Abstract
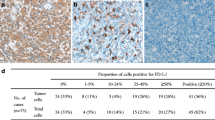
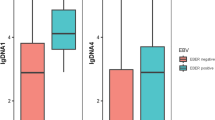
Although gemcitabine, oxaliplatin and L-asparaginase/pegylated asparaginase (P-GEMOX) treatment for early-stage extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma (ENKTL) is effective, some patients die within 1 year of diagnosis. We attempted to determine an optimal biomarker for identifying such patients. We enrolled 71 patients with ENKTL who received P-GEMOX between January 2011 and January 2014. We classified the patients according to the outcome into worse (died within 1 year) or better groups (survival time ≥ 3, 4 or 5 years). The area under the curve (AUC) was determined to identify the optimal biomarker for differentiating the groups. The AUC was highest in patients who were plasma Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) DNA-positive post-treatment. The AUC was 0.82, 0.86 and 0.86 when the worse group was compared to the better group, respectively. Among the post-treatment EBV DNA-positive patients, as compared to EBV DNA-negative patients, pre-treatment EBV DNA-positive patients had a higher proportion of CD4 + CD25 + T cells. There was higher programmed cell death protein ligand-1(PD-L1) expression in post-treatment EBV DNA-positive patients. Post-treatment positive EBV DNA status maybe a useful biomarker of worse outcomes in early stage ENKTL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D, International TCLP (2008) International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26(25):4124–4130
Lim MS, de Leval L, Quintanilla-Martinez L (2009) Commentary on the 2008 WHO classification of mature T- and NK-cell neoplasms. J Hematop 2(2):65–73
Li CC, Tien HF, Tang JL, Yao M, Chen YC, Su IJ, Hsu SM, Hong RL (2004) Treatment outcome and pattern of failure in 77 patients with sinonasal natural killer/T-cell or T-cell lymphoma. Cancer 100(2):366–375
Chim CS, Ma SY, Au WY, Choy C, Lie AK, Liang R, Yau CC, Kwong YL (2004) Primary nasal natural killer cell lymphoma: long-term treatment outcome and relationship with the International Prognostic Index. Blood 103(1):216–221
Huang MJ, Jiang Y, Liu WP, Li ZP, Li M, Zhou L, Xu Y, Yu CH, Li Q, Peng F, Liu JY, Luo F, Lu Y (2008) Early or up-front radiotherapy improved survival of localized extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type in the upper aerodigestive tract. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70(1):166–174
Guo Y, Lu JJ, Ma X, Wang B, Hong X, Li X, Li J (2008) Combined chemoradiation for the management of nasal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma: elucidating the significance of systemic chemotherapy. Oral Oncol 44(1):23–30
Wang L, Wang WD, Xia ZJ, Zhang YJ, Xiang J, Lu Y (2014) Combination of gemcitabine, L-asparaginase, and oxaliplatin (GELOX) is superior to EPOCH or CHOP in the treatment of patients with stage IE/IIE extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma: a retrospective study in a cohort of 227 patients with long-term follow-up. Med Oncol 31(3):860
Wang L, Wang ZH, Chen XQ, Li YJ, Wang KF, Xia YF, Xia ZJ (2013) First-line combination of gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and L-asparaginase (GELOX) followed by involved-field radiation therapy for patients with stage IE/IIE extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer 119(2):348–355
Bi XW, Xia Y, Zhang WW, Sun P, Liu PP, Wang Y, Huang JJ, Jiang WQ, Li ZM (2015) Radiotherapy and PGEMOX/GELOX regimen improved prognosis in elderly patients with early-stage extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 94(9):1525–1533
Huang JJ, Jiang WQ, Lin TY, Huang Y, Xu RH, Huang HQ, Li ZM (2011) Absolute lymphocyte count is a novel prognostic indicator in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Annals of Oncology: Official Journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology/ESMO 22(1):149–155
Cai Q, Luo X, Liang Y, Rao H, Fang X, Jiang W, Lin T, Lin T, Huang H (2013) Fasting blood glucose is a novel prognostic indicator for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Br J Cancer 108(2):380–386
Li YJ, Li ZM, Xia Y, Huang JJ, Huang HQ, Xia ZJ, Lin TY, Li S, Cai XY, Wu-Xiao ZJ, Jiang WQ (2013) Serum C-reactive protein (CRP) as a simple and independent prognostic factor in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. PLoS One 8(5):e64158
Yamaguchi M, Kwong YL, Kim WS, Maeda Y, Hashimoto C, Suh C, Izutsu K, Ishida F, Isobe Y, Sueoka E, Suzumiya J, Kodama T, Kimura H, Hyo R, Nakamura S, Oshimi K, Suzuki R (2011) Phase II study of SMILE chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage IV, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: the NK-cell tumor study group study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 29(33):4410–4416
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee JH, Lee DH, Huh J, Oh SY, Kwon HC, Kim HJ, Lee SI, Kim JH, Park J, Oh SJ, Kim K, Jung C, Park K, Kim WS (2006) Extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: a prognostic model from a retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 24(4):612–618
Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Jaccard A, Chng WJ, Lim ST, Hong H, Park Y, Chang KM, Maeda Y, Ishida F, Shin DY, Kim JS, Jeong SH, Yang DH, Jo JC, Lee GW, Choi CW, Lee WS, Chen TY, Kim K, Jung SH, Murayama T, Oki Y, Advani R, d’Amore F, Schmitz N, Suh C, Suzuki R, Kwong YL, Lin TY, Kim WS (2016) A prognostic index for natural killer cell lymphoma after non-anthracycline-based treatment: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. The Lancet Oncology 17(3):389–400
Sabattini E, Bacci F, Sagramoso C, Pileri SA (2010) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues in 2008: an overview. Pathologica 102(3):83–87
Fryer JF, Heath AB, Wilkinson DE, Minor PD, Collaborative Study Group (2016) A collaborative study to establish the 1st WHO international standard for Epstein-Barr virus for nucleic acid amplification techniques. Biologicals: Journal of the International Association of Biological Standardization 44(5):423–433
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, Lister TA, Vose J, Grillo-Lopez A, Hagenbeek A et al (1999) Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. NCI sponsored international working group. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 17(4):1244
Paydas S, Bagir E, Seydaoglu G, Ercolak V, Ergin M (2015) Programmed death-1 (PD-1), programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), and EBV-encoded RNA (EBER) expression in Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann Hematol 94(9):1545–1552
Wang ZY, Liu QF, Wang H, Jin J, Wang WH, Wang SL, Song YW, Liu YP, Fang H, Ren H, Wu RY, Chen B, Zhang XM, Lu NN, Zhou LQ, Li YX (2012) Clinical implications of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA in early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma patients receiving primary radiotherapy. Blood 120(10):2003–2010
Kwong YL, Pang AW, Leung AY, Chim CS, Tse E (2014) Quantification of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA in NK/T-cell lymphoma treated with the SMILE protocol: diagnostic and prognostic significance. Leukemia 28(4):865–870
Wang L, Wang H, Wang JH, Xia ZJ, Lu Y, Huang HQ, Jiang WQ, Zhang YJ (2015) Post-treatment plasma EBV-DNA positivity predicts early relapse and poor prognosis for patients with extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma in the era of asparaginase. Oncotarget 6(30):30317–30326
Kim SJ, Choi JY, Hyun SH, Ki CS, Oh D, Ahn YC, Ko YH, Choi S, Jung SH, Khong PL, Tang T, Yan X, Lim ST, Kwong YL, Kim WS, Asia Lymphoma Study Group (2015) Risk stratification on the basis of Deauville score on PET-CT and the presence of Epstein-Barr virus DNA after completion of primary treatment for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: a multicentre, retrospective analysis. The Lancet Haematology 2(2):e66–e74
Lei KI, Chan LY, Chan WY, Johnson PJ, Lo YM (2002) Diagnostic and prognostic implications of circulating cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Clinical Cancer Research: An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 8(1):29–34
Au WY, Pang A, Choy C, Chim CS, Kwong YL (2004) Quantification of circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in the diagnosis and monitoring of natural killer cell and EBV-positive lymphomas in immunocompetent patients. Blood 104(1):243–249
Ishii H, Ogino T, Berger C, Kochli-Schmitz N, Nagato T, Takahara M, Nadal D, Harabuchi Y (2007) Clinical usefulness of serum EBV DNA levels of BamHI W and LMP1 for nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. J Med Virol 79(5):562–572
Kim HS, Kim KH, Kim KH, Chang MH, Ji SH, Lim DH, Kim K, Kim SJ, Ko Y, Ki CS, Jo SJ, Lee JW, Kim WS (2009) Whole blood Epstein-Barr virus DNA load as a diagnostic and prognostic surrogate: extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia & Lymphoma 50(5):757–763
Suzuki R, Yamaguchi M, Izutsu K, Yamamoto G, Takada K, Harabuchi Y, Isobe Y, Gomyo H, Koike T, Okamoto M, Hyo R, Suzumiya J, Nakamura S, Kawa K, Oshimi K, the NK-cell Tumor Study Group (2011) Prospective measurement of Epstein-Barr virus-DNA in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 118(23):6018–6022
Ito Y, Kimura H, Maeda Y, Hashimoto C, Ishida F, Izutsu K, Fukushima N, Isobe Y, Takizawa J, Hasegawa Y, Kobayashi H, Okamura S, Kobayashi H, Yamaguchi M, Suzumiya J, Hyo R, Nakamura S, Kawa K, Oshimi K, Suzuki R (2012) Pretreatment EBV-DNA copy number is predictive of response and toxicities to SMILE chemotherapy for extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Clinical Cancer Research: An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 18(15):4183–4190
Lu TX, Liang JH, Miao Y, Fan L, Wang L, Qu XY, Cao L, Gong QX, Wang Z, Zhang ZH, Xu W, Li JY (2015) Epstein-Barr virus positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma predict poor outcome, regardless of the age. Sci Rep 5:12168
Cardenas D, Velez G, Orfao A, Herrera MV, Solano J, Olaya M, Uribe AM, Saavedra C, Duarte M, Rodriguez M et al (2015) Epstein-Barr virus-specific CD8(+) T lymphocytes from diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients are functionally impaired. Clin Exp Immunol 182(2):173–183
Cui Q, Gandhi MK (2016) Whole blood EBV-DNA: a surrogate for immune dysfunction in aggressive lymphoma? Leukemia & Lymphoma 57(3):507–508
Kwong YL, Chan TSY, Tan D, Kim SJ, Poon LM, Mow B, Khong PL, Loong F, Au-Yeung R, Iqbal J, Phipps C, Tse E (2017) PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing l-asparaginase. Blood 129(17):2437–2442
Acknowledgments
We thank the pathologists Dr. Jie-wei Chen and Xin-ke Zhang for their pathological review and we also thank the radiologist Dr. Zi-zheng Xiao for their imaging review of the patients included in this study.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Scientific Research Fund of China (grant number 8150010416).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the study: Peng-fei Li and Yi-ze Mao. Performed the study: Peng-fei Li, Yu-jing Zhang, Zhi-ming Li, Wen-qi Jiang and Hui-qiang Hui. Analysed the data: Yan Gao and Bing Bai. Wrote the paper: Peng-fei Li and Yi-ze Mao.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
As a retrospective analysis of prognostic factors, no approval from the Regional Committee for Medical and Health Research Ethics was necessary.
Consent for publication
We obtained informed consent for collecting and publishing medical information from all patients at their first visit.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
EBV DNA levels decreased after treatment in 49 of 71 patients. (PNG 654 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
The OS and PFS of the patients with ≦4 cycles and > 4 cycles of P-GEMOX. (PNG 311 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Pf., Mao, Yz., Bai, B. et al. Persistent peripheral blood EBV-DNA positive with high expression of PD-L1 and upregulation of CD4 + CD25 + T cell ratio in early stage NK/T cell lymphoma patients may predict worse outcome. Ann Hematol 97, 2381–2389 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3467-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3467-6