Abstract
Background
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EP) is a severe necrotizing infection of the renal parenchyma which is associated with significant case mortality. We sought to identify the incidence and predictive risk factors associated with EP mortality.
Methods
Two electronic databases, PubMed and Web of Science, were searched from their inception until June 06, 2021 for relevant articles. Two independent teams reviewed abstracts and extracted data from the selected manuscripts. A meta-analysis has been reported in line with PRISMA 2020 and AMSTAR Guidelines.
Results
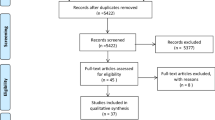
Of the 1080 retrieved abstracts, 79 underwent full-text review and 45 studies were included in the final analysis, comprising a total cohort of 1303 patients and 177 mortalities. The pooled prevalence of mortality among the patients with EP disease was 13%. Our analysis found a significantly decreasing trend in mortality rates, an increasing trend in minimally invasive intervention and decreasing trends in emergency nephrectomy in the EP studies from 1985 to 2020. Significant risk factors that were associated with a negative impact on survival of EP patients included sepsis (OR = 15.99), shock (OR = 15.57), disturbance of consciousness (OR = 12.11), thrombocytopenia (OR 7.85), acute renal failure (OR = 5.41), Wan classification I (OR = 4.57), emergency nephrectomy (OR = 3.73), Huang–Tseng classification III–IV (OR = 2.4) and medical management alone (OR = 2.04). Female sex (OR = 0.52) and minimally invasive intervention (OR = 0.47) (percutaneous nephrostomy or ureteral stent placement) were associated with decreased mortality rates.
Conclusions
Our study results demonstrated several significant risk factors that could help guide treatment to reduce the mortality risk of EP patients. Clinically, early treatment with a combination of minimally invasive intervention and appropriate medical management may be protective for reducing mortality risk in EP patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computer tomography
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- EN:
-
Emergency nephrectomy
- EP:
-
Emphysematous pyelonephritis
- NOS:
-
Newcastle–Ottawa scale
- PCD:
-
Percutaneous drainage
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Shokeir AA, El-Azab M, Mohsen T, El-Diasty T (1997) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 15-year experience with 20 cases. Urology 49(3):343–346
Elbaset MA, Zahran MH, Hashem A et al (2019) Could platelet to leucocytic count ratio (PLR) predict sepsis and clinical outcomes in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis? J Infect Chemother 25(10):791–796
Jain A, Manikandan R, Dorairajan L, Sreenivasan S, Bokka S (2019) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: does a standard management algorithm and a prognostic scoring model optimize patient outcomes? Urol Ann 11(4):414–420
Rahim MA, Ananna MA, Iqbal S, Uddin KN, Latif ZA (2021) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: experience at a tertiary care hospital in Bangladesh. J R Coll Phys Edinb 51(1):19–23
Ozawa M, Ichiyanagi O, Fujita S et al (2019) Risk of SOFA deterioration in conservative treatment for emphysematous pyelonephritis: pitfalls of current trends in therapeutics from multicenter clinical experience. Curr Urol 12:134–141
Sharma PK, Sharma R, Vijay MK, Tiwari P, Goel A, Kundu AK (2013) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: our experience with conservative management in 14 cases. Urol Ann 5(3):157–162
Eswarappa M, Suryadevara S, John MM, Kumar M, Reddy SB, Suhail M (2018) Emphysematous pyelonephritis case series from south India. Kidney Int Rep 3(4):950–955
Adapala RR, Shetty R, Venugopal P, Prabhu GGL, Yalla D, Unnikrishnan B (2020) Renal salvage, an achievable goal in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis: Outcomes of an algorithmic renal preserving strategy. Urol Ann 12(2):156–162
Misgar R, Mubarik I, Wani A, Bashir M, Ramzan M, Laway B (2016) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 10-year experience with 26 cases. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 20(4):475–480
Tsitouridis I, Michaelides M, Sidiropoulos D, Arvanity M (2010) Renal emphysema in diabetic patients: CT evaluation. Diagn Interv Radiol 16(3):221–226
Huang JJ, Tseng CC (2000) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: clinicoradiological classification, management, prognosis, and pathogenesis. Arch Intern Med 160(6):797–805
Wan YL, Lee TY, Bullard MJ, Tsai CC (1996) Acute gas-producing bacterial renal infection: correlation between imaging findings and clinical outcome. Radiology 198(2):433–438
Lu YC, Chiang BJ, Pong YH et al (2014) Predictors of failure of conservative treatment among patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis. BMC Infect Dis 14(1):1–8
Kapoor R, Muruganandham K, Gulia AK et al (2010) Predictive factors for mortality and need for nephrectomy in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis. BJU Int 105(7):986–989
Yap XH, Ng CJ, Hsu KH et al (2019) Predicting need for intensive care unit admission in adult emphysematous pyelonephritis patients at emergency departments: comparison of five scoring systems. Sci Rep 9(1):1–7
Sanford TH, Myers F, Chi T, Bagga HS, Taylor AG, Stoller ML (2016) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: the impact of urolithiasis on disease severity. Transl Androl Urol 5(5):774–779
Irfaan AM, Shaikh NA, Jamshaid A, Qureshi AH (2020) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a single center review. Pak J Med Sci 36(1):S83–S86
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg 88:105906
Vassar M, Atakpo P, Kash MJ (2016) Manual search approaches used by systematic reviewers in dermatology. J Med Libr Assoc 104(4):302–304
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, et al (2000) The Newcastle–Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomized studies in meta-analysis.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558
Ioannidis JP, Patsopoulos NA, Evangelou E (2007) Uncertainty in heterogeneity estimates in meta-analyses. BMJ 335(7626):914–916
Ahlering TE, Boyd SD, Hamilton CL et al (1985) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 5-year experience with 13 patients. J Urol 134(6):1086–1088
Patel NP, Lavengood RW, Fernandes M, Ward JN, Walzak MP (1992) Gas-forming infections in genitourinary tract. Urology 39(4):341–345
Pontin AR, Barnes RD, Joffe J, Kahn D (1995) Emphysematous pyelonephritis in diabetic patients. Br J Urol 75(1):71–74
Wan YL, Lo SK, Bullard MJ, Chang PL, Lee TY (1998) Predictors of outcome in emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Urol 159(2):369–373
Narlawar RS, Raut AA, Nagar A, Hira P, Hanchate V, Asrani A (2004) Imaging features and guided drainage in emphysematous pyelonephritis: a study of 11 cases. Clin Radiol 59(2):192–197
Abdul-Halim H, Kehinde EO, Abdeen S, Lashin I, Al-Hunayan AA, Al-Awadi KA (2005) Severe emphysematous pyelonephritis in diabetic patients: diagnosis and aspects of surgical management. Urol Int 75(2):123–128
Park BS, Lee SJ, Kim YW, Huh JS, Kim JI, Chang SG (2006) Outcome of nephrectomy and kidney-preserving procedures for the treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 40(4):332–338
Wang J-M, Lim H-K, Pang K-K (2007) Emphysematous pyelonephritis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 41(3):223–229
Aswathaman K, Gopalakrishnan G, Gnanaraj L, Chacko NK, Kekre NS, Devasia A (2008) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: outcome of conservative management. Urology 71(6):1007–1009
Khaira A, Gupta A, Rana DS, Gupta A, Bhalla A, Khullar D (2009) Retrospective analysis of clinical profile prognostic factors and outcomes of 19 patients of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Int Urol Nephrol 41(4):959–966
Kuo CY, Lin CY, Chen TC et al (2009) Clinical features and prognostic factors of emphysematous urinary tract infection. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 42(5):393–400
Lin WC, Chen YF, Lin CH et al (2009) Reappraisal of the management and outcome of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 25(1):16–24
Dhabalia JV, Nelivigi GG, Kumar V, Gokhale A, Punia MS, Pujari N (2010) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: tertiary care center experience in management and review of the literature. Urol Int 85(3):304–308
Dubey IB, Agrawal V, Jain BK (2011) Five patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis. Iran J Kidney Dis 5(3):204–206
El-Nahas AR, Shokeir AA, Eziyi AK et al (2011) Kidney preservation protocol for management of emphysematous pyelonephritis: treatment modalities and follow-up. Arab J Urol 9(3):185–189
Kuzgunbay B, Turunc T, Tokmak N et al (2011) Tailored treatment approach for emphysematous pyelonephritis. Urol Int 86(4):444–447
Cherif M, Kerkeni W, Bouzouita A, et al (2012) La pyélonéphrite emphysémateuse. Particularités épidémiologiques , clinico-biologiques , bactériologiques , radiologiques , thérapeutiques et évolutives . Etude rétrospective de 30 cas. 90:725–729.
Lin YC, Lin YC, Lin HD, Lin LY (2012) Risk factors of renal failure and severe complications in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis-a single-center 15-year experience. Am J Med Sci 343(3):186–191
Bhat RA, Khan I, Khan I, Palla N, Mir T (2013) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: Outcome with conservative management. Indian J Nephrol 23(6):444–447
Fatima R, Jha R, Muthukrishnan J et al (2013) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a single center study. Indian J Nephrol 23(2):119–124
Ali SN, Ahmed N, Naushad A, Naushad M (2014) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a review of six cases. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 26(4):591–597
Behera V, Vasantha Kumar RS, Mendonca S, Prabhat P, Naithani N, Nair V (2014) Emphysematous infections of the kidney and urinary tract: a single-center experience. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 25(4):823–829
Kumar S, Ramachandran R, Mete U et al (2014) Acute pyelonephritis in diabetes mellitus: single center experience. Indian J Nephrol 24(6):367–371
Lin WR, Chen M, Hsu JM, Wang CH (2014) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: patient characteristics and management approach. Urol Int 93(1):29–33
Olvera-Posada D, Armengod-Fischer G, Vázquez-Lavista LG et al (2014) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: multicenter clinical and therapeutic experience in mexico. Urology 83(6):1280–1284
Alsharif M, Mohammedkhalil A, Alsaywid B, Alhazmy A, Lamy S (2015) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: is nephrectomy warranted? Urol Ann 7(4):494–498
Kangjam SM, Irom KS, Khumallambam IS (2015) Sinam RS 2015 role of conservative management in emphysematous pyelonephritis - a retrospective study. J Clin Diagn Res 9(11):09–11
Lu YC, Hong JH, Chiang BJ et al (2016) Recommended initial antimicrobial therapy for emphysematous pyelonephritis. Medicine (United States) 95(21):1–7
Boakes E, Batura D (2017) Deriving a management algorithm for emphysematous pyelonephritis: can we rely on minimally invasive strategies or should we be opting for earlier nephrectomy? Int Urol Nephrol 49(12):2127–2136
Grigore N, Pirvut V, Totan M et al (2017) The evaluation of biochemical and microbiological parameters in the diagnosis of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Rev Chim 68(6):1383–1386
Karthikeyan VS, Manohar CMS, Mallya A, Keshavamurthy R, Kamath AJ (2018) Clinical profile and successful outcomes of conservative and minimally invasive treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Cent Eur J Urol 71(2):228–233
Fan H, Zhao Y, Sun M, Zhu JH (2019) Thrombocytopenia as a predictor of acute kidney injury in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis. Int J Clin Exp Med 12(1):849–854
Kamath SU, Patil B, Shelke U, Patwardhan SK (2019) Comparing diabetic and nondiabetic emphysematous pyelonephritis and evaluating predictors of mortality. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant Off Publ Saudi Center Organ Transplant Saudi Arab 30(6):1266–1275
Punatar C, Jadhav K, Kumar V, Joshi V, Sagade S (2019) Neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio as a predictive factor for success of nephron-sparing procedures in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis. Perm J 23:18–044
Krishnamoorthy S, Zumla A, Sekar H, Muneer A, Thiruvengadam G, Kumaresan N (2021) Prognostic scoring system and risk stratification in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis: an 11-year prospective study at a tertiary referral centre. BJU Int 127(4):418–427
Somani BK, Nabi G, Thorpe P, Hussey J, Cook J, N’Dow J (2008) Is percutaneous drainage the new gold standard in the management of emphysematous pyelonephritis? evidence from a systematic review. J Urol 179(5):1844–1849
Falagas ME, Alexiou VG, Giannopoulou KP, Siempos II (2007) Risk factors for mortality in patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis: a meta-analysis. J Urol 178(3):880–885
Aboumarzouk OM, Hughes O, Narahari K et al (2014) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: time for a management plan with an evidence-based approach. Arab J Urol 12(2):106–115
Desai R, Batura D (2022) A systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factors and treatment choices in emphysematous pyelonephritis. Int Urol Nephrol 54(4):717–736
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW et al (2016) The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA 315(8):801–810
Geerlings SE, Hoepelman AIM (1999) Immune dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 26(3–4):259–265
Trevelin SC, Carlos D, Beretta M, da Silva JS, Cunha FQ (2017) Diabetes mellitus and sepsis: a challenging association. Shock 47(3):276–287
Elawdy MM, Osman Y, Abouelkheir RT, El-Halwagy S, Awad B, El-Mekresh M (2019) Emphysematous pyelonephritis treatment strategies in correlation to the CT classification: have the current experience and prognosis changed? Int Urol Nephrol 51(10):1709–1713
Sokhal AK, Kumar M, Purkait B et al (2017) Emphysematous pyelonephritis: Changing trend of clinical spectrum, pathogenesis, management and outcome. Turk J Urol 43(2):202–209
Goldsmith ZG, Oredein-McCoy O, Gerber L et al (2013) Emergent ureteric stent vs percutaneous nephrostomy for obstructive urolithiasis with sepsis: patterns of use and outcomes from a 15-year experience. BJU Int 112(2):E122–E128
Pandey S, Sharma D, Sankhwar S et al (2018) Are there any predictive risk factors for failure of ureteric stent in patients with obstructive urolithiasis with sepsis? Investig Clin Urol 59(6):371–375
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study receives no funding support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XTN and TTN contributed to project development, data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing. RWD and MST contributed to data analysis and manuscript writing and editing. DHV, VDLQ, KQ, THL, TDH, HTTN and TNKV contributed to data collection and data analysis. HYT contributed to protocol development and manuscript writing and editing. HGV contributed to project development, data analysis, and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable since this is a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Registration of research
Registry used: Prospero.
Unique Identifying number or registration ID: CRD42021289574.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ngo, X.T., Nguyen, T.T., Dobbs, R.W. et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Mortality in Emphysematous Pyelonephritis Patients: A Meta-Analysis. World J Surg 46, 2377–2388 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-022-06647-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-022-06647-1