–109
Lang T, Klein K, Fischer J, Nussler AK, Neuhaus P, Hofmann U, Eichelbaum M, Schwab M, Zanger UM (2001) Extensive genetic polymorphism in the human CYP2B6 gene with impact on expression and function in human liver. Pharmacogenetics 11:399–415
Jinno H, Tanaka-Kagawa T, Ohno A, Makino Y, Matsushima E, Hanioka N, Ando M (2003) Functional characterization of cytochrome P450 2B6 allelic variants. Drug Metab Dispos 31:398–403
Fernandes BJD, Silva CDM, Andrade JM, Matthes Ado C, Coelho EB, Lanchote VL (2011) Pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide enantiomers in patients with breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68:897–904
Afsar NA, Ufer M, Haenisch S, Remmler C, Mateen A, Usman A, Ahmed KZ, Ahmad HR, Cascorbi I (2012) Relationship of drug metabolizing enzyme genotype to plasma levels as well as myelotoxicity of cyclophosphamide in breast cancer patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68:389–395
Lamba V, Lamba J, Yasuda K, Strom S, Davila J, Hancock ML, Fackenthal JD, Rogan PK, Ring B, Wrighton SA, Schuetz EG (2003) Hepatic CYP2B6 expression: gender and ethnic differences and relationship to CYP2B6 genotype and CAR (constitutive androstane receptor) expression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:906–922
Hesse LM, He P, Krishnaswamy S, Hao Q, Hogan K, von Moltke LL, Greenblatt DJ, Court MH (2004) Pharmacogenetic determinants of interindividual variability in bupropion hydroxylation by cytochrome P450 2B6 in human liver microsomes. Pharmacogenetics 14:225–238
Takada K, Arefayene M, Desta Z, Yarboro CH, Balow JE, Flockhart DA, Illei GG (2004) Cytochrome P450 pharmacogenetics as a predictor of toxicity and clinical response to pulse cyclophosphamide in lupus nephritic. Arth Rheum 50:2202–2210
Ossaily S, Zgheib NK (2014) The pharmacogenetics of drug metabolizing enzymes in the Lebanese population. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 29:81–90
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Joseph Simaan for reviewing and editing the manuscript. This study was funded by American University of Beirut Medical Practice Plan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. Haroun and L. Al-Shaar made equal contribution.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haroun, F., Al-Shaar, L., Habib, R.H. et al. Effects of CYP2B6 genetic polymorphisms in patients receiving cyclophosphamide combination chemotherapy for breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 75, 207–214 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2632-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2632-4