Abstract
Background
To clarify factors related to vitamin E malabsorption after gastric surgery, we evaluated serum vitamin E levels in patients who had undergone gastrectomy for gastric cancer.
Methods
We studied 39 patients (26 men, 13 women; mean age, 61.7 years) who underwent gastrectomy for early gastric cancer. Surgical procedures included 24 subtotal gastrectomies and 15 total gastrectomies. We measured serum levels of vitamin E before and 3, 6, 9, and 12 months after gastrectomy. A level of less than 0.75 mg/dl was defined as a low vitamin E level.
Results
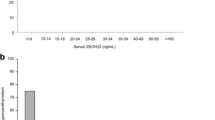
Serum vitamin E levels decreased to less than 0.75 mg/dl in 6 (15.4 %) of the 39 patients within 6 months after gastrectomy and in 7 (17.9 %) of the 39 patients within 1 year after gastrectomy. The proportion of patients with a low serum vitamin E level was significantly higher in the total gastrectomy group (p = 0.002). A low vitamin E level was significantly associated with a low total cholesterol level. Total cholesterol levels in low vitamin E levels patients were lower than normal vitamin E levels patients. None of the patients with a low vitamin E level had neuropathy.
Conclusions
The type of operation performed (total vs. subtotal gastrectomy) may be the major cause of vitamin E malabsorption after gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Vitamin E deficiency probably begins within 6 months after gastrectomy for gastric cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- WBC:
-
White blood cells
- RBC:
-
Red blood cells
- Hb:
-
Hemoglobin
- Hct:
-
Hematocrit
- Plt:
-
Platelets
- FA:
-
Folic acid
- TC:
-
Total cholesterol
- TG:
-
Triglycerides
- TP:
-
Total protein
- Alb:
-
Albumin
References
Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM et al (2012) Textbook of surgery. In: Mahvi DM, Krantz SB (eds) Stomach, 19th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1182–1226
Rino Y (1996) Clinical study of the relationship between a metabolic bone disorder and an amount of daily food intake. Yokohama Med 47:25–29
Imawari M, Kozawa K, Akanuma Y et al (1980) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and vitamin D-binding protein levels and mineral metabolism after partial and total gastrectomy. Gastroenterology 79:255–258
Rino Y, Imada T, Yamamoto Y et al (2000) The efficacy of 1α-hydroxy vitamin D3 treatment of the metabolic bone disorder in patients who underwent gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 47:1498–1500
Ueda N, Suzuki Y, Rino Y et al (2009) Correlation between neurological dysfunction with vitamin E deficiency and gastrectomy. J Neurol Sci 287:216–220
Ueda N, Suzuki Y, Takahashi T et al (2005) Treatment of neurological complication due to postgastrectomy vitamin E deficiency. No To Shinkei 57:145–148
Rino Y, Ueda N, Yukawa N et al (2007) Clinical impact of change of vitamin A and E after gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg 40:1763–1768
Rino Y, Suzuki Y, Kuroiwa Y et al (2007) Vitamin E malabsorption and neurological consequences after gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 54:1858–1861
Japanese Classification of Gastric Cancer Association (2011) Japanese classification of gastric carcinoma: 3rd English edn. Gastric Cancer 14:101–112
Kayden HJ, Traber MG (1993) Absorption, lipoprotein transport, and regulation of plasma concentration of vitamin E in humans. J Lipid Res 34:343–358
Traber MG, Kayden HJ (1989) Alpha-tocopherol as compared with gamma-tocopherol is preferentially secreted in human lipoproteins. Ann NY Acad Sci 570:95–108
Weder B, Meienberg O, Wildi E et al (1984) Neurologic disorder of vitamin E deficiency in acquired intestinal malabsorption. Neurology 34:1561–1565
Brin MF, Fetell MR, Green PHA et al (1985) Blind loop syndrome, vitamin E malabsorption, and spinocerebellar degeneration. Neurology 35:338–342
Muller DPR, Lloyd JK, Wolff OH (1983) Vitamin E and neurological function. Lancet 1:225–228
Linton MF, Farese RV Jr, Young SG (1993) Familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Lipids Res 34:521–541
Sharp D, Blinderman L, Combs KA et al (1993) Cloning and gene defects in microsomal triglyceride transfer protein associated with abetalipoproteinaemia. Nature 365:65–69
Traber MG, Sokol RJ, Burton GW et al (1990) Impaired ability of patients with familial isolated vitamin E deficiency to incorporate alpha-tocopherol into lipoproteins secreted by the liver. J Clin Invest 85:397–407
Ueno M, Jyonoshita Y, Nagakura S et al (1991) Absorption of d-alfa-tocopherol solubilized in micellar solutions of various bile salts by rat small intestine. J Jpn Oil Chem Soc 40:400–405
Walther B, Clementsson C, Vallgren S et al (1989) Fat malabsorption in patients before and after total gastrectomy, studied by the triolein breath test. Scand J Gastroenterol 24:309–314
Banerji NK, Hurwitz LJ (1971) Nervous system manifestation after gastric surgery. Acta Neurol Scand 47:485–513
Ghalaut VS, Ghalaut PS, Kharb S et al (1995) Vitamin E in intestinal fat malabsorption. Ann Nutr Metab 39:296–301
Ko HY, Park-Ko I (1999) Electrophysiologic recovery after vitamin E-deficient neuropathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 80:964–967
Bousvaros A, Zurakowski D, Duggan C et al (1998) Vitamins A and E serum levels in children and young adults with inflammatory bowel disease: effect of disease activity. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 26:129–135
Ministry of Healthy, Labour, and Welfare, Japan (2005) Dietary reference intakes for Japanese [in Japanese]. Daiichi-Shuppan Co, Tokyo
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have received financial support from the Fund for Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Fund for Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rino, Y., Yukawa, N., Sato, T. et al. Vitamin E Deficiency Begins within 6 Months after Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer. World J Surg 38, 2065–2069 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2515-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-014-2515-1