Abstract
Purpose
To compare the safety and efficacy of integrated iodine-125 (I-125) seed implantation (sequential implantation of helical I-125 seed implant into the main portal vein and of I-125 seeds into the branch tumor thrombus directly forming main portal vein tumor thrombus (MPVTT)) combined with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) versus TACE alone for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with MPVTT.
Materials and Methods
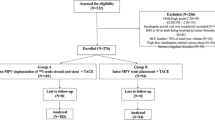
From December 2016 to January 2020, 46 HCC patients with MPVTT were analyzed. In the combination group, 21 patients received helical I-125 seed implantation in the main portal vein through a patent small portal vein branch and TACE in a single session. After 7–10 days, I-125 seeds were implanted percutaneously into the branch tumor thrombus directly forming MPVTT. In the TACE group, 25 patients received TACE alone. Thereafter, TACE was repeated as needed in both groups. Adverse events, tumor response, and overall survival (OS) of the two groups were compared.
Results
No adverse events grade ≥ 3 were observed in either group. The optimal objective response rate and disease control rate for MPVTT in the combination group and TACE group were 52.4% versus 4.0% (P < 0.001) and 85.7% versus 32.0% (P < 0.001), respectively. Median OS in the combination group (9.8 months) was longer than in the TACE group (5.2 months) (P = 0.024). Multivariate analysis revealed that, compared with the TACE group, the mortality risk in the combination group significantly decreased (hazard ratio: 0.444; P = 0.020).
Conclusion
Integrated I-125 seed implantation combined with TACE is a safe and effective treatment for HCC with MPVTT.
Level of Evidence
Level 3, Non-randomized controlled cohort/follow-up study.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Minagawa M, Makuuchi M. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma accompanied by portal vein tumor thrombus. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(47):7561–7.
Llovet JM, Bustamante J, Castells A, Vilana R, Ayuso Mdel C, Sala M, et al. Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology. 1999;29(1):62–7.
Villa E, Moles A, Ferretti I, Buttafoco P, Grottola A, Del Buono M, et al. Natural history of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: estrogen receptors’ status in the tumor is the strongest prognostic factor for survival. Hepatology. 2000;32(2):233–8.
Shen J, Wang WS, Zhu XL, Ni CF. High epithelial cell adhesion molecule-positive circulating tumor cell count predicts poor survival of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2018;29(12):1678–84.
Chung JW, Park JH, Han JK, Choi BI, Han MC. Hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein invasion: results of treatment with transcatheter oily chemoembolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1995;165(2):315–21.
Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30(1):52–60.
Luo J, Yan Z, Liu Q, Qu X, Wang J. Endovascular placement of iodine-125 seed strand and stent combined with chemoembolization for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombus in main portal vein. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22(4):479–89.
Luo JJ, Zhang ZH, Liu QX, Zhang W, Wang JH, Yan ZP. Endovascular brachytherapy combined with stent placement and TACE for treatment of HCC with main portal vein tumor thrombus. Hepatol Int. 2016;10(1):185–95.
Lu J, Guo JH, Zhu HD, Zhu GY, Chen L, Teng GJ. Safety and efficacy of irradiation stent placement for malignant portal vein thrombus combined with transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-center experience. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017;28(6):786-94.e3.
Yu TZ, Zhang W, Liu QX, Li WH, Ma JQ, Zhang ZH, et al. Endovascular brachytherapy combined with portal vein stenting and transarterial chemoembolization improves overall survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with main portal vein tumor thrombus. Oncotarget. 2017;8(7):12108–19.
Wang W, Shen J, Wang C, Ren B, Zhu X, Ni C. Safety and feasibility of helical I-125 seed implants combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinomas with main portal vein tumor thrombus. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2019;42(10):1420–8.
Yang M, Fang Z, Yan Z, Luo J, Liu L, Zhang W, et al. Transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE) combined with endovascular implantation of an iodine-125 seed strand for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumour thrombosis versus TACE alone: a two-arm, randomised clinical trial. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140(2):211–9.
Shuqun C, Mengchao W, Han C, Feng S, Jiahe Y, Guanghui D, et al. Tumor thrombus types influence the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with the tumor thrombi in the portal vein. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007;54(74):499–502.
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42(5):1208–36.
Huang M, Lin Q, Wang H, Chen J, Bai M, Wang L, et al. Survival benefit of chemoembolization plus Iodine125 seed implantation in unresectable hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma with PVTT: a retrospective matched cohort study. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(10):3428–36.
Geschwind JF, Kudo M, Marrero JA, Venook AP, Chen XP, Bronowicki JP, et al. TACE treatment in patients with sorafenib-treated unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in clinical practice: final analysis of GIDEON. Radiology. 2016;279(2):630–40.
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(1):25–34.
Zhang L, Hu B, Li W, Huang P, Zhang S, Zhong BY, et al. 125 I Irradiation stent for hepatocellular carcinoma with main portal vein tumor thrombosis: a systematic review. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2020;43(2):196–203.
Yuan DY, Gao Z, Zhao J, Zhang HT, Wang J. 125 I seed implantation for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brachytherapy. 2019;18(4):521–9.
Kim PH, Choi SH, Kim JH, Park SH. Comparison of radioembolization and sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of safety and efficacy. Korean J Radiol. 2019;20(3):385–98.
Nakazawa T, Hidaka H, Shibuya A, Okuwaki Y, Tanaka Y, Takada J, et al. Overall survival in response to sorafenib versus radiotherapy in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with major portal vein tumor thrombosis: propensity score analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014;14:84.
Li XL, Guo WX, Hong XD, Yang L, Wang K, Shi J, et al. Efficacy of the treatment of transarterial chemoembolization combined with radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a propensity score analysis. Hepatol Res. 2016;46(11):1088–98.
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
This study was supported by the Suzhou Science and Technology Bureau Project (No.SYS2019036), Suzhou People’s Livelihood Science and Technology Project (No. SS202059), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Talent funding (No.ZDRCA2016038), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81771945).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This retrospective study was approved by the local ethics committee. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Consent for publication
For this type of study, consent for publication is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Wang, C., Shen, J. et al. Integrated I-125 Seed Implantation Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Main Portal Vein Tumor Thrombus. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 44, 1570–1578 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-021-02887-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-021-02887-1