Abstract
Background
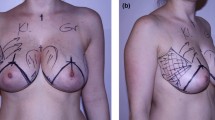
In a vertical mammaplasty, various types of pedicles have been proposed for the nipple-areola transposition. The preparation of any type of nipple-areola flap necessitates disconnecting the nipple-areola from the breast gland, except for the pedicle bearing glandular part. These flap-dependent techniques not only impair the functions of the breast but also do not provide enough fullness to the upper pole.
Method
No specific nipple-areola flap preparation is made. Reduction is obtained by a transverse excision from the lowermost part of the breast gland. Apart from this, no cut into the gland is needed. Liposuction, wide skin elevation and extended retromammary dissection permit the en bloc suspension of the breast.
Patients and Results
The study enrolled a total of 85 patients with 170 breasts. Mastopexy or minor reduction less than 100 gr was applied for 49 breasts; moderate reduction, 100–399 gr, for 67 breasts; and a large reduction of more than 400 gr for 54 breasts. No complete or incomplete nipple-areola necrosis was seen. The success rate for achieving upper pole fullness was compared between groups for reduction amount, age and body mass index (BMI).
Conclusion
The functions of the breast organ are preserved in the en bloc suspension technique. In patients with dense breasts, a good upper pole fullness was achieved with a high success rate. Young patients and patients with a body mass index below 25 are suitable for this technique. However, the same success rate could not be achieved in elderly patients with fatty breasts.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lejour M (1994) Vertical mammaplasty and liposuction of the breast. Plast Reconstr Surg 94:100–114
Asplund O, Davies DM (1996) Vertical scar breast reduction with medial flap or glandular transposition of the nipple areola. Br J Plast Surg 49:507–514
Hall-Findlay EJ (1999) A simplified vertical reduction mammaplasty: shortening the learning curve. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:748–759
Chen CM, White C, Warren SM, Cole J, Isik FF (2004) Simplifying the vertical reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:162–172
Lista F, Ahmad J (2006) Vertical scar reduction mammaplasty: a 15-year experience including a review of 250 consecutive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:2152–2165
Lista F, Austin RE, Singh Y, Ahmad J (2015) Vertical scar reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:23–25
Palumbo SK, Shifren J, Rhee C (1998) Modifications of the Lejour vertical mammaplasty: analysis of results in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Plast Surg 40:354–359
Blondeel PN, Hamdi M, Van de Sijpe KA, Van Landuyt KH, Thiessen FE, Monstrey SJ (2003) The latero-central glandular pedicle technique for breast reduction. Br J Plast Surg 56:348–359
Hammond DC (1999) Short scar periareolar inferior pedicle reduction (SPAIR) mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:890–901
Khan UD (2007) Vertical scar with the bipedicle technique: a modified procedure for breast reduction and mastopexy. Aesthetic Plast Surg 31:337–342
Datta G, Carlucci S (2009) Selective breast reduction: a personal approach with a central-superior pedicle. Plast Reconstr Surg 123:433–442
Shin KS, Chung S, Lee HK, Lew JD (1996) Reduction mammaplasty by central pedicle flap with short submammary scar. Aesthetic Plast Surg 20:69–76
Hagerty RC, Nowicky DJ (1998) Integration of the central mound technique with the vertical skin takeout reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 102:1182–1187
Kim YS, Hwang K, Kim JH, Kim TH, Kim HM (2017) Central pedicle reduction mammaplasty with a vertical scar: a technical modification. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 51:436–445
Leone MS, Franchelli S, Berrino P, Santi PL (1997) Vertical mammaplasty: a personal approach. Aesthetic Plast Surg 21:356–361
Würinger E (1999) Refinement of the central pedicle breast reduction by application of the ligamentous suspension. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1400–1410
Van Deventer PV, Page BJ, Graewe FR (2008) The safety of pedicles in breast reduction and mastopexy procedures. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32:307–312
Hamdi M, Van Landuyt K, Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Monstrey S (2009) Septum-based mammaplasty: a surgical technique based on Würinger’s septum for breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 123:443–454
Bayramiçli M (2012) The central pillar technique: a new septum-based pedicle design for reduction mammaplasty. Aesthet Surg J 32:578–590
Gulyás G (1996) Combination of the vertical and periareolar mammaplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 20:369–375
Mottura AA (2003) Circumvertical reduction mastoplasty: new considerations. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27:85–93
Atiyeh BS, Rubeiz MT, Hayek SN (2005) Refinements of vertical scar mammaplasty: circumvertical skin excision design with limited inferior pole subdermal undermining and liposculpture of the inframammary crease. Aesthetic Plast Surg 29:519–531
Würinger E, Mader N, Posch E, Holle J (1998) Nerve and vessel supplying ligamentous suspension of the mammary gland. Plast Reconstr Surg 101:1486–1493
Hammond DC, Loffredo M (2012) Breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:829e–839e
Maliniac JW (1943) Arterial blood supply of the breast: revised anatomic data relating to reconstructive surgery. Arch Surg 47:329–343
van Deventer PV (2004) The blood supply to the nipple-areola complex of the human mammary gland. Aesthetic Plast Surg 28:393–398
mon O’Dey D, Prescher A, Pallua N (2007) Vascular reliability of nipple-areola complex–bearing pedicles: an anatomical microdissection study. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:1167–1177
van Deventer PV, Graewe FR (2016) The blood supply of the breast revisited. Plast Reconstr Surg 137:1388–1397
Palmer JH, Taylor GI (1986) The vascular territories of the anterior chest wall. Br J Plast Surg 39:287–299
Sarhadi NS, Dunn JS, Lee FD, Soutar DS (1996) An anatomical study of the nerve supply of the breast, including the nipple and areola. Br J Plast Surg 49:156–164
Schlenz I, Kuzbari R, Gruber H, Holle J (2000) The sensitivity of the nipple-areola complex: an anatomic study. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:905–909
Sarhadi NS, Soutar DS (1997) Nerve supply of the nipple: only from the fourth or from several intercostal nerves? Eur J Plast Surg 20:209–211
Schlenz I, Rigel S, Schemper M, Kuzbari R (2005) Alteration of nipple and areola sensitivity by reduction mammaplasty: a prospective comparison of five techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 115:743–751
Ribeiro L, Accorsi JA, Buss A, Marcal-Pessoa M (2002) Creation and evolution of 30 years of the inferior pedicle in reduction mammaplasties. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:960–970
Graf R, Ricardo Dall Oglio Tolazzi A, Balbinot P, Pazio A, Miguel Valente P, da Silva Freitas R (2016) Influence of the pectoralis major muscle sling in chest wall-based flap suspension after vertical mammaplasty: ten-year follow-up. Aesthet Surg J 36:1113–1121
Hall-Findlay EJ (2010) The three breast dimensions: analysis and effecting change. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:1632–1642
Checka CM, Chun JE, Schnabel FR, Lee J, Toth H (2012) The relationship of mammographic density and age: implications for breast cancer screening. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198:W292–W295
Maskarinec G, Pagano I, Lurie G, Kolonel LN (2006) A longitudinal investigation of mammographic density: the multiethnic cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15:732–739
Kelemen LE, Pankratz VS, Sellers TA, Brandt KR, Wang A, Janney C, Fredericksen ZS, Cerhan JR, Vachon CM (2008) Age-specific trends in mammographic density: the Minnesota Breast Cancer Family Study. Am J Epidemiol 167:1027–1036
Kuran I, Tumerdem B (2007) Vertical reduction mammaplasty: preventing skin redundancy at the vertical scar in women with large breasts or poor skin elasticity. Aesthet Surg J 27:336–341
Acknowledgements
The author would especially like to thank his assistants, nurse Ebru Yavuz, for her help in the operations of the patients, biologist Betül Karöz, for her help in collecting and processing data from patients’ files, and graphic designer Gülşah Ertekin for taking photos of the patients and for her contribution to the drawings in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Informed Consent
All patients signed informed consent for surgery and pictures for academic and study purposes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (WMV 19744 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (WMV 68330 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (WMV 67002 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seyhan, A. Vertical Mammaplasty with Retromammary En Bloc Breast Suspension. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 78–91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01862-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01862-4