Abstract
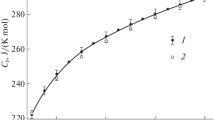
The unite cell parameters and heat capacities of a series of synthetic clinopyroxenes on the join Ca-Tschermak (CaTs)−diopside (Di) were measured using X-ray powder diffraction and calorimetric methods, respectively. The volume of mixing at 298 K shows a negative asymmetric deviation from ideality. A two-parameter Margules fit to the data yields W VCaTs−Di = −0.29 ± 0.11 cm3 mol−1 and W VDi−CaTs = −1.14 ± 0.14 cm3 mol−1. Heat capacities were determined between 5 and 923 K by heat-pulse at 5−302 K and differential-scanning calorimetry at 143−923 K. The precision of the low and high temperature C p data is better than ±1%. Polynomials of the form C p = a + bT −1/2 + cT −2 + dT −3 were fitted to the C p data in the temperature range between 250 and 925 K. Thermal entropy values [S 298 − S 0] and [S 900 −S 0] as well as enthalpies [H 298 − H 0] and [H 900 − H 0] were calculated for all members of the solid solution series. No significant deviation from ideal mixing behavior was observed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman RG, Brown TH (1985) Heat capacity of minerals in the system Na2O−K2O−CaO−MgO−FeO−Fe2O3−Al2O3−SiO2−TiO2−H2O−CO2; representation, estimation, and high temperature extrapolation. Contrib Mineral Petrol 89:168−183
Bosenick A, Geiger CA, Cemic L (1996) Heat capacity measurements of synthetic pyrope−grossular garnets between 320 and 1000 K by differential scanning calorimetry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:3215−3227
Cammenga HK, Eysel W, Gmelin E, Hemminger W, Höhne GWH, Sarge SM (1992) Die Temperaturkalibrierung dynamischer Kalorimeter II. Kalibrierungssubstanzen PTB Mitteilungen 102:13−18
Carswell DA (1991) The garnet−orthopyroxene Al barometer: problematic application to natural garnet lherzolite assemblages. Min Mag 55:19−31
Clark JR, Schairer JF, Neufville J (1962) Phase relations in the system CaMgSi2O6−CaAl2SiO6−SiO2 at low and high pressure. Carnegie Inst Wash Yearb 61:59−68
Cohen RE (1986) Thermodynamic solution properties of aluminous clinopyroxenes: nonlinear least square refinements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50:563−575
Dachs E, Bertoldi Ch (2005) Precision and accuracy of the heat-pulse calorimetric technique: low-temperature heat capacities of milligram-sized synthetic mineral samples. Eur J Min 17:251−261
Dachs E, Geiger CA (2006) Heat capacities and vibrational entropies of mixing of pyrope-grossular (Mg3Al2Si3O12−Ca3Al2Si3O12) garnet solid solutions: a low temperature calorimetric and thermodynamic investigation. Am Min 91:894−906
Ditmars DA, Douglas DB (1971) Measurements of the relative enthalpy of pure α−Al2O3 (NBS Heat capacity and enthalpy reference material No. 720) from 273 to 1173 K. J Res 75A:583−593
Ditmars DA, Ishihara S, Chang SS, Bernstein G, West ED (1981) Enthalpy and heat capacity standard reference material: synthetic sapphire (α−Al2O3) from 10 to 2250 K. J Res Nat Bur Stand 87:159−163
Gasparik T (1981) Mixing properties of the binary Jd-CaTs. EOS 62:412
Gasparik T (1984a) Experimental study of subsolidus phase relations and mixing properties of pyroxene in the system CaO−Al2O3−SiO2. Am Min 48:2537−2545
Gasparik T (1984b) Experimentally determined stability of clinopyroxene + garnet + corundum in the system CaO−MgO−Al2O3−SiO2. Am Min 69:1025−1035
Geiger CA (2001) Thermodynamic mixing properties of binary oxide and silicate solid solutions determined by direct measurements: the role of strain. In: Geiger CA (ed) European notes in mineralogy—solid solutions in silicate and oxide systems of geological importance, vol 3. Eötvös University Press, Budapest, pp71−100
Haselton HTJr, Hovis GL, Hemingway BS, Robie RA (1983) Calorimetric investigation of the excess entropy of mixing in analbite-sanidine solid solutions: lack of evidence for Na,K short-range order and implications for two-feldspar thermometry. Am Min 86:398−413
Haselton HT, Hemingway BS, Robie RA (1984) Low−temperature heat capacities of CaAl2SiO6 glass and pyroxene and thermal expansion of CaAl2SiO6 pyroxene. Am Min 69:481−489
Hays JF (1966) Lime-alumina-silica. Carnegie Inst Wash Yearb 65:234−239
Herzberg CT (1978) Pyroxene geothermometry and geobarometry: experimental and thermodynamic evaluation of some sub-solidus phase relations involving pyroxenes in the system CaO−MgO−Al2O3−SiO2. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:945−957
Krupka KM, Robie RA, Hemingway BS, Kerrick DM, Ito J (1985a) Low-temperature heat capacities and derived thermodynamic properties of anthophyllite, diopside, enstatite, bronzite and wollastonite. Am Min 70:249−260
Krupka KM, Hemingway BS, Robie RA, Kerrick DM (1985b) High-temperature heat capacities and derived thermodynamic properties of anthophyllite, diopside, dolomite, enstatite, bronzite, talc, tremolite and wollastonite. Am Min 70:261−271
Mraw SC (1988) Differential scanning calorimetry. In: Ho CY (ed) Data series on material properties, pp 395−437
Newton RC, Charlu TV, Kleppa OJ (1977) Thermochemistry of high pressure garnets and clinopyroxenes in the system CaO−MgO−Al2O3−SiO2. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 41:369−377
Nimis P (1995) A clinopyroxene geobarometer for basaltic systems based on crystal−structure modelling. Contrib Min Petrol 121:115−125
Nimis P (1999) Clinopyroxene geobarometry of magnetic rocks. Part 2. Structural geobarometers for basic to acid, tholeiitic and mildly alkaline magmatic systems. Contrib Min Petrol 135:62−74
Nimis P, Ulmer P (1998) Clinopyroxene geobarometry of magmatic rocks. Part 1. An expanded structural geobarometer for anhydrous and hydrous basic and ultrabasic systems. Contrib Min Petrol 133:122−135
Okamura FP, Ghose S, Ohashi H (1974) Structure and crystal chemistry of calcium Tschermak’s pyroxene, CaAlAlSiO6. Am Min 59:549−557
Putirka K, Johnson M, Kinzler R, Longhi J, Walker D. (1996) Thermobarometry of mafic igneous rocks based on clinopyroxene−liquid equilibria, 0−30 kbar. Contrib Min Petrol 123:92−108
Rodrigez-Carvajal J (1990) Fullprof: a program for Rietveld refinement and pattern matching analysis. In: Abstracts of the satelite meeting on powder diffraction of XVth congress of International Union of Crystallogrphy. Toulouse, France p 127
Taylor WR (1998) An experimental test of some geothermometer and geobarometer formulations for upper mantle peridotites with application to the thermobarometry of fertile lherzloite and garnet websterite. N Jb Min Abh 172:381−408
Thompson AB (1984) Mineral reactions and mineral equilibria and their use in geothermometry, geobarometry and geohygrometry. In: Lagache M (ed) Thermometrie et barometrie geologiques. Soc Franc Mineral Cristall 1:179–199
Thompson AB, Perkins III D, Sonderegger U, Newton RC (1978) Heat capacities of synthetic CaAl2SiO6−CaMgSi2O6−Mg2Si2O6 pyroxenes. EOS 59:395
Warren MC, Dove MT, Myers ER, Bosenick A., Palin EJ, Sainz−Diou CI, Guiton BS, Rdfern SAT (2001) Monte Carlo methods for the study of cation ordering. Min Mag 65:221−248
Wood BJ (1976) Mixing properties of tschermakitic clinopyroxenes. Am Min 61:599−602
Wood BJ (1979) Activity-composition relationships in Ca(Mg,Fe)Si2O6−CaAl2SiO6 clinopyroxene solid solutions. Am J Sci 279:854−875
Wood BJ, Henderson CMB (1978) Compositions and unit-cell parameters of synthetic non-stoichiometric tschermakitic clinopyroxenes. Am Min 63:66−72
Yoshino T, Yamamoto H, Okudaira T, Torium M (1998) Crustal thickening of the lower crust of the Kohistan arc (N. Pakistan) deduced from Al zoning in clinopyroxene and plagioklase. J Metamorph Geol 16:729−748
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft for the financial support (Ce 10/13-3). Thanks are due also to Mrs. P. Kluge for her help in recording the differential−scanning−calorimetry (DSC) data at the University of Kiel. The PPMS measurements were supported by the Austrian Science Fund under the project number P15880-N11, which is gratefully acknowledged. We want to thank C.A. Geiger helpful discussions and for proof reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etzel, K., Benisek, A., Dachs, E. et al. Thermodynamic mixing behavior of synthetic Ca-Tschermak–diopside pyroxene solid solutions: I. Volume and heat capacity of mixing. Phys Chem Minerals 34, 733–746 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-007-0191-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-007-0191-5