Abstract
Background
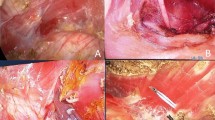
Although transaxillary breast augmentation (TBA) is a well-studied procedure, few previous reports exist concerning the subfascial technique, especially without endoscopic assistance. This study aimed to analyze the feasibility of the technique after breast augmentation in terms of its indication, surgical technique, limitations, and clinical outcome.
Methods
For this study, 42 patients underwent TBA without endoscopic assistance. The technique was indicated for patients with breasts of small or moderate volume without ptosis, patients who wanted no breast scars, and patients who had a poorly defined inframammary fold. The mean follow-up period was 16 months. Implant and incision approach complications were evaluated. Information on patient satisfaction was collected.
Results
A total of 14 complications occurred in 42 patients, all of them minor. Axillary incision–related complications occurred in 26% of the patients, as represented by a late axillary subcutaneous band (119%), sensory loss in the inner aspect of the arm (71%), and a hypertrophic scar and small wound dehiscence (71%). No patient presented with capsular contracture, visible rippling, or infection. Most of the patients (93%) were either very satisfied or satisfied with their result, and none regretted the surgery.
Conclusion
The TBA procedure without endoscopic assistance is a simple and reliable technique for breast augmentation. Most of the complications in this study were minor and predictable. They did not interfere with the aesthetic outcome nor the normal postoperative recovery. With TBA, success depends on patient selection as well as careful intra- and postoperative management.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benito-Ruiz J: Subfascial breast implant. Plast Reconstr Surg 113:1088, 2004
Bosworth JL, Chossein NA: Limited surgery and radiotherapy in the treatment of localized breast cancer: An overview. Surg Clin North Am 64:1115, 1984
Dowden RV: Dispelling the myths and misconceptions about transumbilical breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:190, 2000
Dowden RV: Subcutaneous fibrous banding after transaxillary subpectoral endoscopic breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 99:257, 1997
Ghaderl B, Hoenig JM, Dado D, Angelats J, Vandevender D: Incidence of intercostobrachial nerve injury after transaxillary breast augmentation. Aesth Surg J 22:26, 2002
Goes JC, Landecker A: Optimizing outcomes in breast augmentation: Seven years of experience with the subfascial plane. Aesth Plast Surg 27:178, 2003
Graf RM, Bernardes A, Auersvald A, Damasio RC: Subfascial endoscopic transaxillary augmentation mammaplasty. Aesth Plast Surg 24:216, 2000
Graf RM, Bernardes A, Rippel R, Araujo LR, Damasio RC, Auersvald A: Subfascial breast implant: A new procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:904, 2003
Gray RJ, Forstner-Barthell AW, Pockaj BA, Schild SE, Halyard MY: Breast-conserving therapy and sentinel lymph node biopsy are feasible in cancer patients with previous implant breast augmentation. Am J Surg 188:122, 2004
Hidalgo DA: Breast augmentation: Choosing the optimal incision, implant, and pocket plane. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:2202, 2000
Hoehler H: Breast augmentation: The axillary approach. Br J Plast Surg 26:373, 1973
Huang GJ, Hardesty RA, Mills D: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in the augmented breast: Role of the transaxillary subpectoral approach. Aesth Surg J 23:184, 2003
Krag D, Weaver D, Ashikaga T, Moffat F, Klimberg VS, Shriver C, Feldman S, Kusminsky R, Gadd M, Kuhn J, Harlow S, Beitsch P: The sentinel node in breast cancer: A multicenter validation study. N Engl J Med 339:941, 1998
Laufer E: Fibrous bands following subpectoral endoscopic breast augmentation. Plast Recons Surg 99:257, 1997
Maximovich SP: Fibrous bands following subpectoral endoscopic breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 97:1304, 1996
McMasters KM, Tuttle TM, Carlson DJ, Brown CM, Noyes RD, Glaser RL, Vennekotter DJ, Turk PS, Tate PS, Sardi A, Cerrito PB, Edwards MJ: Sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer: A suitable alternative to routine axillary dissection in multi-institutional practice when optimal technique is used. J Clin Oncol 18:2560, 2000
Munhoz AM, Aldrighi C, Buschpiegel C, Ono C, Montag E, Fells K, Arruda E, Sturtz G, Kovac P, Filassi JR, Gemperli R, Ferreira MC: The feasibility of sentinel lymph node detection in patients with previous transaxillary implant breast augmentation: Preliminary results. Aesth Plast Surg 29:163, 2005
Serra-Renom J, Garrido MF, Yoon T: Augmentation mammaplasty with anatomic soft, cohesive silicone implant using the transaxillary approach at a subfascial level with endoscopic assistance. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:640, 2005
Smith JW, Shaw LW, Friedland JA: Endoscopic transaxillary subpectoral augmentation mammaplasty: A comparative analysis of endoscopic versus nonendoscopic transaxillary subpectoral augmentation mammaplasty using smooth saline implants. Plast Surg Forum 21:127, 1998
Solomon JA, Barton FE: Augmentation mammaplasty. Selected Read Plast Surg 8:1, 1997
Solz H: Transaxillary breast augmentation without endoscopic assistance. Personal communication, 2005
Spear SL, Bulan EJ, Venturi ML: Breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:73, 2004
Stoff-Khalili MA, Scholze R, Morgan WR, Metcalf JD: Subfascial periareolar augmentation mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:1280, 2004
Tebbetts JB: Does fascia provide additional meaningful coverage over a breast implant? Plast Reconstr Surg 113:777, 2004
Tebbetts JB: Dual-plane breast augmentation: Optimizing implant–soft-tissue relationships in a wide range of breast types. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:1255, 2001
Tebbetts JB: Transaxillary subpectoral augmentation mammaplasty: Long-term follow-up and refinements. Plast Reconstr Surg 74:636, 1984
Temple WJ, Ketcham AS: Preservation of the intercostobrachial nerve during axillary dissection for breast cancer. Am Surg 150:585, 1985
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V, Viale G, Zurrida S, Bedoni M, Costa A, de Cicco C, Geraghty JG, Luini A, Sacchini V, Veronesi P: Sentinel node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative nodes. Lancet 349:1864, 1997
Veronesi U, Saccozzi R, Delvecchio M: Comparing radical mastectomy with quadrantectomy, axillary dissection, and radiotherapy in patients with small cancers of breast. N Engl J Med 305:6, 1981
Wright JH, Bevin AG: Augmentation mammaplasty by the transaxillary approach. Plast Reconstr Surg 58:429, 1976
Young RV, Bindrup JR: Transaxillary submuscular augmentation and subcutaneous fibrous bands. Plast Recons Surg 99:257, 1997
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Teresa Curi for English revision. No financial benefit was received by the authors for this study. The Silimed implants were donated by the manufacturers for the patients submitted to the surgery at the Hospital das Clínicas-University of São Paulo Medical School (HC-FMUSP) as a branch of a prospective protocol. The McGhan implants were purchased by the hospital and patients and not donated by the manufacturers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munhoz, A.M., Fells, K., Arruda, E. et al. Subfascial Transaxillary Breast Augmentation Without Endoscopic Assistance: Technical Aspects and Outcome. Aesth Plast Surg 30, 503–512 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0017-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0017-8