Abstract
Background
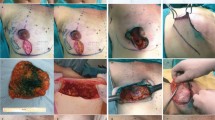
Large volume breast reductions are at increased risk of nipple ischemia and necrosis due to tenuous blood supply of long pedicles. We adapted incisional negative pressure wound therapy to augment nipple survival in such patients undergoing mammaplasty by inferior pedicle technique.
Methods
Patients with nipple-to-inframammary fold distance >14 cm were informed of increased risk of requiring free nipple graft. All patients underwent inferior pedicle technique with Wise pattern skin incision. Once incisions were closed and the nipple-areolar complex was inset, the complex was assessed for vascularity. In 12 cases there was evidence of compromised arterial inflow or venous outflow. For these patients, incisional negative pressure wound therapy was applied to the bilateral nipple-areolar complexes for 5-7 days.
Results
None of the 12 patients (24 breasts) in this series experienced nipple-areolar complex ischemia or necrosis. Only 2 patients experienced delayed wound healing which was successfully managed by local wound care.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates the utility of negative pressure wound therapy in nipple survival for at-risk patients. We believe it augments healing by allowing improved micro-circulation.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each submission to which Evidence-Based Medicine rankings are applicable. This excludes Review Articles, Book Reviews, and manuscripts that concern Basic Science, Animal Studies, Cadaver Studies, and Experimental Studies. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozerdem OR, Anlatici R, Maral T, Demiralay A (2002) Modified free nipple graft reduction mammaplasty to increase breast projection with superior and inferior dermoglandular flaps. Ann Plast Surg 49(5):506–510. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-200211000-00011 (PMID: 12439019)
Hawtof DB, Levine M, Kapetansky DI, Pieper D (1989) Complications of reduction mammaplasty: comparison of nipple-areolar graft and pedicle. Ann Plast Surg 23(1):3–10. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-198907000-00002 (PMID: 2764458)
Stranz G, Petri E (1999) Unterschiedliche Mammareduktionstechniken im Vergleich mit klinischen und ästhetischen Komplikationen sowie dem Zufriedenheitsgrad der Patientinnen Different techniques of reduction mammaplasty comparing clinical and esthetic complications with patient satisfaction]. Zentralbl Gynakol 121(9):434–40 (German. PMID: 10522376)
van Deventer PV, Page BJ, Graewe FR (2008) The safety of pedicles in breast reduction and mastopexy procedures. Aesthet Plast Surg 32(2):307–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-007-9070-1
Romano JJ, Francel TJ, Hoopes JE (1992) Free nipple graft reduction mammoplasty. Ann Plast Surg 28(3):271–276. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199203000-00012 (PMID: 1575429)
Craig RD, Sykes PA (1970) Nipple sensitivity following reduction mammaplasty. Br J Plast Surg 23(2):165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-1226(70)80034-0 (PMID: 5464107)
Hoopes JE, Jabaley ME (1969) Reduction mammaplasty: amputation and augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 44(5):441–446 (PMID: 5345482)
Bostwick J (1990) Reduction mammaplasty, free nipple graft. In: Plastic and reconstructive breast surgery. Quality Medical Pub, pp 377–386
Karsidag S, Akcal A, Karsidag T, Yesiloglu N, Yesilada AK, Ugurlu K (2011) Reduction mammaplasty using the free-nipple-graft vertical technique for severe breast hypertrophy: improved outcomes with the superior dermaglandular flap. Aesthet Plast Surg 35(2):254–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9592-9
Al-Shaham A (2010) Pedicle viability as the determinant factor for conversion to free nipple graft. Can J Plast Surg 18(1):e1–e4. https://doi.org/10.4172/plastic-surgery.1000643
Lo AY, Yu RP, Raghuram A et al (2020) Patient characteristics associated with free nipple graft reduction mammoplasty. Cureus 12(7):e9063. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.9063
Galiano RD, Hudson D, Shin J, van der Hulst R, Tanaydin V, Djohan R, Duteille F, Cockwill J, Megginson S, Huddleston E (2018) Incisional negative pressure wound therapy for prevention of wound healing complications following reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6(1):e1560
Tanaydin V, Beugels J, Andriessen A, Sawor JH, van der Hulst RRWJ (2018) A prospective study of patients undergoing breast reduction surgery: health-related quality of life and clinical outcomes. Aesthet Plast Surg 42(4):927–935
Hamdi M, Greuse M, De Mey A, Webster MH (2001) A prospective quantitative comparison of breast sensation after superior and inferior pedicle mammaplasty. Br J Plast Surg 54(1):39–42. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjps.2000.3456 (PMID: 11121316)
Ahmed OA, Kolhe PS (2000) Comparison of nipple and areolar sensation after breast reduction by free nipple graft and inferior pedicle techniques. Br J Plast Surg 53(2):126–129. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjps.1999.3235 (PMID: 10878835)
Muenchow S, Horch RE, Dragu A (2019) Effects of topical negative pressure therapy on perfusion and microcirculation of human skin. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 72(4):365–374. https://doi.org/10.3233/CH-180536 (PMID: 30909192)
Huang C, Leavitt T, Bayer LR, Orgill DP (2014) Effect of negative pressure wound therapy on wound healing. Curr Probl Surg 51(7):301–331. https://doi.org/10.1067/j.cpsurg.2014.04.001 (Epub 2014 Apr 26 PMID: 24935079)
Yin Y, Zhang R, Li S, Guo J, Hou Z, Zhang Y (2018) Negative-pressure therapy versus conventional therapy on split-thickness skin graft: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 50:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.12.020 (Epub 2017 Dec 29 PMID: 29292216)
Karacor-Altuntas Z, Dadaci M, Ince B, Karamese M, Savaci N (2016) Central pedicle reduction in gigantomastia without free nipple graft. Ann Plast Surg 76(4):383–387. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000000388
Horta R, Silva P, Filipe R, Costa J, Bartosh I, Amarante J, Silva A (2010) Use of Doppler in breast reduction with superomedial or superolateral pedicles. Aesthet Plast Surg 34(5):680–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9491-0 (PMID: 20333517)
Elmelegy N, Shokr T, Osama M (2019) Nipple-Areola complex ischemia or necrosis in freestyle perforator flap reduction mammoplasty operations. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(6):1506–1514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01511-5
Hudson DA, Adams KG, Van Huyssteen A, Martin R, Huddleston EM (2015) Simplified negative pressure wound therapy: clinical evaluation of an ultraportable, no-canister system. Int Wound J 12(2):195–201. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12080 (Epub 2013 May 7 PMID: 23647737)
Nelson JA, Fischer JP, Chung CU, West A, Tuggle CT, Serletti JM, Kovach SJ (2014) Obesity and early complications following reduction mammaplasty: an analysis of 4545 patients from the 2005–2011 NSQIP datasets. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 48(5):334–339. https://doi.org/10.3109/2000656X.2014.886582 (Epub 2014 Feb 10 PMID: 24506446)
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients in this case series.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engel, R., Greenberg, Y. & Siddiqui, A. Negative Pressure Wound Therapy for Improved Nipple Survival in Large Volume Reduction Mammaplasty. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 108–112 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02492-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02492-0