Abstract
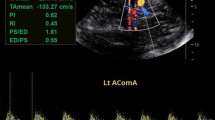
The threshold velocity ≥200 cm/s at transcranial Doppler (TCD) evaluation is a useful cut-off for preventing the stroke (STOP trial) in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease (SCD), term including different types of sickle genotypes. Scanty data are available for adult SCD patients. We compared intracranial blood flow velocities between adult SCD patients and controls using transcranial color Doppler (TCCD), measuring the peak of systolic velocity (PSV) with the insonation angle correction and the pulsatility index (PI), an indicator of endothelial elasticity. Fifty-three adult SCD patients (aged >18 years) were enrolled (15 sickle cell anemia, 26 sickle cell thalassemia, and 12 HbS/HbC). None of the patients presented neurological signs. PSVs in middle cerebral artery (MCA) were higher in SCD patients than in controls (p = 0.001). In sickle cell anemia patients, PSVs were higher when compared to HbS/βThal (p < 0.0060) and HbS/HbC patients (p < 0.0139). PI was within the lower range of normality in SCD patients compared to controls. Moreover, MCA-PSV was higher with lower Hb levels and higher HbS%; PI did not change with variation of Hb levels and HbS%.
PSV and PI in SCD adult patients could be a relevant index to indicate the abnormal cerebral blood flow and to detect the sickle endothelial damage, in order to prevent cerebrovascular accidents.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rees DC, Williams TN, Gladwin MT (2010) Sickle-cell disease. Lancet 376:2018–2031
Ohene-Frempong K, Weiner SJ, Sleeper LA et al (1998) The cooperative study of sickle cell disease: cerebrovascular accidents in sickle cell disease: rates and risk factors. Blood 91:288–294
Pandey DK, Gorelick PB (2005) Epidemiology of stroke in African Americans and Hispanic Americans. Med Clin North Am 89:739–752
NHLBI Clinical Alert: Periodic transfusions lower stroke risk in children with sickle cell anemia (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/databases/alerts/sickle97.html). Bethesda, MD; National Institutes of Health (1997). Accessed August 6 (2005)
Adams RJ, Nichols FT, Figueroa R et al (1992) Transcranial Doppler correlation with cerebral angiography in sickle cell disease. Stroke 23:1073–1077
Adams RJ, McKie V, Nichols F et al (1992) The use of transcranial ultrasonography to predict stroke in sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med 326:605–610
Adams RJ, McKie VC, Hsu L et al (1998) Prevention of a first stroke by transfusions in children with sickle cell anemia and abnormal results on transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. N Engl J Med 339:5–11
Jones AM, Seibert JJ, Nichols FT et al (2001) Comparison of transcranial color Doppler imaging (TCDI) and transcranial Doppler (TCD) in children with sickle cell anemia. Pediatr Radiol 31:461–469
Kreiza J, Rudzinski W, Pawlak MA et al (2007) Angle-corrected imaging transcranial Doppler sonography versus imaging and nonimaging transcranial Doppler sonography in children with sickle cell disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1613–1618
Jones AM, Granger S, Brambilla D et al (2005) Can peak systolic velocities be used for prediction of stroke in sickle cell anemia? Pediatr Radiol 35:66–72
Bulas DI, Jones AM, Siebert JJ et al (2000) Transcranial Doppler (TCD) screening for stroke prevention in sickle cell anemia: pitfalls in technique variation. Pediatr Radiol 3:733–738
Nichols FT, Jones AM, Adams RJ (2001) Stroke prevention in sickle cell disease (STOP) study guidelines for transcranial Doppler testing. J Neuroimaging 11:354–362
Naffaa LN, Tandon YK, Irani N (2015) Transcranial Doppler screening in sickle cell disease: the implications of using peak systolic criteria. World J Radiol 7:52–56
Alexandrov AV, Vital D, Brodie DS et al (1997) Grading carotid stenosis with ultrasound. An interlaboratory comparison. Stroke 28:1208–1210
Musallam KM, Taher AT, Karimi M, Rachmilewitz EA (2012) Cerebral infarction in beta thalassemia intermedia: breaking the silence. Thromb Res 130:695–702
Silva GS, Vicari P, Figueiredo MS et al (2006) Transcranial Doppler in adult patients with sickle cell disease. Cerebrovasc Dis 21:38–41
Silva GS, Vicari P, Figueiredo MS et al (2009) Brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in adult patients with sickle cell disease correlation with transcranial Doppler findings. Stroke 40:2408–2412
Brass LM, Pavlakis SG, De Vivo D et al (1988) Transcranial Doppler measurements of the middle cerebral artery. Effect of hematocrit. Stroke 19:1466–1469
Valadi N, Silva GS, Bowman LS et al (2006) Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography in adults with sickle cell disease. Neurology 67:572–574
Sloan MA, Alexandrov AV, Tegeler CH et al (2004) Therapeutics and technology assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of neurology: assessment: transcranial Doppler ultrasonography: report of the therapeutics and technology assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of neurology. Neurology 69:1468–1481
Calviere L, Viguier A, Guidolin B et al (2007) Cervical artery stenoses in sickle cell disease. Eur Neurol 58:120–121
Deane CR, Goss D, Bartram J et al (2010) Extracranial internal carotid arterial disease in children with sickle cell anemia. Haematologica 95:1287–1292
Ishola T, Quinn C (2013) Transcranial doppler peak systolic velocities overestimate the risk of stroke in sickle cell anemia. Abstract, American Society of Hematology. Blood 323:a2240
Graziadei G, Casoni FM, Ridolfi P et al (2013) Transcranial color doppler sonography and magnetic resonance imaging in adult patients with sickle cell disease. Abstract, American Society of Hematology. Blood 122:a2245
Manwani D, Frenette PS (2013) Vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease: pathophysiology and novel target tharapies. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program:362–369
Connes P, Verlhac S, Bernaudin F (2013) Advances in understanding the pathogenesis of cerebrovascular vasculopathy in sickle cell anaemia. Br J Haematol 161:484–498
Brandão RA, de Carvalho GT, Reis BL et al (2009) Surgical intracranial aneurysms in sickle cell patients: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Surg Neurol 72:296–299
Acknowledgments
We thank all the patients for participation in this study. GG and FMC coordinated the study design and contributed to data preparation and analysis; GG and FMC wrote the paper; FA and FMC did transcranial color Doppler; PR and AM recruited the patients; PR, IG, and EDP collected data; IC made statistical analysis; MDC contributed to review and final approval for submission. All authors read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript. This work was supported by Ministry of Health, Italy [RC-2016].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of our Institution and the procedures were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All subjects received verbal and written explanation of the aims and procedure of the study and written informed consent was obtained.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graziadei, G., Casoni, F.M., Annoni, F. et al. Transcranial color Doppler in stroke-free adult patients with sickle cell disease. Ann Hematol 96, 1547–1555 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3071-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-017-3071-1