Abstract
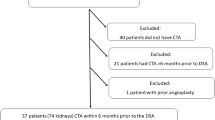
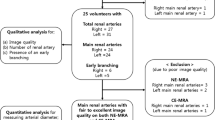
The purpose of this study was to assess interobserver variability and accuracy in the evaluation of renal artery stenosis (RAS) with gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography (MRA) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) in patients with hypertension. The authors found that source images are more accurate than maximum intensity projection (MIP) for depicting renal artery stenosis. Two independent radiologists reviewed MRA and DSA from 38 patients with hypertension. Studies were postprocessed to display images in MIP and source images. DSA was the standard for comparison in each patient. For each main renal artery, percentage stenosis was estimated for any stenosis detected by the two radiologists. To calculate sensitivity, specificity and accuracy, MRA studies and stenoses were categorized as normal, mild (1–39%), moderate (40–69%) or severe (≥70%), or occluded. DSA stenosis estimates of 70% or greater were considered hemodynamically significant. Analysis of variance demonstrated that MIP estimates of stenosis were greater than source image estimates for both readers. Differences in estimates for MIP versus DSA reached significance in one reader. The interobserver variance for MIP, source images and DSA was excellent (0.80< κ≤ 0.90). The specificity of source images was high (97%) but less for MIP (87%); average accuracy was 92% for MIP and 98% for source images. In this study, source images are significantly more accurate than MIP images in one reader with a similar trend was observed in the second reader. The interobserver variability was excellent. When renal artery stenosis is a consideration, high accuracy can only be obtained when source images are examined.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
NM Kaplan (1994) Hypertension in the population at large In: Kaplan NM (ed) Clinical hypertension Williams and Wilkins Baltimore 1–22
BJ Hillmann (1989) ArticleTitleImaging advances in the diagnosis of renovascular hypertension AJR Am J Roentgenol 153 5–14 Occurrence Handle2660537
MR Prince (1994) ArticleTitleGadolinium enhanced MR aortography Radiology 191 155–164 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC1c7ns1M%3D Occurrence Handle8134563
SO Schoenberg MR Prince MV Knopp JR Allenberg (1998) ArticleTitleRenal MR angiography Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 6 351–370 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3ivVersg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9560490
InstitutionalAuthorNameNorth American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators (1991) ArticleTitleBeneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high grade stenosis N Engl J Med 325 445–453 Occurrence Handle1852179
M Volk M Strotzer M Lenhart (2000) ArticleTitleTime-resolved contrast-enhanced MR angiography of renal artery stenosis: Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver variability AJR Am J Roentgenol 174 1583–1588 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czgt1SqtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10845486
E Fommei S Ghione AJ Hilson (1993) ArticleTitleCaptopril radionuclide test in renovascular hypertension: A European multicenter study Eur J Nucl Med 20 617–623 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00176558 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA1c%2Fks1A%3D Occurrence Handle8370384
VP Pottumarthi J Goldfarb Ch Sundaram A Priatna W Li RR Edelman (2000) ArticleTitleCaptopril MR renography in a swine model: Toward a comprehensive evaluation of renal arterial stenosis Radiology 217 813–818 Occurrence Handle11110948
DA Leung U Hoffmann T Pfammatter (1999) ArticleTitleMagnetic resonance angiography versus duplex sonography for diagnosing renovascular disease Hypertension 33 726–731 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7kvVajtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10024336
M Galanski M Prokop A Chavan (1993) ArticleTitleRenal artery stenoses: Helical CT angiography Radiology 189 185–192 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA1czgsFc%3D Occurrence Handle8372191
JP Beregi M Elkohen G Deklunder (1996) ArticleTitleHelical CT angiography compared with arteriography in the detection of renal artery stenosis AJR Am J Roentgenol 167 495–501 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymA3c3gtlM%3D Occurrence Handle8686635
SO Schoenberg M Essig M Bock (1999) ArticleTitleComprehensive MR evaluation of renovascular disease in five breath holds J Magn Reson Imaging 10 347–356 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1522-2586(199909)10:3<347::AID-JMRI17>3.3.CO;2-1 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mvjsl2hsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10508296
J Bakker FJ Beek JJ Beutler (1998) ArticleTitleRenal artery stenosis and accessory renal arteries: Accuracy of detection and visualization with gadolinium-enhanced breath-hold MR angiography Radiology 207 497–504 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3jvVelsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9577501
MR Prince SO Schoenberg JS Ward (1997) ArticleTitleHemodynamically significant artheriosclerotic renal artery stenosis: MR angiographic features Radiology 205 128–136 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiH28%2FlvFY%3D Occurrence Handle9314974
F De Cobelli A Vanzulli S Sironi (1997) ArticleTitleRenal artery stenosis: Evaluation with breath-hold, three-dimensional, dynamic, gadolinium-enhanced versus three-dimensional phase contrast MR angiography Radiology 205 689–695 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FlsFansg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9393522
TF Hany DA Leung T Pfammatter JF Debatin (1998) ArticleTitleContrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of the renal arteries: Original investigation Invest Radiol 33 653–669 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00004424-199809000-00021 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvjvFWrtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9766050
JJ Snidow MS Johnson VJ Harris (1996) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography for aortoiliac inflow assessment plus renal artery screening in a single breath hold Radiology 198 725–732 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC1MvgvVQ%3D Occurrence Handle8628861
JC Steffens J Link J Grassner (1997) ArticleTitleConrast-enhanced, k-space-centered, breath-hold MR angiography of the renal arteries and the abdominal aorta J Magn Reson Imaging 7 617–622 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA1cjjsVE%3D Occurrence Handle9243378
PT Johnson EJ Halpern BS Kuszyk (1999) ArticleTitleRenal artery stenosis: CT angiography-comparison of real time volume rendering and maximum intensity projection algorithms Radiology 211 337–343 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3ksFWqtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10228511
PS Calhoun BS Kuszyk DG Heath JC Carley EK Fishman (1999) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional volume rendering of spiral CT data: Theory and method RadioGraphics 19 745–764 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3mslansQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10336201
V Baskaran FS Pereles AA Nemcek JC Carr FH Miller J Ly E Krupinski JP Finn (2002) ArticleTitleGadolinium-enhanced 3D MR angiography of renal artery stenosis: A pilot comparison of maximum intensity projection, multiplanar reformatting, and 3D volume-rendering postprocessing algorithms Acad Radiol 9 50–59 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1076-6332(03)80296-9 Occurrence Handle11918359
Acknowledgement
We thank the technician staff of the department of magnetic resonance for preparing the postprocessing images. Thanks also to Mrs. Genie Lamont for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wehrschuetz, M., Aschauer, M., Portugaller, H. et al. Review of Source Images is Necessary for the Evaluation of Gadolinium-Enhanced MR Angiography for Renal Artery Stenosis. CVIR 27, 441–446 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0047-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0047-z