Abstract
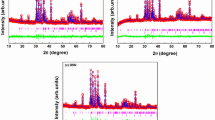
A natural sample of clinochlore from the Longitudinal Valley area of northeastern Taiwan has been characterized by using the powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), differential thermal analysis and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopic techniques. The lattice parameters of the monoclinic (IIb) clinochlore with the composition (Mg2.988 Al1.196 Fe1.6845 Mn0.026)5.8945 (Si2.559 Al1.441)4 O10 (OH)8 have been calculated from the powder XRD data and are found to be a = 5.347 Å, b = 9.223 Å, c = 14.250 Å, β = 97.2° and Z = 2. The thermal behaviour of the sample showed the typical behaviour of clinochlore with a hydroxyl content of 12.5 wt%. The EPR spectrum at room temperature exhibits two resonance signals centred at g ≈ 2.0 and g ≈ 8.0. The signal at g ≈ 2.0 shows a six-line hyperfine structure which is a characteristic of Mn2+ ions in octahedral symmetry. The resonance signal at g ≈ 8.0 is a characteristic of Fe3+ ions. The EPR spectra have also been recorded at different temperatures (123–295 K). The population of spin levels (N) has been calculated for g ≈ 2.0 and g ≈ 8.0 resonance signals. It is observed that N increases with decreasing temperature. From EPR spectra, the spin-Hamiltonian parameters have been evaluated. The zero-field splitting parameter (D) is found to be temperature dependent. The peak-to-peak width of the g ≈ 8.0 resonance signal is found to increase with decrease in temperature.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasa R (1970) Powder line shapes in the electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of high-spin ferric complexes. J Chem Phys 52:3919. doi:10.1063/1.1673591
Abragam A, Bleaney B (1970) Electron paramagnetic resonance of transition ions. Clarendon, Oxford, 203 p
Allen BT (1965) Zero-Field Splitting Parameter of the Mn2+ ion in glassy and in polycrystalline media. J Chem Phys 43:3820. doi:10.1063/1.1696569
Bai TB, Guggenheim S, Wang SJ, Rancourt DG, Koster van Gross AF (1993) Metastable phase relations in the chlorite–H2O system. Am Mineral 78:1208
Bailey SW (1988) Chlorites: structures and crystal chemistry. Rev Mineral 19:347
Balan E, Allarad T, Boizot B, Morin G, Muller JP (2000) Quantitative measurement of paramagnetic Fe3+ in kaolinite. Clays Clay Miner 48:439. doi:10.1346/CCMN.2000.0480404
Ballet O, Coey JMD (1982) Magnetic properties of sheet silicates; 2:1 layer minerals. Phys Chem Miner 8:218. doi:10.1007/BF00309481
Coey JMD, Ballet O, Moukarika A, Soubey Roux JL (1981) Magnetic properties of sheet silicates; 1:1 layer minerals. Phys Chem Miner 7:141. doi:10.1007/BF00308232
Diaz JM, Farach HA, Poole CP Jr (1990) Electron-spin-resonance study of Mn2+ in natural wollastonite. Am Mineral 75:262
Gaite JM, Ermakoff P, Muller JP (1993) Characterization and origin of two Fe3+ EPR spectra in kaolinite. Phys Chem Miner 20:242. doi:10.1007/BF00208137
Gaite JM, Ermakoff P, Allard TH, Muller JP (1997) Paramagnetic Fe3+: a sensitive probe for disorder in kaolinite. Clays Clay Miner 45:496. doi:10.1346/CCMN.1997.0450402
Gopal NO, Narasimhulu KV, Rao JL (2004a) EPR, optical, infrared and Raman spectral studies of Actinolite mineral. Spectrochim Acta [A] 60:2441. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2003.12.021
Gopal NO, Narasimhulu KV, Lakshmana Rao J (2004b) Optical absorption, EPR, infrared and Raman spectral studies of clinochlore mineral. J Phys Chem Solids 65:1887. doi:10.1016/j.jpcs.2004.07.003
Ho CS (1986) A synthesis of the geologic evolution of Taiwan. Tectonophysics 125:1. doi:10.1016/0040-1951(86)90004-1
Hurlbut Jr CS, Klien C (1977) Manual of mineralogy, 19th edn. Wiley
Kleppe AK, Jephcoat AP, Welch MD (2003) The effect of pressure upon hydrogen bonding in Chlorite: a Raman spectroscopic study of clinochlore to 26.5 GPa. Am Mineral 88:567
Luca V, Cardile CM (1989) Cation migration in smectite minerals: electron spin resonance of exchanged Fe3+ probes. Clays Clay Miner 37:325. doi:10.1346/CCMN.1989.0370405
Meads RE, Malden PJ (1975) Electron spin resonance in natural kaolinites containing Fe3+ and other transition metal ions. Clay Miner 10:313. doi:10.1180/claymin.1975.010.5.01
Muller JP, Manceau A, Calas G, Allard T, Ildefouse P, Hazemann JL (1995) Crystal chemistry of kaolinite and Fe-Mn oxides; relation with formation conditions of low-temperature systems. Am J Sci 295:1115
Ohkubo Y (1963) Electron spin resonance spectra of divalent manganese ions in natural apatite single crystals. J Phys Soc Jpn 18:916. doi:10.1143/JPSJ.18.916
Parthasarathy G, Chetty TRK, Haggerty SE (2002) Thermal stability and spectroscopic studies of zemkorite: a carbonate from the Venkatampalle kimberlite of southern India. Am Mineral 87:1384
Parthasarathy G, Choudary BM, Sreedhar B, Kunwar AC, Srinivasan R (2003) Ferrous saponite from the Deccan Trap, India, and its application in adsorption and reduction of hexavalent chromium. Am Mineral 88:1983
Peacock S (1990) Fluid processes in subduction zones. Science 248:329. doi:10.1126/science.248.4953.329
Prieto AC, Dubessy J, Cathelineau M (1991) Structure–composition relationships in trioctahedral Chlorites; a vibrational spectroscopy study. Clays Clay Miner 39:531. doi:10.1346/CCMN.1991.0390508
Prissok F, Lehmann G (1986) An EPR study of Mn2+ and Fe3+ in dolomites. Phys Chem Miner 13:331. doi:10.1007/BF00308350
Sei J, Toure AA, Oliver-Fourcade J, Quiquampoix H, Staunton S, Jumas JC, Womes M (2004) Characterization of kaolinitic clays from the Ivory Coast: identification of structural Fe. Hyperfine Interact 155:51. doi:10.1023/B:HYPE.0000035159.17646.e0
Sreedhar B, Arundhathi R, Reddy MA, Parthasarathy G (2008) Highly efficient heterogenous catalyst of alcohols and amines using natural ferrous chamosite. Appl Clay Sci (in press). doi:10.1016/j.clay.2008.10.001
Townsend MG, Longworth G, Kodama H (1986) Magnetic interaction at low temperature in chlorite and its products of oxidation; a Mossbauer investigation. Can Mineral 24:105
Villieras F, Yvon J, Cases JM, De Donato P, Lhote F, Baeza R (1994) Development of microporosity in clinochlore upon heating. Clays Clay Miner 42:679. doi:10.1346/CCMN.1994.0420604
Watanabe T, Shimizu H, Masuda A, Saito H (1983) Studies of 29Si-spin lattice relaxation times and paramagnetic impurities in clay minerals by magic-angle spinning 29Si-NMR and EPR. Chem Lett 12:1293. doi:10.1246/cl.1983.1293
Weil JA, Bolton JR, Wertz JE (1994) Electron paramagnetic resonance: elementary theory and practical applications. Wiley, New York, 498 p
Wieringen V (1955) Paramagnetic resonance of divalent manganese incorporated in various lattices. Discuss Faraday Soc 19:118. doi:10.1039/df9551900118
Yu S, Jackson DD, Yu GK, Liu CC (1990) Dislocation model for crustal deformation in the Longitudinal Valley area, eastern Taiwan. Tectonophysics 183:97. doi:10.1016/0040-1951(90)90190-J
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Pamela Burnley, USA, and two anonymous reviewers for very useful comments and suggestions, which helped us to improve the manuscript. The authors are thankful to Dr K.·V. Narasimhulu (USA) for providing the samples used in the present work. We thank Dr. V.·P. Dimri, Director, NGRI, Dr. H. S. Maiti, Director, CGCRI and Dr. Ranjan Sen, Head, GTL lab, CGCRI for their support and encouragements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemanthkumar, G.N., Parthasarathy, G., Chakradhar, R.P.S. et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on clinochlore from Longitudinal Valley area, northeastern Taiwan. Phys Chem Minerals 36, 447–453 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-009-0291-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-009-0291-5