Abstract
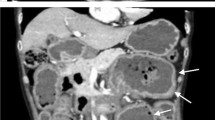
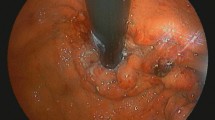
Amyloidosis is characterized by the extracellular deposition of amyloid protein in various organs. Gastrointestinal involvement in amyloidosis is common, but a diagnosis of amyloidosis is often delayed. Severe gastrointestinal hemorrhage in amyloidosis is rare but can be fatal in some cases. We experienced a case of a 49-year-old man who presented with recurrent massive hematochezia. Although embolization was performed eight times for bleeding from different sites of the small intestine, hematochezia did not cease. We report the case, with a review of the literature.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Westermark P (2005) Aspects on human amyloid forms and their fibril polypeptides. FEBS J 272:5942–5949
Ebert EC, Naqar M (2008) Gastrointestinal manifestations of amyloidosis. Am J Gastroenterol 103:776–787
Greenstein AJ, Sachar DB, Panday AK et al (1992) Amyloidosis and inflammatory bowel disease. A 50-year experience with 25 patients. Medicine 71:261–270
Azzopardi JG, Lehner T (1966) Systemic amyloidosis and malignant disease. J Clin Pathol 19:539
Maeshima E, Yamada Y, Yukawa S (1999) Massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage in a case of amyloidosis secondary to rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 28:262–264
Kaiserling E, Krober S (1995) Massive intestinal hemorrhage associated with intestinal amyloidosis. An investigation of underlying pathologic processes. Gen Diagn Pathol 141:147–154
Tada S, Iida M, Yao T et al (1994) Gastrointestinal amyloidosis: radiologic features by chemical types. Radiology 190:37–42
Kim SH, Han JK, Lee KH et al (2003) Abdominal amyloidosis: spectrum of radiological findings. Clin Radiol 58:610–620
Araoz PA, Batts KP, MacCarty RL (2000) Amyloidosis of the alimentary canal: radiologic-pathologic correlation of CT findings. Abdom Imaging 25:38–44
Schroeder FM, Miller FJ, Nelson JA et al (1978) Gastrointestinal angiographic findings in systemic amyloidosis. Am J Roentgenol 131:143–146
Hazenberg BPC, van Rijswijk MH, Piers A et al (2006) Diagnostic performance of 123I-labeled serum amyloid P component scintigraphy in patients with amyloidosis. Am J Med 119:355.E15–24
Fujihara S, Balow JE, Costa JC, Glenner GG (1980) Identification and classification of amyloid in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections by the unlabeled immunoperoxidase method. Lab Invest 43:358–365
Usui M, Matsuda S, Suzuki H et al (2000) Gastric amyloidosis with massive bleeding requiring emergency surgery. J Gastroenterol 35:924–928
Kuo WT, Lee DE, Saad WE et al (2003) Superselective microcoil embolization for the treatment of lower gastrointestinal hemorrhage. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14(12):1503–1509
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.H., Kang, E.J., Park, J.W. et al. Gastrointestinal Amyloidosis Presenting with Multiple Episodes of Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32, 577–580 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9429-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-008-9429-y