Abstract
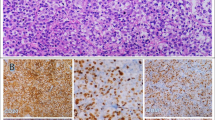
Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) express CD20. CD20 expression is described as negative, weak, or normal as determined by flow cytometry (FCM) and is an important target for the treatment of DLBCL. However, the impact of CD20 levels at onset of the disease on patient prognosis has not been fully elucidated. We analyzed 174 DLBCL cases newly diagnosed between January 1998 and April 2010. The relationship of the association between CD20 levels and patients’ backgrounds and prognoses was analyzed using the Kaplan–Meier method and Cox proportional hazard regression. Of the 174 patients, three cases (1.7%) were defined as CD20 negative based on immunohistochemistry (IHC). Although the other 171 cases were positive by IHC, eight cases (4.7%) were defined as negative and 33 cases (19.3%) were defined as weak when analyzed by FCM. Of the 105 patients who received rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone therapy, those who were CD20 negative (FCM) showed significantly inferior overall (hazard ratios (HR): 6.79, 95% CI: 1.32–34.96, p = 0.04) and progression-free survival (HR: 7.3, 95% CI: 1.49–35.8, p = 0.04) compared to patients who were CD20 normal. Our findings indicate that the CD20 level (FCM) at onset is an independent predictor of the prognosis of patients with DLBCL.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stein H, Chan JKC, Warnke RA, Gatter KC, Chan WC, Campo E, Jaffe ES (2008) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL et al (eds) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. WHO, Geneva, pp 233–237
Aoki R, Karube K, Sugita Y, Nomura Y, Shimizu K, Kimura Y, Hashikawa K, Suefuji N, Kikuchi M, Ohshima K (2008) Distribution of malignant lymphoma in Japan: analysis of 2,260 cases, 2001–2006. Pathol Int 58(3):174–182. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1827.2007.02207.x
Tedder TF, Engel P (1994) CD20: a regulator of cell-cycle progression of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today 15(9):450–454
Ernst JA, Li H, Kim HS, Nakamura GR, Yansura DG, Vandlen RL (2005) Isolation and characterization of the B-cell marker CD20. Biochemistry 44(46):15150–15158. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0511078
O’Keefe TL, Williams GT, Davies SL, Neuberger MS (1998) Mice carrying a CD20 gene disruption. Immunogenetics 48(2):125–132
Kuijpers TW, Bende RJ, Baars PA, Grummels A, Derks IA, Dolman KM, Beaumont T, Tedder TF, van Noesel CJ, Eldering E, van Lier RA (2010) CD20 deficiency in humans results in impaired T cell-independent antibody responses. J Clin Invest 120(1):214–222. doi:https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI40231
Maloney DG, Liles TM, Czerwinski DK, Waldichuk C, Rosenberg J, Grillo-Lopez A, Levy R (1994) Phase I clinical trial using escalating single-dose infusion of chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (IDEC-C2B8) in patients with recurrent B-cell lymphoma. Blood 84(8):2457–2466
Alduaij W, Ivanov A, Honeychurch J, Cheadle EJ, Potluri S, Lim SH, Shimada K, Chan CH, Tutt A, Beers SA, Glennie MJ, Cragg MS, Illidge TM (2011) Novel type II anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (GA101) evokes homotypic adhesion and actin-dependent, lysosome-mediated cell death in B-cell malignancies. Blood 117(17):4519–4529. doi:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-07-296913
Avivi I, Robinson S, Goldstone A (2003) Clinical use of rituximab in haematological malignancies. Br J Cancer 89(8):1389–1394. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601187
Beers SA, French RR, Chan HT, Lim SH, Jarrett TC, Vidal RM, Wijayaweera SS, Dixon SV, Kim H, Cox KL, Kerr JP, Johnston DA, Johnson PW, Verbeek JS, Glennie MJ, Cragg MS (2010) Antigenic modulation limits the efficacy of anti-CD20 antibodies: implications for antibody selection. Blood 115(25):5191–5201. doi:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-01-263533
Cheson BD (2010) Ofatumumab, a novel anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B-cell malignancies. J Clin Oncol 28(21):3525–3530. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.27.9836
Seki R, Ohshima K, Nagafuji K, Fujisaki T, Uike N, Kawano F, Gondo H, Makino S, Eto T, Moriuchi Y, Taguchi F, Kamimura T, Tsuda H, Ogawa R, Shimoda K, Yamashita K, Suzuki K, Suzushima H, Tsukazaki K, Higuchi M, Utsunomiya A, Iwahashi M, Imamura Y, Tamura K, Suzumiya J, Yoshida M, Abe Y, Matsumoto T, Okamura T (2010) Rituximab in combination with CHOP chemotherapy for the treatment of diffuse large B cell lymphoma in Japan: a retrospective analysis of 1,057 cases from Kyushu Lymphoma Study Group. Int J Hematol 91(2):258–266. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-009-0475-2
Feugier P, Van Hoof A, Sebban C, Solal-Celigny P, Bouabdallah R, Ferme C, Christian B, Lepage E, Tilly H, Morschhauser F, Gaulard P, Salles G, Bosly A, Gisselbrecht C, Reyes F, Coiffier B (2005) Long-term results of the R-CHOP study in the treatment of elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study by the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. J Clin Oncol 23(18):4117–4126. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.09.131
Pfreundschuh M, Trumper L, Osterborg A, Pettengell R, Trneny M, Imrie K, Ma D, Gill D, Walewski J, Zinzani PL, Stahel R, Kvaloy S, Shpilberg O, Jaeger U, Hansen M, Lehtinen T, Lopez-Guillermo A, Corrado C, Scheliga A, Milpied N, Mendila M, Rashford M, Kuhnt E, Loeffler M (2006) CHOP-like chemotherapy plus rituximab versus CHOP-like chemotherapy alone in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: a randomised controlled trial by the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. Lancet Oncol 7(5):379–391. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70664-7
Sehn LH, Donaldson J, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Klasa R, MacPherson N, O’Reilly S, Spinelli JJ, Sutherland J, Wilson KS, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM (2005) Introduction of combined CHOP plus rituximab therapy dramatically improved outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in British Columbia. J Clin Oncol 23(22):5027–5033. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2005.09.137
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, Morel P, Van Den Neste E, Salles G, Gaulard P, Reyes F, Lederlin P, Gisselbrecht C (2002) CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346(4):235–242. doi:https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa011795
Coiffier B (2002) Rituximab in combination with CHOP improves survival in elderly patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Semin Oncol 29(2 Suppl 6):18–22
Olejniczak SH, Stewart CC, Donohue K, Czuczman MS (2006) A quantitative exploration of surface antigen expression in common B-cell malignancies using flow cytometry. Immunol Invest 35(1):93–114. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/08820130500496878
Johnson NA, Boyle M, Bashashati A, Leach S, Brooks-Wilson A, Sehn LH, Chhanabhai M, Brinkman RR, Connors JM, Weng AP, Gascoyne RD (2009) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: reduced CD20 expression is associated with an inferior survival. Blood 113(16):3773–3780. doi:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-09-177469
Geary WA, Frierson HF, Innes DJ, Normansell DE (1993) Quantitative criteria for clonality in the diagnosis of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma by flow cytometry. Mod Pathol 6(2):155–161
Yamaguchi M, Nakamura N, Suzuki R, Kagami Y, Okamoto M, Ichinohasama R, Yoshino T, Suzumiya J, Murase T, Miura I, Ohshima K, Nishikori M, Tamaru J, Taniwaki M, Hirano M, Morishima Y, Ueda R, Shiku H, Nakamura S (2008) De novo CD5+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results of a detailed clinicopathological review in 120 patients. Haematologica 93(8):1195–1202. doi:https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.12810
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, Lister TA, Vose J, Grillo-Lopez A, Hagenbeek A, Cabanillas F, Klippensten D, Hiddemann W, Castellino R, Harris NL, Armitage JO, Carter W, Hoppe R, Canellos GP (1999) Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol 17(4):1244
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman JW (eds) (2008) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymhoid tissues. WHO classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymhoid Tissues. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Shenkin M, Babu R, Maiese R (2007) Accurate assessment of cell count and viability with a flow cytometer. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 72(5):427–432. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.b.20179
Mason DY, Comans-Bitter WM, Cordell JL, Verhoeven MA, van Dongen JJ (1990) Antibody L26 recognizes an intracellular epitope on the B-cell-associated CD20 antigen. Am J Pathol 136(6):1215–1222
Dong HY, Browne P, Liu Z, Gangi M (2008) PAX-5 is invariably expressed in B-cell lymphomas without plasma cell differentiation. Histopathology 53(3):278–287. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2559.2008.03091.x
Korganow AS, Knapp AM, Nehme-Schuster H, Soulas-Sprauel P, Poindron V, Pasquali JL, Martin T (2010) Peripheral B cell abnormalities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in quiescent phase: decreased memory B cells and membrane CD19 expression. J Autoimmun 34(4):426–434. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2009.11.002
Nutt SL, Urbanek P, Rolink A, Busslinger M (1997) Essential functions of Pax5 (BSAP) in pro-B cell development: difference between fetal and adult B lymphopoiesis and reduced V-to-DJ recombination at the IgH locus. Genes Dev 11(4):476–491
Katzenberger T, Lohr A, Schwarz S, Dreyling M, Schoof J, Nickenig C, Stilgenbauer S, Kalla J, Ott MM, Muller-Hermelink HK, Ott G (2003) Genetic analysis of de novo CD5+ diffuse large B-cell lymphomas suggests an origin from a somatically mutated CD5+ progenitor B cell. Blood 101(2):699–702. doi:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-06-1726
Molica S, Levato D, Dattilo A, Mannella A (1998) Clinico-prognostic relevance of quantitative immunophenotyping in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia with emphasis on the expression of CD20 antigen and surface immunoglobulins. Eur J Haematol 60(1):47–52. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07012.x
Tam CS, Otero-Palacios J, Abruzzo LV, Jorgensen JL, Ferrajoli A, Wierda WG, Lerner S, O’Brien S, Keating MJ (2008) Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia CD20 expression is dependent on the genetic subtype: a study of quantitative flow cytometry and fluorescent in-situ hybridization in 510 patients. Br J Haematol 141(1):36–40. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07012.x
Ginaldi L, De Martinis M, Matutes E, Farahat N, Morilla R, Catovsky D (1998) Levels of expression of CD19 and CD20 in chronic B cell leukaemias. J Clin Pathol 51(5):364–369
Morton LM, Wang SS, Devesa SS, Hartge P, Weisenburger DD, Linet MS (2006) Lymphoma incidence patterns by WHO subtype in the United States, 1992–2001. Blood 107(1):265–276. doi:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-06-2508
Muller-Hermelink HK, Montserrat E, Catovsky D, Campo E, Harris NL, Stein H (2008) Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL et al (eds) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. WHO, Geneva
Niitsu N, Okamoto M, Aoki S, Okumura H, Yoshino T, Miura I, Hirano M (2006) Multicenter phase II study of the CyclOBEAP (CHOP-like + etoposide and bleomycin) regimen for patients with poor-prognosis aggressive lymphoma. Ann Hematol 85(6):374–380. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-006-0080-x
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank our colleagues, especially Ms. Tsuruta for IHC and DVM Taira for collecting FCM data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, Y., Yoshida, T., Wang, G. et al. Association of CD20 levels with clinicopathological parameters and its prognostic significance for patients with DLBCL. Ann Hematol 91, 997–1005 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1407-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-012-1407-4