Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the influence of continuous infusion of acetic acid 50% during radiofrequency ablation (RFA) on the size of the thermal lesion produced.
Methods
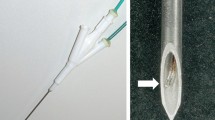
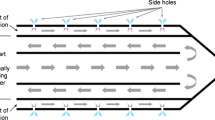
Radiofrequency (RF) was applied to excised bovine liver by using an expandable needle electrode with 10 retractable tines (LeVeen Needle Electrode, RadioTherapeutics, Sunnyvale, CA) connected to a commercially available RF generator (RF 2000, RadioTherapeutics, Sunnyvale, CA). Experiments were performed using three different treatment modalities: RF only (n = 15), RF with continuous saline 0.9% infusion (n = 15), and RF with continuous acetic acid 50% infusion (n = 15). RF duration, power output, tissue impedance, and time to a rapid rise in impedance were recorded. The ablated lesions were evaluated both macroscopically and histologically.
Results
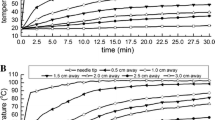
The ablated lesions appeared as spherical or ellipsoid, well-demarcated pale areas with a surrounding brown rim with both RF only and RF plus saline 0.9% infusion. In contrast, thermolesions generated with RF in combination with acetic acid 50% infusion were irregular in shape and the central portion was jelly-like. Mean diameter of the coagulation necrosis was 22.3 ± 2.1 mm (RF only), 29.2 ± 4.8 mm (RF + saline 0.9%) and 30.7 ± 5.7 mm (RF + acetic acid 50%), with a significant increase in the RF plus saline 0.9% and RF plus acetic acid 50% groups compared with RF alone. Time to a rapid rise in impedance was significantly prolonged in the RF plus saline 0.9% and RF plus acetic acid 50% groups compared with RF alone.
Conclusions
A combination of RF plus acetic acid 50% infusion is able to generate larger thermolesions than RF only or RF combined with saline 0.9% infusion.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodd GD III, Soulen MC, Kane RA, Livraghi T, Lees WR, Yamashita Y, Gillams AR, Karahan OI, Rhim H (2000) Minimally invasive treatment of malignant hepatic tumors: At the threshold of a major breakthrough. RadioGraphics 20:9–27
de Tucker Sanctis J, Goldberg SN, Mueller PR (1998) Percutaneous treatment of hepatic neoplasms: A review of current techniques. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 21:273–296
Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Hahn PF, Cosman E, Conrad JE, Fogle R, Gazelle GS (1998) Large-volume tissue ablation with radio frequency by using a clustered, internally cooled electrode technique: Laboratory and clinical experience in liver metastases. Radiology 209:371–379
Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, Gazelle GS, Kruskal JB, Huertas JC, Halpern EF, Oliver BS, Lenkinski RE (2001) Radio-frequency thermal ablation with NaCl solution injection: Effect of electrical conductivity on tissue heating and coagulation—phantom and porcine liver study. Radiology 219:157–165
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Monti F, Bizzini A, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Pellicano S, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS (1997) Saline-enhanced radio-frequency tissue ablation in the treatment of liver metastases. Radiology 202:205–210
De Baere T, Denys A, Wood BJ, Lassau N, Kardache M, Vilgrain V, Menu Y, Roche A (2001) Radiofrequency liver ablation: Experimental comparative study of water-cooled versus expandable systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:187–192
Ni Y, Miao Y, Mulier S, Yu J, Baert AL, Marchal G (2000) A novel “cooled-wet” electrode for radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol 10:852–854
Goldberg NS, Gazelle GS, Compton CC, Mueller PR, Tanabe KK (2000) Treatment of intrahepatic malignancy with radiofrequency ablation. Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Cancer 88:2452–2463
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Ierace T, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma: Radio-frequency ablation of medium and large lesions Radiology 214:761–768
Rossi S, Di Stasi M, Buscarini E, Quaretti P, Garbagnati F, Squassante L, Paties CT, Silverman DE, Buscarini L (1996) Percutaneous RF interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 167:759–768
Dupuy DE, Zagoria RJ, Akerley W, Mayo-Smith WW, Kavanagh PV, Safran H (2000) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of malignancies in the lung. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:57–59
Wood BJ, Bates S (2001) Radiofrequency thermal ablation of a splenic metastasis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:261–263
McGahan JP, Dodd III GD (2001) Radiofrequency ablation of the liver: Current status. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176:3–16
Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, Di Stasi M, Quaretti P, Rago M, Zangrandi A, Andreola S, Silverman D, Buscarini L (1998) Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. AJR Am J Roentgenol 170:1015–1022
Goldberg SN, Hahn PF, Halpern EF, Fogle RM, Gazelle GS (1998) Radio-frequency tissue ablation: Effect of pharmacologic modulation of blood flow on coagulation diameter. Radiology 209:761–767
Ohnishi K, Yoshioka H, Ito S, Fujiwara K (1996) Treatment of nodular hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 3 cm with ultrasound-guided percutaneous acetic acid injection. Hepatology 24:1379–1385
Liang H-L, Yang C-F, Pan H-B, Lai K-H, Cheng J-S, Lo G-H, Chen CKH, Lai P-H (2000) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Safety and efficacy of single high-dose percutaneous acetic acid injection for treatment. Radiology 214:769–774
Ohnishi K, Yoshioka K, Ito S, Fujiwara K (1998) Prospective randomized controlled trial comparing percutaneous acetic acid injection and percutaneous ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 27:67–72
Ohnishi K (1998) Comparison of percutaneous acetic acid injection and percutaneous ethanol injection for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepato-Gastroenterology 45:1254–1258
Lee JM, Lee YH, Kim YK, Kim SW, Kim CS (2004) Combined therapy of radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection of rabbit liver: An in vivo feasibility study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 27:151–157
Goldberg SN, Kruskal JB, Oliver BS, Clouse ME, Gazelle GS (2000) Percutaneous tumor ablation: Increased coagulation by combining radio-frequency ablation and ethanol instillation in a rat breast tumor model. Radiology 217:827–831
Shiina S, Tagawa K, Unuma T, Takanashi R, Yoshiura K, Komatsu Y, Hata Y, Niwa Y, Shiratori Y, Terano A (1991) Percutaneous ethanol injection therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. A histopathologic study. Cancer 68:1524–1530
Koda M, Okamoto K, Miyoshi Y, Kawasaki H (1992) Hepatic vascular and bile duct injury after ethanol injection therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastrointest Radiol 17:167–169
Shah SS, Jacobs DL, Krasinkas AM, Furth EE, Itkin M, Clark TW (2004) Percutaneous ablation of VX2 carcinoma-induced liver tumors with use of ethanol versus acetic acid: Pilot study in a rabbit model. J Vasc Interv Radiol 15:63–67
Lee JM, Kim YK, Kim SW, Han JK, Kim SH, Choi BI (2004) Combined radiofrequency ablation and acetic acid hypertonic saline solution instillation: An in vivo study of rabbit liver. Korean J Radiol 5:31–38
Lee JM, Lee YH, Kim YK, Kim SW, Kim SH, Han JK, Choi BI (2004) Combined treatment of radiofrequency ablation and acetic acid injection: An in vivo feasibility study in rabbit liver. Eur Radiol 14:1303–1310
Dodd GD, Frank MS, Aribandi M, Chopra S, Chintapalli KN (2002) Radiofrequency thermal ablation: Computer analysis created by overlapping ablations. AJR Am J Roentgenol 177:777–782
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lubienski, A., Düx, M., Lubienski, K. et al. Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation: Increase in Lesion Diameter with Continuous Acetic Acid Infusion. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28, 789–794 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0022-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-005-0022-3