Abstract
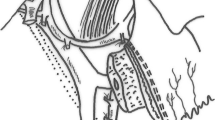
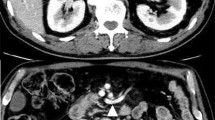
Intraabdominal bleeding, the most life-threatening complication following pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD), most often is associated with failure of a pancreaticojejunostomy anastomosis or with intraabdominal infection. We investigated whether placement of an omental flap around the splanchnic vessels in PD could reduce the occurrence of intraabdominal bleeding and other postoperative complications. One hundred consecutive patients who underwent PD at the authors’ institution between January 2000 and October 2004 were enrolled in this prospective study. After dissection of the hepatoduodenal ligament, the major splanchnic arteries and the portal vein were covered by the omental flap. Preoperative condition, incidence of pancreatic fistula, intra-abdominal bleeding, other complications, treatment mortality, and hospital stay were analyzed for interrelationships. The frequency of pancreatic fistula (20%) differed little from those in previous reports. However, intraabdominal bleeding was observed in only 1 (1.0%) patient, who was considered to have too thin a flap. No intraabdominal abscess was encountered. No mortality or complications occurred in relation to the omental flap. Thus, wrapping an omental flap around dissected splanchnic vessels in PD reduced postoperative intraabdominal bleeding and infection, but failed to prevent pancreatic fistulas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afsari A, Zhandoug Z, Young S, et al. Outcome analysis of pancreaticoduodenectomy at a community hospital. Am. Surg. 2002;68:281–284
Conlon KC, Labow D, Leung D, et al. Prospective randomized clinical trial of the value of intraperitoneal drainage after pancreatic resection. Ann. Surg. 2001;234:487–493
Gouma DJ, van Geenen RC, van Gulik TM, et al. Rates of complications and death after pancreaticoduodenectomy: risk factors and the impact of hospital volume. Ann. Surg. 2000;232:786–795
Buchler MW, Friess H, Wagner M, et al. Pancreatic fistula after pancreatic head resection. Br. J. Surg. 2000;87:883–889
Povoski SP, Karpeh MS Jr, Conlon KC, et al. Association of preoperative biliary drainage with postoperative outcome following pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann. Surg. 1999;230:131–142
Roder JD, Stein HJ, Bottcher KA, et al. Stented versus nonstented pancreaticojejunostomy after pancreatoduodenectomy: a prospective study. Ann. Surg. 1999;229:41–48
Sato N, Yamaguchi K, Chijiiwa K, et al. Risk analysis of pancreatic fistula after pancreatic head resection. Arch. Surg. 1998;133:1094–1098
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Sohn TA, et al. Six hundred fifty consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies in the 1990s: pathology, complications, and outcomes. Ann. Surg. 1997;226:248–257
Marcus SG, Cohen H, Ranson JH. Optimal management of the pancreatic remnant after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann. Surg. 1995;221:635–645
Cullen JJ, Sarr MG, Ilstrup DM. Pancreatic anastomotic leak after pancreaticoduodenectomy: incidence, significance, and management. Am. J. Surg. 1994; 168:295–298
Miedema BW, Sarr MG, van Heerden JA, et al. Complications following pancreaticoduodenectomy. Current management. Arch. Surg. 1992; 127:945–949
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Sohn TA, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy with or without extended retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy for periampullary adenocarcinoma: comparison of morbidity and mortality and short-term outcome. Ann. Surg. 1999;229:613–622
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, et al. Does prophylactic octreotide decrease the rates of pancreatic fistula and other complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy? Results of a prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial. Ann. Surg. 2000;232:419–429
Grobmyer SR, Rivadeneira DE, Goodman CA, et al. Pancreatic anastomotic failure after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Am. J. Surg. 2000;180:117–120
Nitecki SS, Sarr MG, Colby TV, et al. Long-term survival after resection for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Is it really improving? Ann. Surg. 1995;221:59–66
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Maher MM, et al. A prospective randomized trial of pancreaticogastrostomy versus pancreaticojejunostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann. Surg. 1995;222:580–588
Kakita A, Yoshida M, Takahashi T. History of pancreaticojejunostomy in pancreaticoduodenectomy: development of a more reliable anastomosis technique. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2001;8:230–237
Jones G, Jurkiewicz MJ, Bostwick J, et al. Management of the infected median sternotomy wound with muscle flaps. The Emory 20-year experience. Ann. Surg. 1997;225:766–776
Losken A, Carlson GW, Culbertson JH, et al. Omental free flap reconstruction in complex head and neck deformities. Head Neck 2002;24:326–331
Hirai I, Murakami G, Kimura W, et al. Long descending lymphatic pathway from the pancreaticoduodenal region to the para-aortic nodes: its laterality and topographical relationship with the celiac plexus. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 2001;77:189–199
Hirai I, Kimura W, Ozawa K, et al. Perineural invasion in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2002;24:15–25
Bhuiya MR, Nimura Y, Kamiya J, et al. Clinicopathologic studies on perineural invasion of bile duct carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 1992;215:344–349
Sobin LH, Wittekind. International Union Against Cancer (UICC) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 6th edition, New York, Wiley-Liss, 2002;87–96
Child CG III. Carcinoma of duodenum: one-stage radical pancreaticoduodenectonly preserving the external pancreatic secretion, case report. Ann. Surg. 1941;118:838–842
Rumstadt B, Schwab M, Korth P, et al. Hemorrhage after pancreatoduodenectomy. Ann. Surg. 1998;227:236–241
Yoshida T, Matsumoto T, Morii Y, et al. Delayed massive intraperitoneal hemorrhage after pancreatoduodenectomy. Int. Surg. 1998;83:131–135
Trede M, Schwall G. The complications of pancreatectomy. Ann. Surg. 1988;207:39–47
Shankar S, Russell RC. Haemorrhage in pancreatic disease. Br. J. Surg. 1989;76:863–866
Patel AG, Toyama MT, Kusske AM, et al. Pylorus-preserving Whipple resection for pancreatic cancer. Is it any better? Arch. Surg. 1995;130:838–842
Wade TP, el-Ghazzawy AG, Virgo KS, et al. The Whipple resection for cancer in U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs Hospitals. Ann. Surg. 1995;221:241–248
Zerbi A, Balzano G, Patuzzo R, et al. Comparison between pylorus-preserving and Whipple pancreatoduodenectomy. Br. J. Surg. 1995;82:975–979
Allema JH, Reinders ME, van Gulik TM, et al. Results of pancreaticoduodenectomy for ampullary carcinoma and analysis ofprognostic factors for survival. Surgery 1995;17:247–253
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy. Role of interventional radiologists in managing patients and complications. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2003;7:209–219
Piano G, Massad MG, Amory DW Jr, et al. Omental transfer for salvage of the moribund lower extremity. Am. Surg. 1998;64:424–427
Liebermann-Meffert D. The greater omentum. Anatomy, embryology, and surgical applications. Surg. Clin. North Am. 2000;80:275–293
Adams W, Ctercteko G, Bilous M. Effect of an omental wrap on the healing and vascularity of compromised intestinal anastomoses. Dis. Colon Rectum 1992;35:731–738
Merad F, Hay JM, Fingerhut A, et al. Omentoplasty in the prevention of anastomotic leakage after colonic or rectal resection: a prospective randomized study in 712 patients. French Associations for Surgical Research. Ann. Surg. 1998;227:179–186
Van Garderen JA, Wiggers T, van Geel AN. Complications of the pedicled omentoplasty. Neth. J. Surg. 1991;43:171–174
Moriura S, Ikeda S, Ikezawa T, et al. The inclusion of an omental flap in pancreatoduodenectomy. Surg. Today 1994;24:940–941
Seyama Y, Kubota K, Kobayashi T, et al. Two-staged pancreatoduodenectomy with external drainage of pancreatic juice andomental graft technique. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1998;187:103–105
Baker RJ, Fischer SK, Lilloemoe KL, et al. Mastery of Surgery, Baltimore, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001;1313
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeda, A., Ebata, T., Kanemoto, H. et al. Omental Flap in Pancreaticoduodenectomy for Protection of Splanchnic Vessels. World J. Surg. 29, 1122–1126 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7900-3
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7900-3