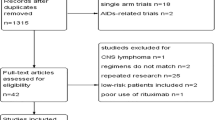
Abstract
Addition of rituximab to chemotherapy (R-chemo) has been shown to improve overall survival (OS) in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Germinal center B cell-like (GCB) subtype of DLBCL has a significantly better clinical outcome than those with non-germinal center B cell-like (non-GCB) subtype. Further research is needed to confirm this difference between those two subtypes treated with R-chemo. We searched for randomized controlled trials that compared R-chemo with identical chemotherapy alone in patients with newly diagnosed or relapsed DLBCL. A random versus fixed effects model was selected according to heterogeneity. Six eligible trials involving 748 adult patients were included in this meta-analysis. Fixed-effects analysis showed OS to be superior for the GCB patients treated with R-chemo (relative risk (RR) = 1.16, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.03–1.31, P = 0.02). Superiority was also observed for the GCB subtype under R-chemo with respect to disease control (RR = 1.16, 95% CI = 0.99–1.36) and overall response (RR = 1.19, 95% CI = 0.99–1.99). Both subtypes showed an increased OS (RR = 1.30, 95% CI = 1.11–1.51; RR = 1.89, 95% CI = 1.52–2.35, respectively) and disease control rate (RR = 1.27, 95% CI = 1.05–1.54, P = 0.01; RR = 2.21, 95% CI = 1.68–2.90, respectively) following R-chemo. Therefore, treated with R-chemo, GCB patients still has a significantly better clinical outcome than those with non-GCB subtype.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morton LM, Wang SS, Devesa SS, Hartge P, Weisenburger DD, Linet MS (2006) Lymphoma incidence patterns by WHO subtype in the United States, 1992–2001. Blood 107:265–276
Anonymous (1997) A clinical evaluation of the International Lymphoma Study Group classification of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. Blood 89:3909–3918
Coiffier B (2001) Diffuse large cell lymphoma. Curr Opin Oncol 13:325–334
Coiffier B (2007) Rituximab therapy in malignant lymphoma. Oncogene 26:3603–3613
Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE et al (2000) Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC et al (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103:275–282
Gao G, Liang X, Jiang J et al (2009) A systematic review and meta-analysis of immunochemotherapy with rituximab for B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Acta Oncol 49:1–11
Lenz G, Wright G, Dave S et al (2007) Gene expression signatures predict overall survial in diffuse large B cell lymphoma treated with rituximab and chop-like chemotherapy. Blood 110:209a, ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts 348
Xia Y, Li ZM, Shi YX, Xia ZJ, Jiang WQ, Huang HQ (2009) Short-term efficacy of rituximab-CHOP and CHOP regimens on two subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Chin J Cancer 28:146–149
Wilson WH, Dunleavy K, Pittaluga S et al (2008) Phase II study of dose-adjusted EPOCH and rituximab in untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with analysis of germinal center and post-germinal center biomarkers. J Clin Oncol 26:2717–2724
Xia ZG, Xu ZZ, Zhao WL et al (2010) The prognostic value of immunohistochemical subtyping in Chinese patients with de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma undergoing CHOP or R-CHOP treatment. Ann Hematol 89:171–177
Nyman H, Adde M, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML et al (2007) Prognostic impact of immunohistochemically defined germinal center phenotype in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with immunochemotherapy. Blood 109:4930–4935
Falagas ME, Matthaiou DK, Bliziotis IA (2006) The role of aminoglycosides in combination with a beta-lactam for the treatment of bacterial endocarditis: a meta-analysis of comparative trials. J Antimicrob Chemother 57:639–647
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME et al (2007) Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:579–586
Saito B, Shiozawa E, Usui T et al (2007) Rituximab with chemotherapy improves survival of non-germinal center type untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 21:2563–2566
Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Choi WWL et al (2008) Addition of rituximab to standard chemotherapy improves the survival of both the germinal center B-cell-like and non-germinal center B-cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 26:4587–4594
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC et al (2002) The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346:1937–1947
Cheson BD (2006) Monoclonal antibody therapy for B-cell malignancies. Semin Oncol 33:S2–S14
Stolz C, Schuler M (2009) Molecular mechanisms of resistance to rituximab and pharmacologic strategies for its circumvention. Leuk Lymphoma 50:873–885
Hilchey SP, Hyrien O, Mosmann TR et al (2009) Rituximab immunotherapy results in the induction of a lymphoma idiotype-specific T-cell response in patients with follicular lymphoma: support for a “vaccinal effect” of rituximab. Blood 113:3809–3812
Jazirehi AR, Huerta-Yepez S, Cheng G, Bonavida B (2005) Rituximab (chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) inhibits the constitutive nuclear factor-{kappa}B signaling pathway in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma B-cell lines: role in sensitization to chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 65:264–276
Davis RE, Brown KD, Siebenlist U, Staudt LM (2001) Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J Exp Med 194:1861–1874
Iqbal J, Neppalli VT, Wright G et al (2006) BCL2 expression is a prognostic marker for the activated B-cell-like type of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 24:961–968
He L, Thomson J, Hemann M et al (2005) A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435:828–833
Chen CZ (2005) MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. N Engl J Med 353:1768–1771
Lawrie CH, Soneji S, Marafioti T et al (2007) MicroRNA expression distinguishes between germinal center B cell-like and activated B cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int J Cancer 121:1156–1161
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM et al (2008) Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 141:672–675
Lawrie CH, Chi J, Taylor S et al (2009) Expression of microRNAs in diffuse large B cell lymphoma is associated with immunophenotype, survival and transformation from follicular lymphoma. J Cell Mol Med 13:1248–1260
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (30871104, 30971296, 30971295).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, C., Xu, W. & Li, JY. A systematic review and meta-analysis of rituximab-based immunochemotherapy for subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 89, 1107–1113 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-0990-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-0990-5