Abstract
Purpose
To analyze the clinical outcome of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for recurrent intrahepatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after variable first-line treatment.
Materials and Methods
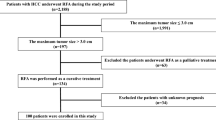
From January 2006 to December 2007, 168 consecutive patients (133 male, 35 female; mean age 66.7 ± 10.1 years) with cirrhosis (Child–Pugh class A/B [146/22]) who underwent RFA for treatment for recurrent intrahepatic HCC ≤5 cm, and in up to three nodules (214 HCCs; mean diameter 20.8 ± 7.5 mm; 38 multinodular forms), were included. Univariate and multivariate analyses for potential clinical, tumor-related, and radiologic factors affecting overall and recurrence-free patient survival were performed using the Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
Major complications occurred in 5 patients (5 of 168, 3.0 %), although there were no procedure-related deaths. Complete ablation was achieved in 161 patients (161 of 168, 95.8 %). After a mean follow-up period of 4 ± 21 months, local tumor progression, distant intrahepatic recurrence, and extrahepatic metastasis occurred in 22, 132, and 41 patients, respectively. Overall 5-year survival and recurrence-free survival were 48.0 and 11.9 %, respectively. Significant predicting factors for overall patient survival were Child–Pugh class B (relative risk [RR] = 4.52, 95 % confidence interval [CI] 1.97–10.34; P < 0.001), serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level (RR = 1.01, 95 % CI 1.01–1.01; P < 0.001), number of HCC nodules (RR = 1.70, 95 % CI 1.04–2.76; P = 0.033), tumor size (RR = 1.40, 95 % CI 1.07–1.83; P = 0.014), and presence of portosystemic collaterals (RR = 1.78, 95 % CI 1.09–2.92; P = 0.022).
Conclusion
RFA is a safe and effective treatment modality for recurrent intrahepatic HCC and has a 5-year survival rate of 48.0 %. Serum AFP level, Child–Pugh class, tumor number and size, and presence of portosystemic collaterals significantly affect overall patient survival.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2001) Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 94(2):153–156
Mazzaferro V (2007) Results of liver transplantation: with or without milan criteria? Liver Transpl 13(11 Suppl 2):S44–S47
Choi BI, Kim HC, Han JK et al (1992) Therapeutic effect of transcatheter oily chemoembolization therapy for encapsulated nodular hepatocellular carcinoma: CT and pathologic findings. Radiology 182(3):709–713
Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J (1999) Intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results of treatment and prognostic factors. Ann Surg 229(2):216–222
Neeleman N, Andersson R (1996) Repeated liver resection for recurrent liver cancer. Br J Surg 83(7):893–901
Sugimachi K, Maehara S, Tanaka S, Shimada M (2001) Repeat hepatectomy is the most useful treatment for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 8(5):410–416
Choi D, Lim HK, Kim MJ et al (2004) Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: percutaneous radiofrequency ablation after hepatectomy. Radiology 230(1):135–141
Sbai Idrissi MS, Vons C, Borgonovo G, Mariette D, Smadja C, Franco D (1998) Treatment of hepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinomas. Ann Chir 52(6):543–546
Suenaga M, Sugiura H, Kokuba Y, Uehara S, Kurumiya T (1994) Repeated hepatic resection for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma in eighteen cases. Surgery 15(4):452–457
Shuto T, Kinoshita H, Hirohashi K et al (1996) Indications for, and effectiveness of, a second hepatic resection for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 43(10):932–937
Shimada M, Takenaka K, Taguchi K et al (1998) Prognostic factors after repeat hepatectomy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 227(1):80–85
Okazaki M, Yamasaki S, Ono H et al (1993) Chemoembolotherapy for recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma in the residual liver after hepatectomy. Hepatogastroenterology 40(4):320–323
Shimada M, Takenaka K, Gion T et al (1996) Prognosis of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a 10-year surgical experience in Japan. Gastroenterology 111(3):720–726
N’Kontchou G, Mahamoudi A, Aout M et al (2009) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results and prognostic factors in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 50(5):1475–1483
Chen MS, Li JQ, Zheng Y et al (2006) A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 243(3):321–328
Lu MD, Kuang M, Liang LJ et al (2006) Surgical resection versus percutaneous thermal ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized clinical trial. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 86(12):801–805
Livraghi T, Benedini V, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Torzilli G, Vettori C (1998) Long term results of single session percutaneous ethanol injection in patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 83(1):48–57
Yang W, Chen MH, Yin SS et al (2006) Radiofrequency ablation of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: therapeutic efficacy on early- and late-phase recurrence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(5 Suppl):S275–S283
Bruix J, Sherman M (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 42(5):1208–1236
Lee JM, Han JK, Kim HC et al (2007) Switching monopolar radiofrequency ablation technique using multiple, internally cooled electrodes and a multichannel generator: ex vivo and in vivo pilot study. Invest Radiol 42(3):163–171
Lee J, Lee JM, Yoon JH et al (2012) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with multiple electrodes for medium-sized hepatocellular carcinomas. Korean J Radiol 13(1):34–43
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF et al (2009) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20(7 Suppl):S377–S390
Crocetti L, de Baere T, Lencioni R (2010) Quality improvement guidelines for radiofrequency ablation of liver tumours. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 33(1):11–17
Nakazawa T, Kokubu S, Shibuya A et al (2007) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation between local tumor progression after ablation and ablative margin. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188(2):480–488
Widmann G, Schullian P, Haidu M, Bale R (2012) Stereotactic radiofrequency ablation (SRFA) of liver lesions: technique effectiveness, safety, and interoperator performance. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 35(3):570–580
Cardella JF, Kundu S, Miller DL, Millward SF, Sacks D (2009) Society of Interventional Radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20(7 Suppl):S189–S191
Choi D, Lim HK, Rhim H et al (2007) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma as a first-line treatment: long-term results and prognostic factors in a large single-institution series. Eur Radiol 17(3):684–692
Shiina S, Tateishi R, Arano T et al (2012) Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: 10-year outcome and prognostic factors. Am J Gastroenterol 107(4):569–577 quiz 57
Takayasu K, Wakao F, Moriyama N et al (1992) Postresection recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma treated by arterial embolization: analysis of prognostic factors. Hepatology 16(4):906–911
Miyaaki H, Nakashima O, Kurogi M, Eguchi K, Kojiro M (2007) Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein and protein induced by vitamin K absence II are potential indicators of a poor prognosis: a histopathological study of surgically resected hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 42(12):962–968
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L et al (2005) Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long-term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 234(3):961–967
Kim SH, Lee JM, Choi JY et al (2008) Changes of portosystemic collaterals and splenic volume on CT after liver transplantation and factors influencing those changes. AJR Am J Roentgenol 191(1):W8–W16
Kang HK, Jeong YY, Choi JH et al (2002) Three-dimensional multidetector row CT portal venography in the evaluation of portosystemic collateral vessels in liver cirrhosis. Radiographics 22(5):1053–1061
Cho KC, Patel YD, Wachsberg RH, Seeff J (1995) Varices in portal hypertension: evaluation with CT. Radiographics 15(3):609–622
Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J (1999) Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology 30(6):1434–1440
Bruix J, Castells A, Bosch J et al (1996) Surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: prognostic value of preoperative portal pressure. Gastroenterology 111(4):1018–1022
Lam VW, Ng KK, Chok KS et al (2008) Risk factors and prognostic factors of local recurrence after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 207(1):20–29
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M et al (2008) Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology 47(1):82–89
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in this study for any of the authors, including Dong Ho Lee, Jeong Min Lee, Jae Young Lee, Se Hyung Kim, Joon Koo Han and Byung Ihn Choi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.H., Lee, J.M., Lee, J.Y. et al. Radiofrequency Ablation for Intrahepatic Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Long-Term Results and Prognostic Factors in 168 Patients with Cirrhosis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37, 705–715 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0708-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0708-x