Abstract
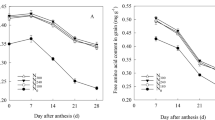
Following reduced irrigation strategies in the north China plain (NCP), nitrogen (N) fertilizer application must be optimized in terms of the food production and resource use efficiency. In this study, experiments were conducted for three consecutive winter wheat seasons in 2013–2016. Treatments included pre-sowing irrigation of 750 m3 ha−1 season−1 with no subsequent irrigation during the whole season (W0) and irrigation of 750 m3 ha−1 season−1 at pre-sowing, jointing and anthesis (W2). N fertilizer was applied at sowing with three levels, i.e., 180 (N1), 225 (N2) and 270 (N3) kg ha−1 for each irrigation regime. Results exhibited that the average wheat yield of W0 was 17.3% lower than that of W2, however, the increased thousand kernel weight under W0 upheld relatively high yield averaging 7328 kg ha−1. In addition, increased water stress under W0 aided to improve pre-anthesis dry matter and N remobilization to grain which in turn, made larger N use efficiency and N harvest index. Furthermore, grain protein content ranged from 13.4 to 13.7% under W0, 13.0 to 13.3% higher than that of W2. At both irrigation levels, grain yield and grain protein content increased with an increase in N application rate, while no significant difference was observed between N2 and N3 under W0. Additionally, the N2 achieved the highest water use efficiency of 1.92 kg m−3 under W0. Overall, N2 appeared to be the optimized N level under W0 in terms of yield and nitrogen use, though it was 13.6% less than the largest net income under W2N3 due to 18.9% of yield loss. Moreover, W0N2 could reduce 1500 m3 ha−1 season−1 irrigation water, 45 kg ha−1 N fertilizer and 289.77 $ ha−1 total input and attain highest cost efficiency. The study demonstrated that disposable water and nitrogen applied at sowing of wheat is feasible, and N application rate of 225 kg ha−1 was recommended for the W0 regime to maximize wheat yield, grain quality, ecological and economic benefits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadian K, Jalilian J, Pirzad A (2021) Nano-fertilizers improved drought tolerance in wheat under deficit irrigation. Agric Water Manag 244:106544
Alghory A, Yazar A (2018) Evaluation of net return and grain quality characteristics of wheat for various irrigation strategies under the Mediterranean climatic conditions. Agric Water Manag 203:395–404
Baethgen WE, Christianson CB, Lamothe AG (1995) Nitrogen fertilizer effects on growth, grain yield, and yield components of malting barley. Field Crops Res 43:87–99
Bouthiba A, Debaeke P, Hamoudi SA (2008) Varietal differences in the response of durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var. durum) to irrigation strategies in a semi-arid region of Algeria. Irrigation Sci 26:239–251
Chen XP, Zhang FS, Römheld V, Horlacher D, Schulz R, Böning Z, Wang P, Claupein W (2006) Synchronizing N supply from soil and fertilizer and N demand of winter wheat by an improved Nmin method. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 74:91–98
Chen XP, Cui ZL, Vitousek PM, Cassman KG, Matson PA, Bai JS, Meng QF, Hou P, Yue SC, Römheld V, Zhang FS (2011) Integrated soil–crop system management for food security. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:6399–6404
Chen XP, Cui ZL, Fan MS, Vitousek P, Zhao M, Ma WQ, Wang ZL, Zhang WJ, Yan XY, Yang JC, Deng XP, Gao Q, Zhang Q, Guo SW, Ren J, Li SQ, Ye YL, Wang ZH, Huang JL, Tang QY, Sun YX, Peng XL, Zhang JW, He MR, Zhu YJ, Xue JQ, Wang GL, Wu L, An N, Wu LQ, Ma L, Zhang WF, Zhang FS (2014) Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 514:486–489
Cui ZL, Chen XP, Zhang FS (2010) Current nitrogen management status and measures to improve the intensive wheat-maize system in China. Ambio 39:376–384
Ferrante A, Savin R, Slafer GA (2013) Floret development and grain setting differences between modern durum wheats under contrasting nitrogen availability. J Exp Bot 64:169–184
Fuertes-Mendizabal T, Aizpurua A, Gonzalez-Moro MB, Estavillo JM (2010) Improving wheat breadmaking quality by splitting the N fertilizer rate. Eur J Agron 33:52–61
Han H, Yang W (2009) Influence of uniconazole and plant density on nitrogen content and grain quality in winter wheat in South China. Plant Soil Environ 55:159–166
Huang P, Zhang JB, Zhu AN, Li XP, Ma DH, Xin XL, Zhang CZ, Wu SJ, Garland G, Pereira EIP (2018) Nitrate accumulation and leaching potential reduced by coupled water and nitrogen management in the Huang-Huai-Hai plain. Sci Total Environ 610:1020–1028
Kang SZ, Hao XM, Du TS, Tong L, Su XL, Lu HN, Li XL, Huo ZL, Li SE, Ding RS (2017) Improving agricultural water productivity to ensure food security in China under changing environment: from research to practice. Agric Water Manag 179:5–17
Li DX, Zhang D, Wang H, Li HG, Fang Q, Li HY, Li RQ (2020) Optimized planting density maintains high wheat yield under limiting irrigation in north China plain. Int J Plant Prod 14:107–117
Liao LW, Long HL, Gao XL, Ma EP (2019) Effects of land use transitions and rural aging on agricultural production in China’s farming area: a perspective from changing labor employing quantity in the planting industry. Land Use Policy 88:104152
Liu H, Wang ZH, Yu R, Li FC, Li KY, Cao HB, Yang N, Li MH, Dai J, Zan YL, Li Q, Xue C, He G, Huang DL, Huang M, Liu JS, Qiu WH, Zhao HB, Mao HB (2016) Optimal nitrogen input for higher efficiency and lower environmental impacts of winter wheat production in China. Agr Ecosyst Environ 224:1–11
Liu WX, Wang JR, Wang CY, Ma G, Wei QR, Lu HF, Xie YX, Ma DY, Kang GZ (2018) Root growth, water and nitrogen use efficiencies in winter wheat under different irrigation and nitrogen regimes in north China plain. Front Plant Sci 9:1798
Liu BY, Zhao X, Li SS, Zhang XZ, Virk AL, Qi JY, Kan ZR, Wang X, Ma ST, Zhang HL (2020) Meta-analysis of management-induced changes in nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat in the north China plain. J Clean Prod 251:119632
Liu X, Xu YY, Engel BA, Sun SK, Zhao XN, Wu PT, Wang YB (2021) The impact of urbanization and aging on food security in developing countries: the view from northwest China. J Clean Prod 292:126067
Ma SC, Wang TC, Guan XK, Zhang X (2018) Effect of sowing time and seeding rate on yield components and water use efficiency of winter wheat by regulating the growth redundancy and physiological traits of root and shoot. Field Crops Res 221:166–174
Moll RH, Kamprath EJ, Jackson WA (1982) Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agron J 74:562–564
National Bureau of Statistics of China (2016) China Statistical yearbook. Beijing, China Statistics Press. (In Chinese)
Piao SL, Ciais P, Huang Y, Shen ZH, Peng SS, Li JS, Zhou LP, Liu HY, Ma YC, Ding YH, Friedlingstein P, Liu CZ, Tan K, Yu YQ, Zhang TY, Fang JY (2010) The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 467:43–51
Plaut Z, Butow BJ, Blumenthal CS, Wrigley CW (2004) Transport of dry matter into developing wheat kernels and its contribution to grain yield under post-anthesis water deficit and elevated temperature. Field Crops Res 86:185–198
Qiu GY, Zhang XN, Yu XH, Zou ZD (2018) The increasing effects in energy and GHG emission caused by groundwater level declines in north China’s main food production plain. Agric Water Manag 203:138–150
Rahman MA, Chikushi J, Saifizzaman M, Lauren JG (2005) Rice straw mulching and nitrogen response of no-till wheat following rice in Bangladesh. Field Crops Res 91:71–81
Richards RA, Lopezcastaneda C, Gomezmacpherson H, Condon AG (1993) Improving the efficiency of water use by plant breeding and molecular biology. Irrigation Sci 14:93–104
Slafer GA, Savin R, Sadras VO (2014) Coarse and fine regulation of wheat yield components in response to genotype and environment. Field Crops Res 157:71–83
Sun HY, Zhang XY, Wang EL, Chen SY, Shao LW (2015) Quantifying the impact of irrigation on groundwater reserve and crop production—a case study in the north China plain. Eur J Agron 70:48–56
Sun ZC, Zhang YH, Zhang Z, Gao YM, Yang YM, Han MK, Wang ZM (2019) Significance of disposable presowing irrigation in wheat in increasing water use efficiency and maintaining high yield under winter wheat-summer maize rotation in the north China plain. Agric Water Manag 225:105766
Tilling AK, O’Leary GJ, Ferwerda JG, Jones SD, Fitzgerald GJ, Rodriguez D, Belford R (2007) Remote sensing of nitrogen and water stress in wheat. Field Crops Res 104:77–85
van Oort PAJ, Wang G, Vos J, Meinke H, Li BG, Huang JK, van der Werf W (2016) Towards groundwater neutral cropping systems in the Alluvial Fans of the north China plain. Agric Water Manag 165:131–140
Wang ZM, Wang P, Li XH, Li JM, Lu LQ (2006) Principle and technology of water-saving, fertilizer-saving, high-yielding and simple cultivation in winter wheat. Rev China Agric Sci Technol 8:38–44 (In Chinese)
Wang EL, Qiang Y, Wu DR, Xia J (2008) Climate, agricultural production and hydrological balance in the north China plain. Int J Climatol 28:1959–1970
Wang X, Shi Y, Guo ZJ, Zhang YL, Yu ZW (2015) Water use and soil nitrate nitrogen changes under supplemental irrigation with nitrogen application rate in wheat field. Field Crops Res 183:117–125
Wang H, Zhang Y, Chen A, Liu H, Zhai L, Lei B, Ren T (2017) An optimal regional nitrogen application threshold for wheat in the north China plain considering yield and environmental effects. Field Crops Res 207:52–61
Wang LL, Palta JA, Chen W, Chen YL, Deng XP (2018a) Nitrogen fertilization improved water-use efficiency of winter wheat through increasing water use during vegetative rather than grain filling. Agric Water Manag 197:41–53
Wang YQ, Zhang YH, Zhang R, Li JP, Zhang M, Zhou SL, Wang ZM (2018b) Reduced irrigation increases the water use efficiency and productivity of winter wheat-summer maize rotation on the north China plain. Sci Total Environ 618:112–120
Xu ZZ, Yu ZW, Zhao JY (2012) Theory and application for the promotion of wheat production in China: past, present and future. J Sci Food Agric 93:2339–2350
Xu XX, Zhang M, Li JP, Liu ZQ, Zhao ZG, Zhang YH, Zhou SL, Wang ZM (2018) Improving water use efficiency and grain yield of winter wheat by optimizing irrigations in the north China plain. Field Crops Res 221:219–227
Yan SC, Wu Y, Fan JL, Zhang FC, Zheng J, Qiang SC, Guo JJ, Xiang YZ, Zou HY, Wu LF (2020) Dynamic change and accumulation of grain macronutrient (N, P and K) concentrations in winter wheat under different drip fertigation regimes. Field Crops Res 250:107767
Zhang FQ, Wang XY, Yu ZW, Wang XZ, Bai HL (2009) Characteristics of accumulation and distribution of nitrogen and dry matter in wheat at yield level of ten thousand kilograms per hectare. Acta Agron Sin 35:1086–1096 (In Chinese)
Zhang XY, Chen SY, Sun HY, Shao LW, Wang YZ (2011) Changes in evapotranspiration over irrigated winter wheat and maize in north China plain over three decades. Agric Water Manag 98:1097–1104
Zhang MM, Dong BD, Qiao YZ, Shi CH, Yang H, Wang YK, Liu MY (2018a) Yield and water use responses of winter wheat to irrigation and nitrogen application in the north China plain. J Integr Agr 17:1194–1206
Zhang YT, Wang HY, Lei QL, Luo JF, Lindsey S, Zhang JZ, Zhai LM, Wu SX, Zhang JS, Liu XX, Ren TZ, Liu HB (2018b) Optimizing the nitrogen application rate for maize and wheat based on yield and environment on the northern China plain. Sci Total Environ 618:1173–1183
Zhang M, Gao YM, Zhang Z, Liu Y, Han MK, Hu NY, Wang ZM, Sun ZC, Zhang YH (2020) Limited irrigation influence on rotation yield, water use, and wheat traits. Agron J 112:241–256
Zhao RF, Chen XP, Zhang FS, Zhang HL, Schroder J, Romheld V (2006) Fertilization and nitrogen balance in a wheat-maize rotation system in north China. Agron J 98:938–945
Zhou YX (2009) A critical review of groundwater budget myth, safe yield and sustainability. J Hydrol 370:207–213
Zhou SL, Wu YC, Wang ZM, Lu LQ, Wang RZ (2008) The nitrate leached below maize root zone is available for deep-rooted wheat in winter wheat-summer maize rotation in the north China plain. Environ Pollut 152:723–730
Zou BL, Mishra AK, Luo BL (2018) Aging population, farm succession, and farmland usage: evidence from rural China. Land Use Policy 77:437–445
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Ministerial and Provincial Co-Innovation Centre for Endemic Crops Production with High-quality and Efficiency in Loess Plateau (No. SBGJXTZXKF-1), the Key Research Projects of Hebei Province (Grant number: 20326405D), the National Wheat Industry Technology System (CARS301), and the 2115 Talent Development Program of China Agricultural University. We appreciate all the colleagues for their contribution in various ways to the successful publication of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Han, M., Zhou, X. et al. Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer application under reduced irrigation strategies for winter wheat of the north China plain. Irrig Sci 40, 255–265 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-021-00764-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-021-00764-w