Abstract
Purpose
To describe a case of a posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) of C2 transverse foramen level vertebral artery (VA) origin that entered the spinal canal via the C1/2 intervertebral space.
Case report
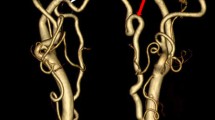
A 48-year-old man with posterior neck pain underwent computed tomography (CT) angiography and selective left vertebral angiography. Arterial dissection was found at the distal V2 segment of the left VA on subtracted CT angiography. The left PICA arising from the VA at the level of C2 transverse foramen was identified on CT angiography with bone imaging. This PICA of extracranial origin entered the spinal canal via the C1/2 intervertebral space, just like a PICA of C1/2 level origin.
Discussion
The origins of PICAs show several variations. PICAs originating at the extracranial C1/2 level VA are relatively rare, with a reported prevalence of approximately 1%. Our patient had a left PICA arising from the VA at the level of the C2 transverse foramen. No similar cases have been reported in the relevant English-language literature. We speculated that the proximal short segment of the PICA arising from the C1/2 level VA regressed incidentally and that the distal segment of the PICA was supplied by the muscular branch of the VA arising from the level of the C2 transverse foramen.
Conclusion
We reported the first case of PICA arising from the C2 transverse foramen level VA. CT angiography with bone imaging is useful for identifying a PICA arising from the extracranial VA.




(Modified from Reference #12)
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Bhat DI, Somanna S, Kovoor J, Chandramoul BA (2009) Aneurysms from extracranial, extradurally originating posterior inferior cerebellar arteries: a rare case report. Surg Neurol 72:406–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2008.09.021
Enomoto N, Yagi K, Matsubara S, Uno M (2021) Case report: bow hunter’s syndrome caused by compression of extracranially originated posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Front Neurol 12:756838. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.756838
Fine AD, Cardoso A, Rhoton AL Jr (1999) Microsurgical anatomy of the extracranial-extradural origin of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. J Neurosurg 91:645–652. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.91.4.0645
Kim MS (2016) Developmental anomalies of the distal vertebral artery and posterior inferior cerebellar artery: diagnosis by CT angiography and literature review. Surg Radiol Anat 38:997–1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1654-5
Lasjaunias P, Braun JP, Hasso AN, Moret J, Manelfe C (1980) True and false fenestration of the vertebral artery. J Neuroradiol 7:157–166
Mubarak AI, Morani AC (2017) C2 segmental type of vertebral artery on the unfused side of partially occipitalized atlas. Radiol Case Rep 13:101–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2017.10.017
Padget DH (1948) The development of the cranial arteries in the human embryo. Contrib Embryol 32:207–261
Pekcevik Y, Pekcevik R (2014) Variations of the cerebellar arteries at CT angiography. Surg Radiol Anat 36:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-013-1208-z
Uchino A, Kakehi Y (2022) Duplicated posterior inferior cerebellar arteries one of which was supplied by the jugular branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery. Surg Radiol Anat 44:1037–1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-022-02984-x
Uchino A, Ohno H, Kondo R, Ishihara S (2021) Ascending pharyngeal artery-posterior inferior cerebellar artery anastomosis via the jugular foramen: a case report and literature review. Surg Radiol Anat 43:1019–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02667-5
Uchino A, Saito N, Uemiya N, Sonoda K (2016) Diagnosis of a C3 segmental type of vertebral artery by magnetic resonance angiography: report of two cases. Surg Radiol Anat 38:873–876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-016-1620-2
Uchino A, Saito N, Watadani T, Okada Y, Kozawa E, Nishi N, Mizukoshi W, Inoue K, Nakajima R, Takahashi M (2012) Vertebral artery variations at the C1–2 level diagnosed by magnetic resonance angiography. Neuroradiology 54:19–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0849-z
Uchino A, Suzuki C (2018) Variant of a persistent hypoglossal artery supplying only the posterior inferior cerebellar artery diagnosed by magnetic resonance angiography: a case report. Surg Radiol Anat 40:807–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-018-1970-z
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AU carried out the study design and drafted the manuscript. AU and YK reviewed the manuscript critically, and have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
The patient signed informed consent regarding publishing his data and figures.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uchino, A., Kakehi, Y. A posterior inferior cerebellar artery of C2 transverse foramen level origin that entered the spinal canal via the C1/2 intervertebral space demonstrated by computed tomography angiography. Surg Radiol Anat 45, 833–837 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03165-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-023-03165-0