Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the rate of short-term complications associated with microwave ablation of lung tumors located near the heart.
Methods
This HIPAA-compliant study was performed with a waiver for informed consent. Patients who underwent microwave ablation of lung tumors located 10 mm or less from the heart were identified by retrospective chart review. Both primary and metastatic tumors were included. Only tumors directly adjacent to one of the four cardiac chambers were included. All patients were treated in a single session using CT guidance with continuous electrocardiographic monitoring. Rates of new-onset arrhythmia and myocardial infarction (MI) within 90 days of the procedure were quantified, and evidence of cardiac or pericardiac injury was assessed for using post-ablation contrast-enhanced chest CT, electrocardiography (EKG), and—when available—echocardiography. Complications were graded using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) system.
Results
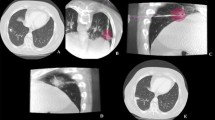
Ten patients (four males, six females; mean age 73.1 ± 9.5 years) met all inclusion criteria. Mean tumor distance from the heart was 3 mm (range, 0–6 mm). New-onset arrhythmia was not observed during or following any of the microwave ablation treatments, and there were no documented 90-day MI events. CTCAE Grade 1 complications were observed by CT in eight patients, most commonly mild focal pericardial thickening. EKG and echocardiography were normal in all patients. No major complications (CTCAE Grade 3 or greater) were observed.
Conclusions
Microwave ablation of lung tumors located 10 mm or less from the heart appears to have low associated short-term morbidity and may be appropriate in selected patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sonntag PD, Hinshaw JL, Lubner MG, Brace CL, Lee FT. Thermal ablation of lung tumors. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2011;20(2):369–87.
Gillams A, Khan Z, Osborn P, Lees W. Survival after radiofrequency ablation in 122 patients with inoperable colorectal lung metastases. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2013;36(3):724–30.
Ambrogi MC, Fanucchi O, Cioni R, et al. Long-term results of radiofrequency ablation treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a prospective intention-to-treat study. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6(12):2044–51.
Beland MD, Wasser EJ, Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE. Primary non-small cell lung cancer: review of frequency, location, and time of recurrence after radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. 2010;254(1):301–7.
Zhu JC, Yan TD, Morris DL. A systematic review of radiofrequency ablation for lung tumors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15(6):1765–74.
Chua TC, Sarkar A, Saxena A, Glenn D, Zhao J, Morris DL. Long-term outcome of image-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung metastases: an open-labeled prospective trial of 148 patients. Ann Oncol. 2010;21(10):2017–22.
Wolf FJ, Grand DJ, Machan JT, Dipetrillo TA, Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE. Microwave ablation of lung malignancies: effectiveness, CT findings, and safety in 50 patients. Radiology. 2008;247(3):871–9.
Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Cioni R, et al. Response to radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary tumours: a prospective, intention-to-treat, multicentre clinical trial (the RAPTURE study). Lancet Oncol. 2008;9(7):621–8.
De Baère T, Aupérin A, Deschamps F, et al. Radiofrequency ablation is a valid treatment option for lung metastases: experience in 566 patients with 1037 metastases. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(5):987–91.
Morrison PR, vanSonnenberg E, Shankar S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of thoracic lesions: part 1, experiments in the normal porcine thorax. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(2):375–80.
Ganesan AN, Shipp NJ, Brooks AG, et al. Long-term outcomes of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2(2):e004549.
Bertaglia E, Stabile G, Pappone A, et al. Updated national multicenter registry on procedural safety of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2013;24(10):1069–74.
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, et al. Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2010;3(1):32–8.
Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Gobara H, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors close to the heart or aorta: evaluation of safety and effectiveness. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18(6):733–40.
Colak E, Tatlı S, Shyn PB, Tuncalı K, Silverman SG. CT-guided percutaneous cryoablation of central lung tumors. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014;20(4):316–22.
Roberts WC. Pericardial heart disease: its morphologic features and its causes. Proceedings of Baylor University Medical Center. 2005;18(1):38–55.
Carberry GA, Nocerino E, Mason PJ, et al. Pulmonary microwave ablation near the heart: antenna positioning can mitigate cardiac complications in a porcine model. Radiology. 2017;282(3):892–902.
Steinke K, Haghighi KS, Wulf S, Morris DL. Effect of vessel diameter on the creation of ovine lung radiofrequency lesions in vivo: preliminary results. J Surg Res. 2005;124(1):85–91.
Lu DS, Raman SS, Limanond P, et al. Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003;14(10):1267–74.
Steinke K, Glenn D, King J, Morris DL. Percutaneous pulmonary radiofrequency ablation: difficulty achieving complete ablations in big lung lesions. Br J Radiol. 2003;76(910):742–5.
Steinke K, Arnold C, Wulf S, Morris DL. Safety of radiofrequency ablation of myocardium and lung adjacent to the heart: an animal study. J Surg Res. 2003;114(2):140–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Aaron W. P. Maxwell, M.D., and Terrance T. Healey, M.D., declare no conflict of interest. Damian E. Dupuy, M.D., received fundings from Medtronic, Galil Medical, and royalties from Springer-Verlag and UpToDate. He is one of the Board of Directors of Perseon Medical.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maxwell, A.W.P., Healey, T.T. & Dupuy, D.E. Microwave Ablation of Lung Tumors Near the Heart: A Retrospective Review of Short-Term Procedural Safety in Ten Patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40, 1401–1407 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1660-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1660-y