Abstract
Background
It may seem questionable if antireflux surgery still has a role in the management of patients with Barrett’s esophagus (BE) in the current era when antireflux surgery is facing a steady decline, obesity is increasing, pharmacologic treatment for gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is in its splendor, and endoscopic techniques are used more frequently. It is questionable if patients with BE should be operated to stop GERD and to prevent cancer. The aim of this study was to determine the role of antireflux surgery in patients with BE.
Methods
Literature review.
Results
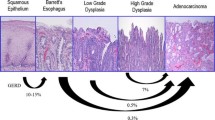
The role of antireflux operations is, in fact, very controversial and neglected. BE is a different phenotype of GERD with a distinct pathophysiology linked to severe reflux of bile and acid, due to a marked anatomic disruption of the gastroesophageal barrier. Published series show that a fundoplication adequately controls GERD and symptoms in BE patients. A fundoplication (or even better a bile diversion antireflux procedure) may prevent esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Conclusions
In conclusion, a fundoplication efficiently controls GERD and symptoms in BE patients. A fundoplication (or even better a bile diversion procedure) may also prevent esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeMeester TR (2002) Surgical therapy for Barrett’s esophagus: prevention, protection and excision. Dis Esophagus 15(2):109–116
Khan F, Maradey-Romero C, Ganocy S, Frazier R, Fass R (2016) Utilisation of surgical fundoplication for patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in the USA has declined rapidly between 2009 and 2013. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43(11):1124–1131
Smith KB, Smith MS (2016) Obesity statistics. Prim Care 43(1):121–135, ix. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2015.10.001
Perry KA, Pham TH, Spechler SJ, Hunter JG, Melvin WS, Velanovich V (2015) 2014 SSAT state-of-the-art conference: advances in diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastrointest Surg 19(3):458–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-014-2724-9
Brar TS, Draganov PV, Yang D (2017) Endoluminal therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. In between the pill and the knife? Dig Dis Sci 62(1):16–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-016-4355-3
Spechler SJ, Lee E, Ahnen D, Goyal RK, Hirano I, Ramirez F, Raufman JP, Sampliner R, Schnell T, Sontag S, Vlahcevic ZR, Young R, Williford W (2001) Long-term outcome of medical and surgical therapies for gastroesophageal reflux disease: follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 285(18):2331–2338
Kahrilas PJ (2008) Clinical practice. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. N Engl J Med 359(16):1700–1707
Spechler SJ, Souza RF (2014) Barrett’s esophagus. N Engl J Med 371(9):836–845. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1314704
DeMeester SR (2015) Barrett’s oesophagus: treatment with surgery. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 29(1):211–217
Desai KM, Soper NJ, Frisella MM, Quasebarth MA, Dunnegan DL, Brunt LM (2003) Efficacy of laparoscopic antireflux surgery in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Surg 186(6):652–659
Beaton H (2017) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication in a community hospital setting. Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg 2:30
Menezes MA, Herbella FAM (2017) Pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Surg 41(7):1666–1671
Peyre CG, Watson TJ (2015) Surgical management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 44(2):459–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2015.02.013
Andrici J, Tio M, Cox MR, Eslick GD (2013) Hiatal hernia and the risk of Barrett’s esophagus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28(3):415–431. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07199.x
Campos GM, DeMeester SR, Peters JH, Oberg S, Crookes PF, Hagen JA, Bremner CG, Sillin LF 3rd, Mason RJ, DeMeester TR (2001) Predictive factors of Barrett esophagus: multivariate analysis of 502 patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Arch Surg 136(11):1267–1273
Herbella FA, Tedesco P, Nipomnick I, Fisichella PM, Patti MG (2007) Effect of partial and total laparoscopic fundoplication on esophageal body motility. Surg Endosc 21(2):285–288
Peng S, Xiao YL, Cui Y, Lin JK, Zhang N, Hu PJ, Chen MH (2012) High-dose esomeprazole is required for intraesophageal acid control in gastroesophageal reflux disease patients with hiatus hernia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(5):893–898. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06969.x
Allaix ME, Patti MG (2015) Antireflux surgery for dysplastic Barrett. World J Surg 39(3):588–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2632-x
Jamieson GG, France M, Watson DI (2002) Results of laparoscopic antireflux operations in patients who have Barrett’s esophagus. Chest Surg Clin N Am 12(1):149–155
Campos GM, Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Oberg S, Crookes PF, Tan S, DeMeester SR, Hagen JA, Bremner CG (1999) Multivariate analysis of factors predicting outcome after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 3(3):292–300
Herbella FA (2017) Secrets for successful laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Ann Laparosc Endosc Surg 2:46–47. https://doi.org/10.21037/ales.2017.02.02
Pouw RE, Bergman JJ (2013) Radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s esophagus, for whom and by whom? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(10):1256–1258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2013.06.014
Fleischer DE, Odze R, Overholt BF, Carroll J, Chang KJ, Das A, Goldblum J, Miller D, Lightdale CJ, Peters J, Rothstein R, Sharma VK, Smith D, Velanovich V, Wolfsen H, Triadafilopoulos G (2010) The case for endoscopic treatment of non-dysplastic and low-grade dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 55(7):1918–1931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1218-1
Skrobić O, Simić A, Radovanović N, Ivanović N, Micev M, Peško P (2016) Significance of Nissen fundoplication after endoscopic radiofrequency ablation of Barrett’s esophagus. Surg Endosc 30(9):3802–3807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4677-9
Johnson CS, Louie BE, Wille A, Dunst CM, Worrell SG, DeMeester SR, Reynolds J, Dixon J, Lipham JC, Lada M, Peters JH, Watson TJ, Farivar AS, Aye RW (2015) The durability of endoscopic therapy for treatment of Barrett’s metaplasia, dysplasia, and mucosal cancer after nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 19(5):799–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2783-6
Shaheen NJ, Kim HP, Bulsiewicz WJ, Lyday WD, Triadafilopoulos G, Wolfsen HC, Komanduri S, Chmielewski GW, Ertan A, Corbett FS, Camara DS, Rothstein RI, Overholt BF (2013) Prior fundoplication does not improve safety or efficacy outcomes of radiofrequency ablation: results from the U.S. RFA Registry. J Gastrointest Surg 17(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-012-2001-8 discussion 28–29
Shaheen NJ, Kim HP, Bulsiewicz WJ, Lyday WD, Triadafilopoulos G, Wolfsen HC et al (2013) Prior fundoplication does not improve safety or efficacy outcomes of radiofrequency ablation: results from the U.S. RFA Registry. J Gastrointest Surg 17(1):21–28 discussion 28–29
Nadaleto BF, Herbella FA, Patti MG (2016) Gastroesophageal reflux disease in the obese: pathophysiology and treatment. Surgery 159(2):475–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2015.04.034
Kindel TL, Oleynikov D (2016) The improvement of gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett’s after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 26(4):718–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-016-2116-1
Williams VA, Watson TJ, Gellersen O, Feuerlein S, Molena D, Sillin LF, Jones C, Peters JH (2007) Gastrectomy as a remedial operation for failed fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 11(1):29–35
Makris KI, Lee T, Mittal SK (2009) Roux-en-Y reconstruction for failed fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 13(12):2226–2232
Csendes A, Bragheto I, Burdiles P, Smok G, Henriquez A, Parada F (2006) Regression of intestinal metaplasia to cardiac or fundic mucosa in patients with Barrett’s esophagus submitted to vagotomy, partial gastrectomy and duodenal diversion. A prospective study of 78 patients with more than 5 years of follow up. Surgery 139(1):46–53
Braghetto I, Papapietro K, Csendes A, Gutierrez J, Fagalde P, Diaz E, Rodriguez A, Undurraga F (2005) Nonesophageal side-effects after antireflux surgery plus acid-suppression duodenal diversion surgery in patients with long-segment Barrett’s esophagus. Dis Esophagus 18(3):140–145
Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM, Shaheen NJ, American Gastroenterological Association (2011) American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology 140(3):e18–e52. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.031 quiz e13
Corey KE, Schmitz SM, Shaheen NJ (2003) Does a surgical antireflux procedure decrease the incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus? A meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 98(11):2390–2394
Chang EY, Morris CD, Seltman AK, O’Rourke RW, Chan BK, Hunter JG, Jobe BA (2007) The effect of antireflux surgery on esophageal carcinogenesis in patients with Barrett esophagus: a systematic review. Ann Surg 246(1):11–21
Li YM, Li L, Yu CH, Liu YS, Xu CF (2008) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the treatment for Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci 53:2837–2846
Kauttu TM, Rantanen TK, Sihvo EI, Räsänen JV, Puolakkainen P, Salo JA (2011) Esophageal adenocarcinoma arising after antireflux surgery: a population-based analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 40(6):1450–1454 discussion 1454
Lagergren J, Viklund P (2007) Is esophageal adenocarcinoma occurring late after antireflux surgery due to persistent postoperative reflux? World J Surg 31(3):465–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0386-9
Allaix ME, Patti MG (2015) Antireflux surgery for dysplastic Barrett. World J Surg 39(3):588–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2632-x
Tse WHW, Kroon HM, van Lanschot JJB (2017) Clinical challenges in upper gastrointestinal malignancies after bariatric surgery. Dig Surg. https://doi.org/10.1159/000477267
Hofstetter WL, Peters JH, DeMeester TR et al (2001) Long-term outcome of antireflux surgery in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Ann Surg 234(4):532–538
Morrow E, Bushyhead D, Wassenaar E, Hinojosa M, Loviscek M, Pellegrini C, Oelschlager B (2014) The impact of laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Surg Endosc 28(12):3279–3284
Desai KM, Soper NJ, Frisella MM, Quasebarth MA, Dunnegan DL, Brunt LM (2003) Efficacy of laparoscopic antireflux surgery in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Surg 186(6):652–659
Patti MG, Arcerito M, Feo CV, Worth S, De Pinto M, Gibbs VC, Gantert W, Tyrrell D, Ferrell LF, Way LW (1999) Barrett’s esophagus: a surgical disease. J Gastrointest Surg 3(4):397–403
Bowers SP, Mattar SG, Smith CD, Waring JP, Hunter JG (2002) Clinical and histologic follow-up after antireflux surgery for Barrett’s esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg 6(4):532–538 discussion 539
Csendes A, Braghetto I, Burdiles P, Smok G, Henríquez A, Burgos AM (2009) Late results of the surgical treatment of 125 patients with short-segment Barrett esophagus. Arch Surg 144(10):921–927. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.2009.83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lecture at the 47th World Congress of Surgery, Basel, August, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herbella, F.A.M., Schlottmann, F. & Patti, M.G. Antireflux Surgery and Barrett’s Esophagus: Myth or Reality?. World J Surg 42, 1798–1802 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4394-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4394-8