Abstract
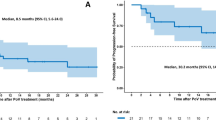
Polatuzumab (Pola)-based regimens and chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T) cells provide superior outcome compared to conventional chemoimmunotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma (R/R DLBCL). Choosing between these strategies remains controversial. The efficacy of CAR T versus Pola-rituximab(R) /Pola-bendamustine(B)-R in R/R DLBCL patients after failing ≥2 lines of treatment was compared in a retrospective, ‘real-world’ study. Propensity score matching, for age, lymphoma category (de-novo/transformed), number of prior lines, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status and lactate dehydrogenase level, was applied to control for differences in patients’ characteristics. Response rate, progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were analyzed. A total of 82 patients, treated with CAR T (n=41) or Pola-based regimens (n=41), were included. No treatment-related deaths occurred with CAR T vs. 3 (7.3%) with Pola. The overall and complete response rates were 83% and 58% with CAR T vs. 66% and 44% with Pola-based-regimens (p=0.077 and p=0.18, respectively). At a median follow-up of 9 months (range 1–19.2) and 16 months (range 0.7–25.3) for the CAR T and Pola arm respectively, the median PFS has not been reached for CAR T vs. 5.6 months for Pola (95% CI 3.6–7.6, p=0.014). Median OS has not been reached for CAR T vs. 10.8 months (95% CI 2.2–19.4) for Pola (p=0.026). To conclude, in a real-world setting, treatment with CAR T achieved superior PFS and OS compared to Pola-based regimens in patients with R/R DLBCL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sehn LH, Herrera AF, Flowers CR, Kamdar MK, McMillan A, Hertzberg M et al (2020) Polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 38(2):155–165
Sehn LH, Herrera AF, Flowers CR, Kamdar MK, McMillan A, Hertzberg M, et al. (2020) Polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In: J Clin Oncol 38(2):155–165
van den Neste E, Schmitz N, Mounier N, Gill D, Linch D, Trneny M et al (2016) Outcome of patients with relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who fail second-line salvage regimens in the International CORAL study. Bone Marrow Transplant 51(1):51–7
Crump M, Neelapu SS, Farooq U, et al. (2017) Outcomes in refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the international SCHOLAR-1 study. Blood 130(16):1800–1808
Segman Y, Ribakovsky E, Avigdor A, Goldhecht Y, Vainstein V, Goldschmidt N, et al. (2021) Outcome of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with polatuzumab vedotin-based therapy: real-life experience. Leuk Lymphoma 62(1):118–124
Dimou M, Papageorgiou SG, Stavroyianni N, Katodritou E, Tsirogianni M, Kalpadakis C, et al. (2021) Real-life experience with the combination of polatuzumab vedotin, rituximab, and bendamustine in aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Hematol Oncol 39(3):336–348
Smith SD, Lopedote P, Samara Y, Mei M, Herrera AF, Winter AM, et al. (2021) Polatuzumab vedotin for relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma: a multicenter post-marketing analysis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 21(3): 170–175
Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, et al. (2017) Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-Cell therapy in refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 377(26):2531-2544
Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Jacobson CA, Miklos DB, Lekakis LJ, Oluwole OO, et al. (2019) Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B-cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20(1):31–42
Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, et al. (2019) Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 380(1):45–56
Neelapu SS (2019) Managing the toxicities of CAR T-cell therapy. Hematol Oncol. 37(S1):48–52
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, et al. (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103(1):275–82
Yakoub-Agha I, Chabannon C, Bader P, Basak GW, Bonig H, Ciceri F, et al. (2020) Management of adults and children undergoing chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy: best practice recommendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) and the Joint Accreditation Committee of ISCT and EBMT (JACIE). Haematologica 105(2):297–316
Lee DW, Santomasso BD, Locke FL, Ghobadi A, Turtle CJ, Brudno JN, et al. (2019) ASTCT consensus grading for cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity associated with immune effector cells. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 25(4):625–638
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF, Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, et al. (2014) Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: the Lugano classification. J Clin Oncol. 32(27):3059–68
Al-Mansour M, Al-Foheidi M, Ibrahim E (2020) Efficacy and safety of second-generation CAR T-cell therapy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis. Mol Clinical Oncol. 13(4):33
Sermer D, Batlevi C, Lia Palomba M, Shah G, Lin RJ, Perales MA, et al. (2020) Outcomes in patients with DLBCL treated with commercial CAR T cells compared with alternate therapies. Blood Adv. 4(19):4669–4678
Hopfinger G, Jäger U, Worel N (2019) CAR-T cell therapy in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: hype and hope. Hemasphere 3(2):e185
Vercellino L, di Blasi R, Kanoun S, Tessoulin B, Rossi C, D’Aveni-Piney M, et al. (2020) Predictive factors of early progression after CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 4(22):5607–5615
Khurana A, Hathcock MA, Habermann TM, al Saleh AS, Gandhi S, Truong TA, et al. (2021) Lines of therapy before autologous stem cell transplant and CAR-T affect outcomes in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 96(10):E386–E389
Hiddemann W, Barbui AM, Canales MA, Cannell PK, Collins GP, Dürig J, et al. (2018) Immunochemotherapy with obinutuzumab or rituximab for previously untreated follicular lymphoma in the GALLIUM study: Influence of chemotherapy on efficacy and safety. J Clin Oncol. 36(23):2395–2404
Martínez-Calle N, Hartley S, Ahearne M, Kasenda B, Beech A, Knight H, et al. (2019) Kinetics of T-cell subset reconstitution following treatment with bendamustine and rituximab for low-grade lymphoproliferative disease: a population-based analysis. Br J Haematol. 184(6):957–968
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by IA, YS and RR. The first draft of the manuscript was written by IA and RR, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
RR received a speaker honorarium from Gilead. Takeda and Novartis. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(JPG 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avivi, I., Perry, C., Segman, Y. et al. Polatuzumab-based regimen or CAR T cell for patients with refractory/relapsed DLBCL—a matched cohort analysis. Ann Hematol 101, 755–762 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04749-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-021-04749-9