Abstract
Purpose
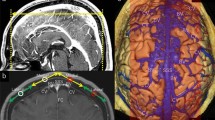
The primary aim of our paper was to describe typical anatomical patterns of the superior sagittal sinus (SSS) and bridging veins (BV) using cerebral venous computed tomographic angiography (CTA) with a focus on the direction of the BV entering the SSS.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed venous CTA of 30 patients to estimate the total number and direction of the BV entering the SSS. Maximum intensive projections were analyzed for length, diameter and cross-sectional area of the SSS.
Results
Thee hundred and fifty-four BV were assessed. The mean total length of the SSS was 25.6 ± 1.6 cm (mean ± 1 SD). The mean horizontal diameter at the level of the coronary suture was 6.7 ± 2.0 mm, and the mean vertical diameter at the coronary suture measured 5.3 ± 1.8 mm. Most BV emptied into the SSS, at the level of or distal to the coronary suture (74%). The BV draining into the SSS at the level of the coronary suture typically joined into a lacunar formation (43%). Veins draining into the sinus more than 3 cm distal from the coronary suture presented a predominantly retrograde inflow direction (77%).
Conclusions
Despite large variations in the location and course of BV, typical anatomical patterns were noted especially in relation to the direction of BV entering the SSS. The present anatomical analysis of the cerebral convexity veins by cerebral venous CTA provides an overview of the configuration of these veins which is useful information in neurosurgical preoperative planning.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews BT, Dujovny M, Mirchandani HG et al (1989) Microsurgical anatomy of the venous drainage into the superior sagittal sinus. Neurosurgery 24:514–520
Borgesen SE, Pieri A, Cappelen J et al (2004) Shunting to the cranial venous sinus using the SinuShunt. Childs Nerv Syst 20:397–404
Braun JP, Tournade A, Panisset JL et al (1978) Anatomical and neuroradiological study of the veins of the tentorium and the floor of the middle cranial fossa, and their drainage to dural sinuses. J Neuroradiol 5:113–132
Dagain A, Vignes R, Dulou R et al (2009) Study of the junction between the cortical bridging veins and basal cranial venous sinus. Neurochirurgie 55:19–24
DiChiro G (1962) Angiographic patterns of cerebral convexity veins and superficial dural sinuses. Am J Roentgenol 87:308–321
Eklund A, Koskinen LO, Malm J (2004) Features of the Sinushunt and its influence on the cerebrospinal fluid system. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:1156–1159
El-Shafei IL, El-Shafei HI (2001) The retrograde ventriculosinus shunt: concept and technique for treatment of hydrocephalus by shunting the cerebrospinal fluid to the superior sagittal sinus against the direction of blood flow. Preliminary report. Childs Nerv Syst 17:457–465 (discussion 466)
Han H, Tao W, Zhang M (2007) The dural entrance of cerebral bridging veins into the superior sagittal sinus: an anatomical comparison between cadavers and digital subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 49:169–175
Hash CJ, Shenkin HA, Crowder LE (1979) Ventricle to sagittal sinus shunt for hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 4:394–400
Jimenez JL, Lasjaunias P, Terbrugge K et al (1989) The trans-cerebral veins: normal and non-pathologic angiographic aspects. Surg Radiol Anat 11:63–72
Kiyosue H, Tanoue S, Sagara Y et al (2008) The anterior medullary-anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural sinuses: normal anatomy and drainage routes from dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neuroradiology 50:1013–1023
Lang J, Schneider W (1989) The superficial cerebral veins. Gegenbaurs Morphol Jahrb 135:271–303
Lasjaunias P, Kwok R, Goh P et al (2004) A developmental theory of the superior sagittal sinus(es) in craniopagus twins. Childs Nerv Syst 20:526–537
O’Connel E (1934) Some observation of the cerebral veins. Brain 57:484–503
Oka K, Rhoton AL Jr, Barry M et al (1985) Microsurgical anatomy of the superficial veins of the cerebrum. Neurosurgery 17:711–748
Ono M, Rhoton AL Jr, Peace D et al (1984) Microsurgical anatomy of the deep venous system of the brain. Neurosurgery 15:621–657
Piechnik SK, Czosnyka M, Richards HK et al (2001) Cerebral venous blood outflow: a theoretical model based on laboratory simulation. Neurosurgery 49:1214–1222 (discussion 1222–1223)
Piffer CR, Horn Y, Hureau J et al (1985) Anatomical study of the superior cerebral veins. Anat Anz 160:271–283
Rhoton AL (2002) The cerebral veins. Neurosurgery 51:159–205
Sampei T, Yasui N, Okudera T et al (1996) Anatomic study of anterior frontal cortical bridging veins with special reference to the frontopolar vein. Neurosurgery 38:971–975
Shao Y, Sun JL, Yang Y et al (2009) Endoscopic and microscopic anatomy of the superior sagittal sinus and torcular herophili. J Clin Neurosci 16:421–424
Sharifi M, Kunicki J, Krajewski P et al (2004) Endoscopic anatomy of the chordae willisii in the superior sagittal sinus. J Neurosurg 101:832–835
Teksam M, Moharir M, Deveber G et al (2008) Frequency and topographic distribution of brain lesions in pediatric cerebral venous thrombosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1961–1965
Ueda K, Nakase H, Miyamoto K et al (2000) Impact of anatomical difference of the cerebral venous system on microcirculation in a gerbil superior sagittal sinus occlusion model. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:75–82
Van Canneyt K, Kips J, Mareels G et al (2008) Experimental and numerical modelling of the ventriculosinus shunt (El-Shafei shunt). Proc Inst Mech Eng H 222:455–464
Vieira JP, Luis C, Monteiro JP et al (2009) Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children: clinical presentation and extension, localization and recanalization of thrombosis. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 14:80–85. doi:10.1016/j.ejpn.2008.12.004
Acknowledgments
I would like to show my gratitude to Prof. em. P. Schmiedek for his ideas, advice and suggestions that have made this study possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brockmann, C., Kunze, S. & Scharf, J. Computed tomographic angiography of the superior sagittal sinus and bridging veins. Surg Radiol Anat 33, 129–134 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0714-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0714-5