Abstract
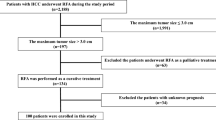
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the long-term survival results and complications of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Between April 1999 and May 2005, 570 patients with 674 early-stage HCCs underwent percutaneous RFA as a first-line treatment option in a single institution. We evaluated the effectiveness rates, local tumor progression rates, survival rates, and complications. We also assessed the prognostic values of survival rates by using Cox proportional hazard models. The primary technique effectiveness rate was 96.7% (652 of 674). The cumulative rates of local tumor progression at 1, 2, and 3 years were 8.1%, 10.9%, and 11.8%, respectively. The cumulative survival rates at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years were 95.2%, 82.9%, 69.5%, 60.8%, and 58.0%, respectively. Patients with Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis, of younger age (≤58 years), or having lower AFP level (≤100 μg/L) demonstrated better survival results (P < 0.05). A total of 11 major complications (1.9% per treatment) were found during the follow-up period. There was no procedure-related death. Percutaneous RFA can be used successfully as a first-line treatment modality for early-stage HCCs. Child-Pugh class, age, and AFP level before RFA were significant prognostic predictors of long-term survival.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okuda K (1992) Hepatocellular carcinoma: recent progress. Hepatology 15(5):948–963
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 362(9399):1907–1917
Song TJ, Ip EW, Fong Y (2004) Hepatocellular carcinoma: current surgical management. Gastroenterology 127(5 Suppl 1):248–260
Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J (1999) Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology 30(6):1434–1440
Jansen MC, van Hillegersberg R, Chamuleau RA, van Delden OM, Gouma DJ, van Gulik TM (2005) Outcome of regional and local ablative therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a collective review. Eur J Surg Oncol 31(4):331–347
Shibata T, Iimuro Y, Yamamoto Y, Maetani Y, Ametani F, Itoh K, Konishi J (2002) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 223(2):331–337
Lencioni RA, Allgaier HP, Cioni D, Olschewski M, Deibert P, Crocetti L, Frings H, Laubenberger J, Zuber I, Blum HE, Bartolozzi C (2003) Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 228(1):235–240
Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC, Hsu CW, Chen YC (2004) Radiofrequency ablation improves prognosis compared with ethanol injection for hepatocellular carcinoma < or =4 cm. Gastroenterology 127(6):1714–1723
Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, Sato S, Tateishi R, Fujishima T, Ishikawa T, Koike Y, Yoshida H, Kawabe T, Omata M (2005) A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation with ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 129(1):122–130
Lin SM, Lin CJ, Lin CC, Hsu CW, Chen YC (2005) Randomised controlled trial comparing percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, and percutaneous acetic acid injection to treat hepatocellular carcinoma of 3 cm or less. Gut 54(8):1151–1156
Buscarini L, Buscarini E, Di Stasi M, Vallisa D, Quaretti P, Rocca A (2001) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinoma: long term results. Eur Radiol 11(6):914–921
Lencioni R, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Franchini C, Pina CD, Lera J, Bartolozzi C (2005) Early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: long-term results of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 234(3):961–967
Tateishi R, Shiina S, Teratani T, Obi S, Sato S, Koike Y, Fujishima T, Yoshida H, Kawabe T, Omata M (2005) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer 103(6):1201–1209
Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, Beaugrand M, Lencioni R, Burroughs AK, Christensen E, Pagliaro L, Colombo M, Rodes J; EASL Panel of Experts on HCC (2001) Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol 35(3):421–430
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, Charboneau JW, Dodd GD 3rd, Dupuy DE, Gervais D, Gillams AR, Kane RA, Lee FT Jr, Livraghi T, McGahan J, Phillips DA, Rhim H, Silverman SG; Society of Interventional Radiology Technology Assessment Committee (2005) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology 235(3):728–739
Choi D, Lim HK, Kim SH, Lee WJ, Jang HJ, Lee JY, Paik SW, Koh KC, Lee JH (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: usefulness of power Doppler US with a microbubble contrast agent in evaluating therapeutic response-preliminary results. Radiology 217(2):558–563
Choi D, Lim HK, Lee WJ, Kim SH, Kim MJ, Kim SK, Jang KM, Lee JY, Lim JH (2004) Radiofrequency ablation of liver cancer: early evaluation of therapeutic response with contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Korean J Radiol 5(3):185–198
Lim HK, Choi D, Lee WJ, Kim SH, Lee SJ, Jang HJ, Lee JH, Lim JH, Choo IW (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma treated with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: evaluation with follow-up multiphase helical CT. Radiology 221(2):447–454
Livraghi T, Festi D, Monti F, Salmi A, Vettori C (1986) US-guided percutaneous alcohol injection of small hepatic and abdominal tumors. Radiology 161(2):309–312
Khan KN, Yatsuhashi H, Yamasaki K, Yamasaki M, Inoue O, Koga M, Yano M (2000) Prospective analysis of risk factors for early intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma following ethanol injection. J Hepatol 32(2):269–278
Choti MA (2002) Surgical management of hepatocellular carcinoma: resection and ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13(9 Pt 2):S197–S203
Buscarini E, Savoia A, Brambilla G, Menozzi F, Reduzzi L, Strobel D, Hansler J, Buscarini L, Gaiti L, Zambelli A (2005) Radiofrequency thermal ablation of liver tumors. Eur Radiol 15(5):884–894
Livraghi T, Solbiati L, Meloni MF, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Goldberg SN (2003) Treatment of focal liver tumors with percutaneous radio-frequency ablation: complications encountered in a multicenter study. Radiology 226(2):441–451
Rhim H, Yoon KH, Lee JM, Cho Y, Cho JS, Kim SH, Lee WJ, Lim HK, Nam GJ, Han SS, Kim YH, Park CM, Kim PN, Byun JY (2003) Major complications after radio-frequency thermal ablation of hepatic tumors: spectrum of imaging findings. Radiographics 23(1):123–134
Shibata T, Shibata T, Maetani Y, Isoda H, Hiraoka M (2006) Radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma: prospective comparison of internally cooled electrode and expandable electrode. Radiology 238(1):346–353
Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, Sohn KL, Choi SH, Choi BI (2005) Bipolar radiofrequency ablation in ex vivo bovine liver with the open-perfused system versus the cooled-wet system. Eur Radiol 15(4):759–764
Burdio F, Navarro A, Sousa R, Burdio JM, Guemes A, Gonzalez A, Cruz I, Castiella T, Lozano R, Berjano E, Figueras J, de Gregorio MA (2006) Evolving technology in bipolar perfused radiofrequency ablation: assessment of efficacy, predictability and safety in a pig liver model. Eur Radiol 16(8):1826–1834
Vilana R, Bianchi L, Varela M, Nicolau C, Sanchez M, Ayuso C, Garcia M, Sala M, Llovet JM, Bruix J, Bru C; BCLC Group (2006) Is microbubble-enhanced ultrasonography sufficient for assessment of response to percutaneous treatment in patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma? Eur Radiol DOI 10.1007/s00330-006-0264-8
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Samsung Medical Center Clinical Research Development Program grant. We thank Sang Hee Han and Kyong Hee Lee at the Samsung Biomedical Research Institute for data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, D., Lim, H.K., Rhim, H. et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma as a first-line treatment: long-term results and prognostic factors in a large single-institution series. Eur Radiol 17, 684–692 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0461-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0461-5