Abstract
Group size is a key component of sociality and can affect individual health and fitness. However, proximate links explaining this relationship remain poorly understood, partly because previous studies neglected potential confounding effects of ecological factors. Here, we correlated group size with various measures of health while controlling for measures of seasonality and habitat quality, to explore trade-offs related to group living in a mainly folivorous primate—Verreaux’s sifakas (Propithecus verreauxi). Over a course of 2 years, we studied 42 individuals of 7 differently sized groups (range 2–10) and combined measures of faecal glucocorticoid metabolites (n > 2300 samples), parasitism (n > 500 samples), ranging and activity patterns, together with estimates of habitat quality (measures of ~ 7000 feeding trees). None of our measures was correlated with group size, while seasonality, but not habitat quality, impacted almost all examined variables. We conclude that group size alone might be insufficient to explain patterns in the sociality-health nexus or that the small range of group sizes in this species does not induce effects suggested for species living in larger groups. An optimal group size balancing the advantages and disadvantages of living in differently sized groups may not exist for Verreaux’s sifakas. Our results do not support predictions of the ecological constraints hypothesis or the optimal group size hypothesis as they may only account for species limited in group size by ecological factors—a condition that may not apply to the majority of folivorous mammals, which seem to be limited by social factors.
Significance statement
Group size is a key component of group living and can crucially impact individual health. Ecological variables may modulate this relationship, but they were often neglected in previous studies. To better understand the links between sociality and health, we, for the first time in a mammal, simultaneously examined variation in ranging patterns, daily activities, glucocorticoid concentrations, and parasitism as a function of group size and under consideration of measures of seasonality and habitat quality in wild Verreaux’s sifakas (Propithecus verreauxi). Group size had no impact on individual health indicators, while seasonal variation in food availability and temperature differences, but not habitat quality, affected the majority of variables. We demonstrate strong impacts of environmental factors on socio-ecological traits and conclude that group size on its own might be insufficient to explain patterns in the sociality-health nexus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Group size has been identified as one key aspect of sociality that influences an individuals’ condition and health (Altizer et al. 2003; Borries et al. 2008; Markham et al. 2015; Ezenwa et al. 2016). According to the ecological constraints hypothesis, feeding competition, parasite infestations, and energy expenditure should be higher in larger groups, whereas smaller groups face higher per capita predation risk and disadvantages during competitive encounters with larger groups (Wrangham et al. 1993; Chapman and Chapman 2000, but see Koch et al. 2016). The optimal group size hypothesis posits that intermediate-sized groups represent a balance between the tendency to aggregate to increase predator safety and the tendency for large groups to fission as a consequence of increased food competition (Terborgh and Janson 1986). Thus, in order to optimize the consequences of group size variation, there should be selection for intermediate-sized or “optimal” group size in which individuals carry the lowest costs of group living and, therefore, ought to be healthiest and fittest (Chapman and Chapman 2000). Yet, intra-specific group size variation persists, but the proximate links between group size and health remain poorly understood.
One important link between sociality and health is the physiological stress response. Stressors are uncontrollable stimuli derived from extrinsic and intrinsic sources that trigger a reaction of the vertebrate hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis leading to the secretion of glucocorticoids (GCs) (Adkins-Regan 2005; Koolhaas et al. 2011). GCs are mainly responsible for the regulation of metabolic functions (Sapolsky et al. 2000; Beehner and Bergman 2017), in particular, mediating energy homeostasis during energetically demanding periods (Romero et al. 2009) and energetically costly behaviours, like locomotion (Dunn et al. 2013). When individuals enter a state of “stress”, a rise of GC secretions initiates various behavioural and physiological changes to cope with the challenge (Busch and Hayward 2009), affecting individuals’ immune functions and, therefore, ultimately also their health (Sapolsky et al. 2000; McEwen and Wingfield 2003; Busch and Hayward 2009).
Studies on group size effects on glucocorticoid output yielded a heterogeneous pattern across taxa, including primates, rodents, ungulates, and birds. While the majority of studies found a positive correlation between GC secretion and group size (Foley et al. 2001; Raouf et al. 2006; Dantzer et al. 2013; Dettmer et al. 2014), there were also studies reporting opposite findings (Michelena et al. 2012; Blondel et al. 2016), or no link (Snaith et al. 2008; Ebensperger et al. 2011). In principle, both, larger and smaller groups inflict energetic costs on individuals based on resource competition and predation risks (Chapman and Chapman 2000), which in turn may cause elevated GC concentrations. Hence, individuals in groups of intermediate or “optimal” sizes may face decreased energetic constraints and exhibit the lowest GC concentrations. However, only two studies, in ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta) and yellow baboons (Papio cynocephalus), found optimal group size effects in GCs (Pride 2005; Markham et al. 2015). The absence of such U-shaped correlations between group size and GCs in other prior investigations might be caused by biases towards studying larger groups (Markham et al. 2015). Hence, a lack of studies taking a species’ full range of group sizes into account might be one explanation for the ambiguous GC patterns found across the literature. Nevertheless, group size-related benefits and costs for social animals are complex and numerous other factors are involved in shaping the relationship between group size and health.
First, the facilitated transmission of parasites and other pathogens constitutes one of the major costs of group living (Côté and Poulin 1995; Altizer et al. 2003; Kappeler et al. 2015; Müller-Klein et al. 2018). Several meta-analyses revealed that group size and parasite transmissions are generally positively correlated, but their relationship turns out to be rather variable and complex (Altizer et al. 2003; Rifkin et al. 2012; Patterson and Ruckstuhl 2013). This complexity is amplified by the interplay of parasites with GC secretion.
GCs can have suppressing effects on host immune function, which may lead to increased susceptibility to pathogens (Norbiato et al. 1997; Elenkov and Chrousos 1999; Turnbull and Rivier 1999). For instance, social stress in wild large vesper mice (Calomys callosus) caused not only elevated GC levels, but also an impaired immune response and increased blood infections with Trypanosoma cruzi (Santos et al. 2008). However, the relationship between GCs and parasites seems to be reciprocal as, for example, infections with Anguillicola novaezelandiae in European eels (Anguilla anguilla) positively affected individual cortisol levels (Dangel et al. 2014). Positive associations between GCs and parasite richness were also found in chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), red colobus (Piliocolobus tephrosceles), and black howler monkeys (Alouatta pigra) (Chapman et al. 2006; Muehlenbein 2006; Martinez-Mota 2015). The multidirectional relationships between social parasite transmission and GCs emphasize the strong link between sociality and health.
Second, local variation in ecological factors, either as a function of variation in habitat quality or seasonal variation in resource availability, may impact group size effects on behavioural and physiological response variables. An implicit, but crucial assumption underlying most previous tests of the ecological constraints hypothesis is that the habitats of different groups do not differ in structure or quality. However, small-scale habitat features, like the distribution of food patches, can affect carrying capacities of home ranges and, therefore, influence population densities and group sizes (Marsh 1981; Iwamoto and Dunbar 1983; McLean et al. 2016; Strandburg-Peshkin et al. 2017). For example, mantled guerezas (Colobus guereza) formed larger groups when habitats provided more food trees (Dunbar 1987). Larger prides in lions (Panthera leo) were more likely to occupy territories of better quality, measured via six different landscape variables (Mosser and Packer 2009), and badger (Meles meles) group sizes increased with the quality of food patches (Kruuk and Parish 1982). Thus, significant local habitat heterogeneity might have important implications for species’ group sizes.
Here, we provide a comprehensive test of the ecological constraints and optimal group size hypotheses by examining behavioural and physiological consequences of group size variation in a wild lemur population, Verreaux’s sifakas (Propithecus verreauxi). These endemic Malagasy primates usually live in multimale-multifemale groups, even though groups can also comprise only single males and/or females. Their groups are comparably small, ranging from 2 to 12 individuals with a mean group size of 6, yet, like other primates (Majolo et al. 2008), they exhibit up to 5-fold variation in size (Jolly et al. 1982; Kappeler and Fichtel 2012; Sussman et al. 2012; Leimberger and Lewis 2015). Over a course of 2 years, we assessed ranging, activity, and dietary patterns of seven adjacent groups. Additionally, we measured individual levels of faecal glucocorticoid metabolites (fGCMs) and examined individual parasite richness. Intestinal parasite richness seems to be generally low in Verreaux’s sifakas (Muehlenbein et al. 2003; Rasambainarivo et al. 2014; Springer and Kappeler 2016). However, here we apply a metabarcoding approach to assess infestations of intestinal helminths using next-generation sequencing of 18S rRNA genes (Hadziavdic et al. 2014). Metabarcoding might be superior to previous methods, like microscopy, when assessing non-invasive parasite infestations as it allows for identification of a wide range of taxa of all life stages (i.e. eggs, larvae, and worms) and can recognize cryptic species (Aivelo and Medlar 2017).
To our knowledge, this is the first study in a mammal to simultaneously examine variation in ranging behaviour, daily activities, glucocorticoid metabolite levels, and parasitism as a function of group size while accounting for ecological stressors, namely food availability and average daily temperature differences. We expected to find one of two patterns in relation to group size: Either mean daily travel distances, home range sizes, parasite richness, and faecal GC metabolite concentrations should increase linearly with group size, according to predictions of the ecological constraints hypothesis, or these variables should follow a U-shaped pattern if groups of intermediate size are favoured, according to predictions of the optimal group size hypothesis. In case we should find heterogeneity among group habitats, we expect larger groups to inhabit areas with better quality, which should result in lower daily travel distances, foraging durations, and fGCMs for the respective groups.
Materials and methods
Study site
This study was conducted at the research station of the German Primate Center in Kirindy Forest, Western Madagascar (44° 39′ E, 20° 03′ S) from April 2016 to March 2018. Kirindy Forest is a protected dry deciduous forest and subject to pronounced seasonality, with a long, cool dry season (April to October) and a hot wet season (November to March) (Kappeler and Fichtel 2012).
Study species
We observed a total of 42 Verreaux’s sifakas living in 7 adjacent groups ranging in size from 2 to 10 individuals, covering a broad range of group sizes found in this species with a maximum range of 1 to 12 individuals (Jolly et al. 1982; Sussman et al. 2012; Leimberger and Lewis 2015) (Table 1). Verreaux’s sifakas are diurnal and arboreal primates with a mainly folivorous diet, but they exhibit pronounced seasonal dietary flexibility (Koch et al. 2017). They inhabit home ranges that remain stable over many years and partially overlap with those of neighbouring groups, but also include core areas of exclusive use (Benadi et al. 2008; Koch et al. 2016). All animals are habituated to human observers and individually marked with unique collars.
Behavioural observations
Focal animal sampling was carried out on all members of the 7 study groups, including adults and juveniles (> 9 months). Observations of 1 h per individual were conducted in an alternating order for 3 h in the morning and 3 h in the afternoon, resulting in a total of 1812 h of behavioural data. We continuously recorded all activities (social and non-social) as well as the identity of feeding plants and parts. As our study involved focal animal observations, it was not possible to record data blind.
GPS data collection
For assessing ranging patterns, one adult male per group was equipped with a GPS collar (e-obs, Grünwald, Germany) during annual captures (for details see Kappeler and Fichtel 2012). All collars were set to record GPS coordinates every 30 min between 04:00 and 20:00 h local time. As sifakas remain stationary on their sleeping tree during the night (Erkert and Kappeler 2004), we did not collect GPS locations between 20:00 and 04:00 h (Koch et al. 2016). On average, we recorded GPS data for 651 days with a mean of 21400 GPS locations per group (Table 1). For estimating home range sizes and core areas, we used monthly 95% and 50% fixed kernels using the adehabitatHR package (Calenge 2006) in R (R Version 3.4.4, R Core Team 2018). Daily travel distances (DTD) were calculated using the points-to-path plugin in Quantum GIS (QGIS Development Team 2018).
Faecal sample collection and analyses
During behavioural observations, fresh faecal samples, uncontaminated by urine, were collected within 3 min after defecation from the forest floor whenever they could be unequivocally assigned to an individual. Samples were collected weekly from all study animals except for dependent offspring.
Hormone analyses
Faecal samples for glucocorticoid metabolite (fGCM) analysis were collected in the morning between 07:00 and11:00 h (n = 2329) and placed in 15-ml polypropylene tubes (Sarstedt, Nümbrecht, Germany) containing 5 ml of 80% ethanol. fGCM concentrations were determined upon subsequent extraction by using a validated enzyme immunoassay (EIA), measuring 5ß-reduced cortisol metabolites (Fichtel et al. 2007) (for details see Online Resource 1).
Parasite analyses
A total of 520 faecal samples were collected during four periods (April–May 2016/2017 and September–October 2016/2017). We collected up to four samples (Ø 3.9) per period from each study animal. Samples were stored in 2-ml polypropylene tubes containing 1 ml RNAlater (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at ambient temperature. After 24 h, when RNAlater had completely soaked the faeces, samples were stored in a freezer at − 20 °C and remained frozen throughout shipping to Germany, where further analysis ensued.
Extraction of DNA, amplification, and sequencing of 18S rRNA genes
We conducted DNA extraction with the PowerSoil DNA isolation kit (MoBio, Carlsbad, Canada). PCR reactions to generate eukaryotic 18S rRNA gene amplicons were performed in triplicates for each sample, then pooled in equimolar amounts and cleaned. Afterwards, we conducted dual-indexed paired-end sequencing with the Illumina MiSeq platform and v3 chemistry (for details see Online Resource 1).
18S rRNA gene amplicon analyses
Amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) were generated with VSEARCH version 2.9.1. We removed chimeric sequences with VSEARCH using UCHIME3 in de novo (--uchime3_denovo) and reference (--uchime_ref) mode against the PR2 database (version 4.11.0) (Guillou et al. 2013). The following steps were conducted with the package ampvis2 (version 2.3.19) (Skytte et al. 2018) in R (version 3.4.4) (R Core Team 2018). We performed sample comparisons at the same surveying effort, using the lowest number of sequences by subsampling (2600 reads per sample). Additionally, we removed chloroplasts and extrinsic domains or unclassified ASVs from the data set (for details see Online Resource 1).
Habitat quality
Fixed area plots are a common sampling method in forest inventories (Scott 1998). For each group, 10 square plots (~ 25 × 25 m) within the corresponding home range were randomly selected and all trees with a larger diameter than 5 cm were identified to the species level and the diameter at breast height (DBH) was measured (for details see Online Resource 1).
For estimating habitat quality, we examined feeding tree characteristics of each home range. We compared density, species richness, and sizes of a total of 6690 feeding trees belonging to 77 different species. These species were consumed during 67 ± 4% SD of time during groups’ foraging bouts. Identification of feeding tree species is based on behavioural observations from June 2016 until March 2018 and comprises 539 h of observed feeding.
Statistical analyses
GLMMs: group size effects on ranging patterns and fGCM concentrations
We applied generalized linear mixed effect models (GLMMs) (Baayen et al. 2008) from the lme4 package (version: 1.1.21) (Bates et al. 2015) in R (version3.5.1) (R Core Team 2018), to test whether group size and group size-squared or group ID affect monthly averaged measures of DTDs, home range sizes, and individual fGCMs. We included study year (first or second), food availability, temperature differences (∆ temperature), and sex (for fGCM models only) as fixed effects to control for ecological and social influences. Food availability was based on monitoring monthly phenology of 690 trees throughout the study period. We used a semi-quantitative method (Fournier 1974) in which the availability for each plant part (i.e. leaves, fruit, flowers) was scored, ranging from 0 (complete absence) to 4 (maximum abundance) (for details, see Koch et al. 2017). ∆ temperatures describe the average monthly differences between daily minimum and maximum temperatures. We also examined interactions between group size and group size-squared with food availability and ∆ temperatures in all respective models, to investigate group size effects on behavioural and physiological adaptations to seasonal changes. To keep type I error rates at the nominal level of 5%, we included random slopes (Barr et al. 2013). p values for individual effects were based on likelihood ratio tests comparing the full with the respective null models using the drop1 function (Barr et al. 2013). If models resulted in significant effects of group ID, we conducted Tukey post hoc tests using the glht function of the package multcomp (version 1.4-10).
GLMMs: group size effects on activity patterns
To examine effects of group size or group ID on mean monthly foraging and resting rates, we calculated binomial models with beta error distribution structures and a logit link function using the glmmTMB package (version 0.2.3) (Brooks et al. 2017). Response variables (foraging and resting rates), predictors (group size or group ID, food availability, ∆ temperatures), control variables (study year), random effects (group and animal ID), and random slopes (group size, food availability, ∆ temperatures, and study year within group and animal ID) were included the same way as described above. We conducted full-null model comparisons and estimations of p values as described above. Models resulting in significant effects of group ID were further analysed by comparing predicted marginal means using the lsmeans function of the package emmeans (version 1.3.3).
In all statistical analyses, our measure of group size comprised all present individuals, including adults (age > 4 years), juveniles (age < 4 years), and dependent infants (age < 9 months) (Kappeler and Fichtel 2012). Yet, especially dependent infants may require and consume considerably less energy compared with juveniles and adults. As this could have important implications for how group size affects fGCM concentrations, activity, and ranging patterns, we re-ran all statistical analyses with a second measure of group size that excluded dependent infants (Online Resource 1, Tables S14-S18). However, we did not find differences in model outcomes when using these two different measures of group size.
Moreover, we examined correlations between group sizes and core areas. As home range sizes were highly correlated with core areas (Pearson, r = 0.987; n = 22; p < 0.001), we only considered home range sizes in our main analyses but added analyses on core areas to Online Resource 1 (Tables S19-S20, Fig. S3a, b).
GLMMs: correlations among fGCMs, activity, and ranging patterns
We additionally examined potential links between individual monthly fGCMs with ranging and activity patterns by applying two GLMMs as described above. We ln-transformed the response value (fGCMs) and included DTD or HR and foraging or resting rates as predictor variables. We included food availability as control variable. Monthly ∆ temperatures were correlated with DTD and HR (Pearson: DTD/∆Temp, r = − 0.82, n = 22, p < 0.001; HR/∆Temp, r − 0.55, n = 22, p < 0.001, Fig. S4c, d), which is why we excluded them from the model. Group and animal ID were utilized as random effects; and DTD or HR, foraging or resting rates, and food availability as random slopes within group and ID, respectively.
ANOVA/Kruskal–Wallis: differences in habitat quality
For comparing feeding tree characteristics (i.e. density, species diversity, and basal areas of all feeding trees) between the habitats, we conducted one-way ANOVAS or Kruskal–Wallis tests. Significant results were further analysed with Tukey tests using the glht function of the package multcomp (version 1.4-10) or with Dunn’s pairwise post hoc tests (Bonferroni correction) using the package FSA (version 0.8.22), respectively.
See Online Resource 1 for more details on all statistical analyses.
Results
Ranging patterns
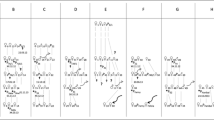
Verreaux’s sifakas inhabited home ranges with a monthly average size of 15 ± 7 ha (mean ± SD) and travelled on average 954 ± 234 m per day. The model examining effects of group size, food availability, ∆ temperatures, and study year on home range sizes was significant (χ2 = 43.492, df = 9 p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.23/0.79); however, group size was not correlated with home range size (Table S1, Fig. 1a). The second model, including group ID instead of group size as predictor variable, was also significant (χ2 = 31.173, df = 6, p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.70/0.72) (Table S2, Fig. 2a), indicating that groups differed significantly in their home range sizes. Specifically, groups M and L had larger and group J had a smaller home range compared with the other groups (Table S5). Results of both models revealed that home range sizes were negatively correlated with food availability and ∆ temperatures, which are smallest during the months of the wet season (Table S1, S2, Fig. S1a, b).
Group size versus different behavioural and physiological variables. In graphs (a–e), boxplots comprise data on mean monthly rates per group (for home range size and daily travel distances) or individual (foraging, resting, fGCMs) and indicate median, upper, and lower quartiles. Whiskers indicate ± 1.5 interquartile ranges and small circles beyond whiskers indicate outliers. In graph (f), data points represent analysed samples and horizontal lines indicate medians
Group ID versus different behavioural and physiological variables. Groups are ordered by mean group size, with the smallest group being depicted on the left. Highlighted graphs indicate significant differences among groups. Boxplots comprise data on mean monthly values per group (for home range size and daily travel distances) or individual (foraging, resting, fGCMs) and indicate median, upper, and lower quartiles. Whiskers indicate ± 1.5 interquartile ranges and small circles beyond whiskers indicate outliers. In graph (f), data points represent analysed samples and horizontal lines indicate medians. Different letters indicate significant differences in means, i.e. groups sharing at least one letter do not differ
The model examining effects of group size, food availability, ∆ temperatures, and study year on daily travel distances was significant (χ2 = 65.410, df = 9 p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.70/0.82). There was an interaction effect with DTDs and ∆ temperatures, i.e. during the dry season when ∆ temperatures are increased, larger groups had shorter DTDs than smaller groups (test of the interaction between ∆ temperatures and group size, χ2 = 6.623; df = 1; p = 0.010) (Table S3). The model including group ID instead of group size as predictor variable was also significant (χ2 = 76.405, df = 9, p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.77/0.81) (Table S2, Fig. 2a) and groups differed significantly in their DTDs. Groups M and L covered longer distances than groups J and F, while group J additionally had shorter DTDs compared with all groups except F1 (Table S5). In addition, DTDs were negatively correlated with food availability and ∆ temperatures, which are smallest during the months of the wet season (Tables S3, S4, Fig. S1a, c).
Daily activities
Verreaux’s sifakas spent on average 47 ± 20% (mean ± SD) of their time resting and 45 ± 20% foraging. The model examining effects of group size, food availability, and ∆ temperatures on monthly foraging rates was not significant (χ2 = 7.379, df = 5, p = 0.194) (Table S6, Fig. 1c). In contrast, the model including group ID instead of group size as predictor variable was significant (χ2 = 21.997, df = 8, p = 0.005) (Table S7, Fig. 2c), as group F1 and G had shorter foraging durations than several other groups (Table S10). Foraging rates were negatively correlated with ∆ temperature, i.e. animals spent less time foraging during seasons with larger daily temperature changes, i.e. during the dry season (Table S7, Fig. S1a, d).
The model examining effects of group size, food availability, and ∆ temperatures on monthly resting rates was not significant (χ2 = 6.195, df = 5, p = 0.288) (Table S8, Fig. 1d), while the model including group ID instead of group size as predictor variable was (χ2 = 21.615, df = 8, p = 0.006) (Table S9, Fig. 2d). Groups differed significantly in resting durations with groups F1 and G resting shorter than several other groups (Table S10). Resting rates were positively correlated with ∆ temperature, i.e. animals spent more time resting during seasons with larger daily temperatures changes, i.e. during the dry season (Tables S9, Fig. S1a, e).
Faecal glucocorticoid metabolites
On average, individuals had mean monthly fGCM concentrations of 0.326 ± 0.181 μg/g (mean ± SD). Males had generally higher average fGCM concentrations (0.360 ± 0.174 μg/g) than females (0.276 ± 0.181 μg/g) (Table S11, S12). The model examining effects of group size, food availability, ∆ temperatures, study year, and sex on monthly fGCM concentrations was significant (χ2 = 51.406, df = 10, p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.20/0.36); however, group size was not correlated with FGCM concentrations (Table S11, Fig. 1e). The model including group ID instead of group size as predictor variable was also significant (χ2 = 55.800, df = 10, p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.21/0.32), but groups did not differ in fGCM concentrations (Table S12, Fig. 2e). Sifaka’s fGCM concentrations were positively correlated with food availability and ∆ temperatures, i.e. which are largest during the dry season (Table S11, S12, Fig. S1, f, g).
Correlations among fGCMs and activity and ranging patterns
The models on links between individual monthly fGCMs with DTDs and foraging rates or HRs and resting rates were both highly significant (DTD + foraging, χ2 = 20.210, df = 2, p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.13/0.29; HR + resting χ2 = 18.981, df = 2, p < 0.001, R2m/c = 0.14/0.31). More precisely, DTDs and HRs were negatively correlated with fGCMs, while time spent resting was positively correlated. Foraging rates were not correlated with fGCMs (Tables S22, S23, Fig. S5).
Parasite richness
After subsampling, 33 of 520 samples were removed due to low read numbers. The remaining 487 faecal samples contained 6587 eukaryotic ASVs and 24.764.794 reads. A total of 2947 of all ASVs could be taxonomically assigned and belonged to nine phyla: Opisthokonta (1288), Archaeplastida (730), Alveolata (628), Rhizaria (194), Amoebozoa (116), Stramenopiles (36), Hacrobia (10), Apusozoa (3), and Excavata (2). In terms of nematodes, 3 different families known to contain parasitic species were present in the samples: Trichostrongylidae, Onchocercidae, and Oxyuridae (Fig. S2).
All individuals repeatedly tested PCR-positive for infestation with nematodes of the family Trichostrongylidae (486/487 samples). Additionally, in 33 samples from 26 individuals representing all study groups, nematodes of the family Oxyuridae appeared at least once (n = 21) and up to three times (n = 5) during both dry seasons. Another 32 samples of 18 individuals were positive for filarial nematodes of the family Onchoceridae. However, parasites of this family are vector-borne and usually occur in body fluids or particular tissues. Finding their DNA in faecal samples might be a result of small perforations of sifakas’ intestines, leading to small amounts of blood containing the parasites entering the colon, or accidental ingestion of vectors during feeding or oral grooming. Prevalence of Onchocercidae was, therefore, not considered in our estimation of gastro-intestinal parasite richness. Hence, with all animals carrying Trichostrongylidae, and Oxyuridae only occurring in a few samples, intestinal parasite richness across all groups averages 1 and is not affected by group size.
Habitat quality
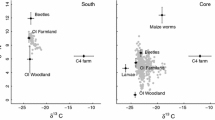
Groups’ habitats differed in food tree density (Kruskal–Wallis, χ2 = 25.723; df = 6; p < 0.001) and species richness (ANOVA, F6,59 = 2.34; p = 0.043); however, these differences were not related to group size (Pearson: food tree density, r = − 0.287, n = 7, p = 0.533; species richness, r = − 0.080, n = 7, p = 865). For tree densities, post hoc Dunn’s test revealed that the habitat of group M harboured significantly more trees than the habitats of groups G, J, and L. Food tree richness only differed between habitats of groups M and J, with M having a higher richness (Table S15; Fig. 3). We found no differences in food tree sizes among the different habitats (Kruskal–Wallis: basal area, χ2 = 4.642; df = 6; p = 0.590) (Fig. 3).
Habitat characteristics of the home ranges of seven sifaka groups. Groups are ordered by mean group size, with the smallest group being depicted on the left. Boxplots show density, richness, and basal areas of the feeding trees of 10 plots per group (6 plots for group F1). Boxplots indicate median, upper, and lower quartiles. Whiskers indicate ± 1.5 interquartile ranges and small circles beyond whiskers indicate outliers. Highlighted graphs indicate significant differences among groups. Different letters indicate significant differences in means, i.e. groups sharing at least one letter do not differ
Discussion
In this study, we examined behavioural and physiological consequences of group size variation in wild Verreaux’s sifakas. None of our measures, i.e. daily travel distances, home range sizes, foraging rates, resting rates, fGCM concentrations, and parasite richness, was correlated with group size. We detected some variation in habitat quality between groups, but this variation was unrelated to group size as well. The most important factor influencing behaviour and physiology in Verreaux’s sifakas seems to be seasonality, which we operationalized via food availability and temperature differences. Altogether, our results indicate that group size on its own is insufficient to explain links between sociality and aspects of health in this lemur population.
Group size, daily activities, and habitat quality
According to the ecological constraints hypothesis, within-group food competition should increase in larger groups and be compensated via two key strategies: (i) longer travel distances and (ii) increased foraging durations (Chapman and Chapman 2000; Pollard and Blumstein 2008). Here, we did not find group size-related differences in ranging and activity patterns. Relying on a mainly folivorous diet, food competition may be reduced in Verreaux’s sifakas compared with more frugivorous species (Janson and Goldsmith 1995; Koenig 2002). Larger groups seem not to be affected by higher costs of intra-group food competition, and smaller groups do not seem to suffer from higher costs of between-group competition. The latter notion is further supported by findings of an earlier study of the same population showing that outcomes of intergroup encounters are unrelated to group size (Koch et al. 2016). Additionally, similar fGCM concentrations across all study groups indicate no need for compensation of energetic disadvantages resulting from variation in group size. Considering that Verreaux’s sifakas form relatively small groups, food competition might also not be strong enough to significantly affect individual energy budgets.
We found, however, variation in habitat quality and varying ranging patterns and daily activity among some groups. Intergroup differences in ranging behaviour have been linked to differences in local food distribution before (Caraco 1979; Altmann and Muruthi 1988; Isbell 1991; Bronikowski and Altmann 1996), and studies in baboons and three Neotropical primates revealed changes in movement patterns as a response to different habitat features (McLean et al. 2016; Strandburg-Peshkin et al. 2017). Yet, variation in habitat quality does not seem to explain different ranging and activity patterns among our study groups. For example, group M’s habitat had a higher density and richness of food trees compared with group J. Hence, group M’s habitat might be of better quality, which should result in reduced energetic costs due to decreased travelling and foraging efforts. Yet, group M had higher daily travel distances than group J, while there was no difference in foraging or resting rates between these two groups. It is possible that this intergroup variation could be related to locations of key food patches within the groups’ habitats. While food abundance within the habitats seems sufficient to provide all groups, suboptimal distributions of preferred food trees might require some groups to travel farther then others within their home ranges. However, we did not determine exact locations of food resources and can therefore not evaluate this hypothesis.
Group size, seasonality, and fGCMs
fGCMs are often used as indicators of energetic trade-offs individuals face when living in groups (Markham and Gesquiere 2017). Life in smaller and larger groups is supposed to inflict higher energetic costs on individuals (Chapman and Chapman 2000). However, average concentrations of fGCMs did not differ with variation in group size in our study population. As none of the other measures (i.e. parasitism, ranging, and activity patterns), which might induce such energetic trade-offs, varied with group size either, these results are conclusive. Since sifaka groups did vary in ranging and activity patterns without varying in fGCM concentrations, they appear to be able to apply behavioural adaptations to environmental and/or social challenges without suffering major energetic disadvantages independent of their group size.
Notably, individual fGCM concentrations were strongly affected by seasonal variation in temperature differences and food availability. Ecological and behavioural season, however, are tightly interwined in sifakas, as the birth season falls into the middle of the cool dry season and mating season takes place around the peak of the hot wet season (Kappeler and Fichtel 2012). Thus, female reproductive state and increased energetic demands for males during the mating season (Fichtel et al. 2007) represent likely confounding factors for glucocorticoid outputs. Additionally, climatic season and unpredictability are more pronounced in Madagascar than in many other tropical regions (Dewar and Richard 2007). In Kirindy Forest, food availability is closely linked to seasonality and known to affect sifakas’ diet, daily activities, and ranging patterns (Norscia et al. 2006; Koch et al. 2017). In sum, as individual variation in GC production is determined by various metabolic, social, and environmental stressors, it can be difficult to identify effects of single variables (Huber et al. 2003; Foerster and Monfort 2010).
Interestingly, ranging patterns where negatively correlated with fGCM concentrations. This finding stands in contrast to the assumption that energetically demanding behaviours, like periods of increased locomotion, are reflected in increased GC secretions (Sapolsky et al. 2000; Beehner and Bergman 2017). Both measures were correlated with seasonal changes; yet, while ranging patterns decreased with food availability and increased with temperature differences, fGCM concentrations showed opposite correlations. This suggests that Verreaux’s sifakas reduce ranging activities to cope with the increased energetic requirements of thermoregulation during the middle of the dry season, when minimum and maximum temperatures differ most strongly and can fall to 3 °C (Kappeler and Fichtel 2012). These energetic requirements appear to result in increased fGCM concentrations and are potentially fortified by the low food availability during this season. The negative correlation between ranging patterns and fGCMs highlights the complexity of fGCMs patterns and emphasizes the potential of confounding factors in studies of fGCMs. In addition, we could show, similar to numerous studies in other vertebrates (Romero 2002), that sifaka’s monthly fGCMs changed simultaneously with behavioural and seasonal patterns.
Group size and parasites
We detected three families of nematodes, two (Trichostrongylidae and Onchocercidae) of which have been previously reported in the same study population (Springer and Kappeler 2016) and one (Oxyuridae) which has been previously reported in the same species but different population (Rasambainarivo et al. 2014). Contrary to our predictions, there was no correlation between group size and intestinal parasite richness. Larger groups are expected to harbour more different parasites due to more opportunities for direct or indirect transmission via social contact or shared environments (Nunn et al. 2003). Although parasites are socially transmitted in Verreaux’s sifakas (Springer and Kappeler 2016), our study animals exhibited low parasite richness, which was prevalent in almost all individuals, making it difficult to determine the mode of transmission. Hence, the costs of sociality in terms of parasite spread could not be estimated in this species.
Seasonality affected the prevalence of Oxyuridae, as they were only detected in samples collected during the dry season, confirming earlier results (Springer and Kappeler 2016). The dry season in Kirindy Forest represents an energetically demanding period as reflected in sifakas reduced ranging patterns and increased fGCM concentrations. It is likely that animals are more susceptible to parasites due to impaired and energetically costly immune functions during this time (Sheldon and Verhulst 1996). Given the complexity of host–parasite interactions, the effects of host group size on parasite richness might depend on various other aspects of sociality, species-specific behaviours, and environmental factors that can affect contact and, therefore, transmission rates (Patterson and Ruckstuhl 2013).
So far, only a handful of studies have used metabarcoding to non-invasively assess intestinal parasites in animals (Wimmer et al. 2004; Tanaka et al. 2014; Avramenko et al. 2015; Srivathsan et al. 2016). This novel approach can facilitate differentiation among closely related species within the same sample and, nowadays, constitutes a faster, cheaper, and more precise method in comparison with many traditional analyses (Aivelo et al. 2018). Accordingly, this approach allowed us to detect a parasite (Oxyuridae) that has not been found in this population before by studies using conventional microscopic methods (Springer and Kappeler 2016).
An optimal group size?
Major costs and benefits of group living are generally linked to predators, pathogens, and resource competition, which ultimately affect individual well-being. Variation in group size reflects adaptations to local ecological conditions and represents one strategy of balancing the various advantages and disadvantages of group living. However, if, for various reasons, groups exceed their upper or lower “optimal” limits in size, the costs of sociality are expected to outweigh the benefits, and groups should, therefore, split or fusion with others (Majolo and Huang 2018).
In Verreaux’s sifakas, even though groups are small with a population-wide average of 6 individuals (Jolly et al. 1982; Sussman et al. 2012; Leimberger and Lewis 2015), they varied up to 5-fold in size in our study. Yet, we did not detect substantial group size-related behavioural or physiological differences between individuals. Maybe not all assumed major costs and benefits of group living apply to this species. For example, predation risk does not seem to strongly impact Verreaux’s sifakas’ group sizes as another population in Berenty Reserve, where terrestrial predators are absent (Jolly 2012), exhibits a similar mean and variance in group size (Jolly et al. 1982; Norscia and Palagi 2008; Kappeler and Fichtel 2012). Additionally, due to their small groups and mainly folivorous diet, competition over food should play a less important role in shaping group size. Like other folivorous taxa, sifakas are expected to form much larger groups than they actually do. The leading hypothesis for this “folivore paradox” invokes social (i.e. male takeovers and infanticide risks) instead of ecological factors as the main constraint on group size (Treves and Chapman 1996; Steenbeek and van Schaik 2001). Thus, in Verreaux’s sifakas, and perhaps other folivorous species in general, group sizes appear to remain below the upper, ecologically “optimal” limits because social rather than ecological factors define these limits. This notion may explain why we did not detect any of the group size-related costs, proposed by the ecological constraints and optimal group size hypotheses. Our findings on between-group variation in daily activities and ranging patterns suggest that differences in microhabitat features shape fine-grained behavioural adaptations. However, these behavioural differences were not reflected in groups’ fGCM concentrations and parasites richness, indicating that all groups, independent of their size, can compensate potential habitat-related challenges without causing health-related costs. An optimal group size might, therefore, not exist in Verrreaux’s sifakas.
Conclusions
This study contributes to the understanding of the relationship between group size, health, and ecology in vertebrates. We show that group size on its own might be insufficient to explain links between sociality and health, probably due to the complex and multifaceted nature of this relationship. We also demonstrate strong impacts of environmental factors on socio-ecological traits that might obscure patterns in the sociality-health nexus. Altogether, our results do not support predictions of the ecological constraints hypothesis and the optimal group size hypothesis as they may only hold true for species limited in group size by ecological factors—a condition that may not apply to the majority of folivorous mammals.
Data availability statement
Sequences have been deposited in the NCBI GenBank under the project number PRJNA527362. All other data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article as supplementary information files (Online Resource 2).
References
Adkins-Regan E (2005) Hormones and animal social behavior. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Aivelo T, Medlar A (2017) Opportunities and challenges in metabarcoding approaches for helminth community identification in wild mammals. Parasitology 145:608–621. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182017000610
Aivelo T, Medlar A, Löytynoja A, Laakonen J, Jernvall J (2018) Metabarcoding gastrointestinal nematodes in sympatric endemic and nonendemic species in Ranomafana National Park, Madagascar. Int J Primatol 39:49–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-017-0010-x
Altizer S, Nunn CL, Thrall PH, Gittleman JL, Antonovics J, Cunningham AA, Dobson AP, Ezenwa V, Jones KE, Pedersen AB, Poss M, Pulliam JRC (2003) Social organization and parasite risk in mammals: integrating theory and empirical studies. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 34:517–547. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.030102.151725
Altmann J, Muruthi P (1988) Differences in daily life between semiprovisioned and wild-feeding baboons. Am J Primatol 15:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.1350150304
Avramenko RW, Redman EM, Lewis R, Yazwinski TA, Wasmuth JD, Gilleard JS (2015) Exploring the gastrointestinal “Nemabiome”: deep amplicon sequencing to quantify the species composition of parasitic nematode communities. PLoS One 10:e0143559. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143559
Baayen RH, Davidson DJ, Bates DM (2008) Mixed-effects modeling with crossed random effects for subjects and items. J Mem Lang 59:390–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2007.12.005
Barr DJ, Levy R, Scheepers C, Tily HJ (2013) Random effects structure for confirmatory hypothesis testing: keep it maximal. J Mem Lang 68:255–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jml.2012.11.001
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48
Beehner JC, Bergman TJ (2017) The next step for stress research in primates: to identify relationships between glucocorticoid secretion and fitness. Horm Behav 91:68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2017.03.003
Benadi G, Fichtel C, Kappeler P (2008) Intergroup relations and home range use in Verreaux’s sifaka (Propithecus verreauxi). Am J Primatol 70:956–965. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.20588
Blondel DV, Wallace GN, Calderone S, Gorinshteyn M, St. Mary CM, Phelps SM (2016) Effects of population density on corticosterone levels of prairie voles in the field. Gen Comp Endocrinol 225:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2015.09.002
Borries C, Larney E, Lu A, Ossi K, Koenig A (2008) Costs of group size: lower developmental and reproductive rates in larger groups of leaf monkeys. Behav Ecol 19:1186–1191. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arn088
Bronikowski AM, Altmann J (1996) Foraging in a variable environment: weather patterns and the behavioral ecology of baboons. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 39:11–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650050262
Brooks ME, Kristensen K, van Benthem KJ, Magnusson A, Berg CW, Nielsen A, Skaug HJ, Machler M, Bolker BM (2017) glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J 9:378–400. https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-b-000240890
Busch DS, Hayward LS (2009) Stress in a conservation context: a discussion of glucocorticoid actions and how levels change with conservation-relevant variables. Biol Conserv 142:2844–2853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2009.08.013
Calenge C (2006) The package “adehabitat” for the R software: a tool for the analysis of space and habitat use by animals. Ecol Model 197:516–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.03.017
Caraco T (1979) Time budgeting and group size: a theory. Ecology 60:611–617. https://doi.org/10.2307/1936081
Chapman CA, Chapman LJ (2000) Determinants of group size in primates: the importance of travel costs. In: Boinski S, Garber PA (eds) On the move: how and why animals travel in groups. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 24–42
Chapman CA, Wasserman MD, Gillespie TR, Speirs ML, Lawes MJ, Saj TL, Ziegler TE (2006) Do food availability, parasitism, and stress have synergistic effects on red colobus populations living in forest fragments? Am J Phys Anthropol 131:525–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.20477
Côté IM, Poulin R (1995) Parasitism and group size in social animals: a meta-analysis. Behav Ecol 6:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/6.2.159
Dangel KC, Keppel M, Tabujew K, Sures B (2014) Effects of Anguillicola novaezelandiae on the levels of cortisol and hsp70 in the European eel. Parasitol Res 113:3817–3822. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4049-8
Dantzer B, Newman AEM, Boonstra R, Palme R, Boutin S, Humphries MM, McAdam AG (2013) Density triggers maternal hormones that increase adaptive offspring growth in a wild mammal. Science 340:1215–1217. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1235765
Dettmer AM, Novak MA, Meyer JS, Suomi SJ (2014) Population density-dependent hair cortisol concentrations in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Psychoneuroendocrinology 42:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2014.01.002
Dewar RE, Richard AF (2007) Evolution in the hypervariable environment of Madagascar. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13723–13727. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704346104
Dunbar RIM (1987) Habitat quality, population dynamics, and group composition in Colobus Monkeys (Colobus guereza). Int J Primatol 8:299–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02737386
Dunn JC, Cristóbal-Azkarate J, Schulte-Herbrüggen B, Chavira R, Veà JJ (2013) Travel time predicts fecal glucocorticoid levels in free-ranging howlers (Alouatta palliata). Int J Primatol 34:246–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-013-9657-0
Ebensperger LA, Ramírez-Estrada J, León C, Castro RA, Ortitz Tolhuysen L, Quirici V, Burger JR, Soto-Gamboa M, Hayes LD (2011) Sociality, glucocorticoids and direct fitness in the communally rearing rodent, Octodon degus. Horm Behav 60:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.07.002
Elenkov IJ, Chrousos GP (1999) Stress hormones, Th1/Th2 patterns, pro/anti-inflammatory cytokines and susceptibility to disease. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10:359–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1043-2760(99)00188-5
Erkert HG, Kappeler PM (2004) Arrived in the light: diel and seasonal activity patterns in wild Verreaux’s sifakas (Propithecus v. verreauxi; Primates: Indriidae). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 57:174–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-004-0845-y
Ezenwa VO, Ghai RR, McKay AF, Williams AE (2016) Group living and pathogen infection revisited. Curr Opin Behav Sci 12:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2016.09.006
Fichtel C, Kraus C, Ganswindt A, Heistermann M (2007) Influence of reproductive season and rank on fecal glucocorticoid levels in free-ranging male Verreaux’s sifakas (Propithecus verreauxi). Horm Behav 51:640–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.03.005
Foerster S, Monfort SL (2010) Fecal glucocorticoids as indicators of metabolic stress in female Sykes’ monkeys (Cercopithecus mitis albogularis). Horm Behav 58:685–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2010.06.002
Foley CAH, Papageorge S, Wasser SK (2001) Noninvasive stress and reproductive measures of social and ecological pressures in free-ranging African elephants. Conserv Biol 15:1134–1142. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.2001.0150041134.x
Fournier LA (1974) Un método cuantitativo para la medición de características fenológicas en árboles. Turrialba 24:422–423
Guillou L, Bachar D, Audic S, Bass D, Berney C, Bittner L, Boutte C, Burgaud G, de Vargas C, Decelle J, del Campo J, Dolan JR, Dunthorn M, Edvardsen B, Holzmann M, Kooistra WHCF, Lara E, le Bescot N, Logares R, Mahé F, Massana R, Montresor M, Morard R, Not F, Pawlowski J, Probert I, Sauvadet AL, Siano R, Stoeck T, Vaulot D, Zimmermann P, Christen R (2013) The Protist Ribosomal Reference database (PR2): a catalog of unicellular eukaryote small sub-unit rRNA sequences with curated taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D597–D604. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1160
Hadziavdic K, Lekang K, Lanzen A, Jonassen I, Thompson EM, Troedsso C (2014) Characterization of the 18S rRNA gene for designing universal eukaryote specific primers. PLoS One 9:e87624. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087624
Huber S, Palme R, Arnold W (2003) Effects of season, sex, and sample collection on concentrations of fecal cortisol metabolites in red deer (Cervus elaphus). Gen Comp Endocrinol 130:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-6480(02)00535-X
Isbell LA (1991) Contest and scramble competition: patterns of female aggression and ranging behavior among primates. Behav Ecol 2:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/2.2.143
Iwamoto T, Dunbar RIM (1983) Thermoregulation, habitat quality and the behavioural ecology of gelada baboons. J Anim Ecol 52:357–366. https://doi.org/10.2307/4559
Janson CH, Goldsmith ML (1995) Predicting group size in primates: foraging costs and predation risks. Behav Ecol 6:326–336. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/6.3.326
Jolly A (2012) Berenty Reserve, Madagascar: a long time in a small space. In: Kappeler PM, Watts DP (eds) Long-term field studies of primates. Springer, Berlin, pp 21–44
Jolly A, Gustafson H, Oliver WLR, O’Connor SM (1982) Propithecus verreauxi population and ranging at Berenty, Madagascar, 1975 and 1980. Folia Primatol 39:124–144. https://doi.org/10.1159/000156071
Kappeler PM, Fichtel C (2012) A 15-year perspective on the social organization and life history of sifaka in Kirindy forest. In: Kappeler PM, Watts DP (eds) Long-term field studies of primates. Springer, Berlin, pp 101–121
Kappeler PM, Cremer S, Nunn CL (2015) Sociality and health: impacts of sociality on disease susceptibility and transmission in animal and human societies. Philos Trans R Soc B 370:20140116. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0116
Koch F, Signer J, Kappeler PM, Fichtel C (2016) The role of the residence-effect on the outcome of intergroup encounters in Verreaux’s sifakas. Sci Rep 6:28457. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28457
Koch F, Ganzhorn JU, Rothman JM, Chapman CA, Fichtel C (2017) Sex and seasonal differences in diet and nutrient intake in Verreaux’s sifakas (Propithecus verreauxi). Am J Primatol 79:e22595. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22595
Koenig A (2002) Competition for resources and its behavioral consequences among female primates. Int J Primatol 23:759–783. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015524931226
Koolhaas JM, Bartolomucci A, Buwalda B, de Boer SF, Flügge G, Korte SM, Meerlo P, Murison R, Olivier B, Palanza P, Richter-Levin G, Sgoifo A, Steimer T, Stiedl O, van Dijk G, Wöhr M, Fuchs E (2011) Stress revisited: a critical evaluation of the stress concept. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:1291–1301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.02.003
Kruuk H, Parish T (1982) Factors affecting population density, group size and territory size of the European badger, Meles meles. J Zool 196:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.1982.tb03492.x
Leimberger KG, Lewis RJ (2015) Patterns of male dispersal in Verreaux’s sifaka (Propithecus verreauxi) at Kirindy Mitea National Park. Am J Primatol 79:e22455. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22455
Majolo B, Huang P (2018) Group living. In: Vonk J, Shackelford T (eds) Encyclopedia of animal cognition and behavior. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–12
Majolo B, de Bortoli VA, Schino G (2008) Costs and benefits of group living in primates: group size effects on behaviour and demography. Anim Behav 76:1235–1247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.06.008
Markham AC, Gesquiere LR (2017) Costs and benefits of group living in primates: an energetic perspective. Philos Trans R Soc B 372:20160239. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0239
Markham AC, Gesquiere LR, Alberts SC, Altmann J (2015) Optimal group size in a highly social mammal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:14882–14887. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1517794112
Marsh CW (1981) Ranging behaviour and its relation to diet selection in Tana River Red colobus (Colobus badius rufomitratus). J Zool 195:473–492. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.1981.tb03479.x
Martinez-Mota R (2015) The effects of habitat disturbance, host traits, and host physiology on patterns of gastrointestinal parasite infection in black howler monkeys (Alouatta pigra). Dissertation, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
McEwen BS, Wingfield JC (2003) The concept of allostasis in biology and biomedicine. Horm Behav 43:2–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0018-506X(02)00024-7
McLean KA, Trainor AM, Asner GP, Crofoot MC, Hopkins ME, Campbell CJ, Martin RE, Kapp DE, Jansen PA (2016) Movement patterns of three arboreal primates in a Neotropical moist forest explained by LiDAR-estimated canopy structure. Landsc Ecol 31:1849–1862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-016-0367-9
Michelena P, Pillot M-H, Henrion C, Toulet S, Boissy A, Bon R (2012) Group size elicits specific physiological response in herbivores. Biol Lett 8:537–539. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2012.0197
Mosser A, Packer C (2009) Group territoriality and the benefits of sociality in the African lion, Panthera leo. Anim Behav 78:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2009.04.024
Muehlenbein MP (2006) Intestinal parasite infections and fecal steroid levels in wild chimpanzees. Am J Phys Anthropol 130:546–550. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajpa.20391
Muehlenbein MP, Schwartz M, Richard A (2003) Parasitologic analyses of the sifaka (Propithecus verreauxi verreauxi) at Beza Mahafaly, Madagascar. J Zoo Wildlife Med 34:274–277. https://doi.org/10.1638/1042-7260(2003)034[0274:PAOTSP]2.0.CO;2
Müller-Klein N, Heistermann M, Strube C, Morbach ZM, Lilie N, Franz M, Schülke O, Ostner J (2018) Physiological and social consequences of gastrointestinal nematode infection in a nonhuman primate. Behav Ecol (published online). https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/ary168
Norbiato G, Bevilacqua M, Vago T, Taddei A, Clerici M (1997) Glucocorticoids and the immune function in the human immunodeficiency virus infection: a study in hypercortisolemic and cortisol-resistant patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:3260–3263. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.10.4304
Norscia I, Palagi E (2008) Berenty 2006: census of Propithecus verreauxi and possible evidence of population stress. Int J Primatol 29:1099–1115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-008-9259-4
Norscia I, Carrai V, Borgognini-Tarli SM (2006) Influence of dry season and food quality and quantity on behavior and feeding strategy of Propithecus verreauxi in Kirindy, Madagascar. Int J Primatol 27:1001–1022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-006-9056-x
Nunn CL, Altizer S, Jones KE, Sechrest W (2003) Comparative tests of parasite species richness in primates. Am Nat 162:597–614. https://doi.org/10.1086/378721
Patterson JEH, Ruckstuhl KE (2013) Parasite infection and host group size: a meta-analytical review. Parasitology 140:803–813. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182012002259
Pollard KA, Blumstein DT (2008) Time allocation and the evolution of group size. Anim Behav 76:1683–1699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2008.08.006
Pride RE (2005) Optimal group size and seasonal stress in ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta). Behav Ecol 16:550–560. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/ari025
QGIS Development Team (2018) QGIS geographic information system. Open Source Geospatial Foundation Project, http://qgis.osgeo.org. Accessed 25 June 2018
R Core Team (2018) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna http://www.R-project.org
Raouf SA, Smith LC, Brown MB, Wingfield JC, Brow CR (2006) Glucocorticoid hormone levels increase with group size and parasite load in cliff swallows. Anim Behav 71:39–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2005.03.027
Rasambainarivo FT, Junge RE, Lewis RJ (2014) Biomedical evaluation of Verreaux’s Sifaka (Propithecus verreauxi) from Kirindy Mitea National Park in Madagascar. J Zoo Wildlife Med 45:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1638/2013-0038R1.1
Rifkin JL, Nunn CL, Garamszegi LZ (2012) Do animals living in larger groups experience greater parasitism? A meta-analysis. Am Nat 180:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1086/666081
Romero LM (2002) Seasonal changes in plasma glucocorticoid concentrations in free-living vertebrates. Gen Comp Endocrinol 128:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-6480(02)00064-3
Romero LM, Dickens MJ, Cyr NE (2009) The reactive scope model — a new model integrating homeostasis, allostasis, and stress. Horm Behav 55:375–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2008.12.009
Santos CD, Toldo MPA, Levy AMA, Prado JC (2008) Trypanosoma cruzi: effects of social stress in Calomys callosus a natural reservoir of infection. Exp Parasitol 119:197–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2008.01.011
Sapolsky RM, Romero LM, Munck AU (2000) How do glucocorticoids influence stress responses? Integrating permissive, suppressive, stimulatory, and preparative actions. Endocr Rev 21:55–89. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.21.1.0389
Scott CT (1998) Sampling methods for estimating change in forest resources. Ecol Appl 8:228–233. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(1998)008[0228:SMFECI]2.0.CO;2
Sheldon BC, Verhulst S (1996) Ecological immunology: costly parasite defences and trade-offs in evolutionary ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 11:317–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(96)10039-2
Skytte KA, Kirkegaard RH, Karst SM, Albertsen M (2018) ampvis2: an R package to analyse and visualise 16S rRNA amplicon data. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/299537
Snaith TV, Chapman CA, Rothman JM, Wasserman MD (2008) Bigger groups have fewer parasites and similar cortisol levels: a multi-group analysis in red colobus monkeys. Am J Primatol 70:1072–1080
Springer A, Kappeler PM (2016) Intestinal parasite communities of six sympatric lemur species at Kirindy Forest, Madagascar. Primate Biol 3:51–63. https://doi.org/10.5194/pb-3-51-2016
Srivathsan A, Ang A, Vogler AP, Meier R (2016) Fecal metagenomics for the simultaneous assessment of diet, parasites, and population genetics of an understudied primate. Front Zool 13:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12983-016-0150-4
Steenbeek R, van Schaik CP (2001) Competition and group size in Thomas’s langurs (Presbytis thomasi): the folivore paradox revisited. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 49:100–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650000286
Strandburg-Peshkin A, Farine DR, Crofoot MC, Couzin ID (2017) Habitat and social factors shape individual decisions and emergent group structure during baboon collective movement. eLife 6:e19505
Sussman RW, Richard AF, Ratsirarson J, Sauther ML, Brockman DK, Gould L, Lawler R, Cuozzo FP (2012) Beza Mahafaly Special Reserve: long-term research on lemurs in southwestern Madagascar. In: Kappeler PM, Watts DP (eds) Long-term field studies of primates. Springer, Berlin, pp 45–66
Tanaka R, Hino A, Tsai IJ, Palomares-Rius JE, Yoshida A, Ogura Y, Hayashi T, Maruyama H, Kikuchi T (2014) Assessment of helminth biodiversity in wild rats using 18S rDNA based metagenomics. PLoS One 9:e110769. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0110769
Terborgh J, Janson CH (1986) The socioecology of primate groups. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 17:111–136. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.17.110186.000551
Treves A, Chapman CA (1996) Conspecific threat, predation avoidance, and resource defense: implications for grouping in langurs. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 39:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650050265
Turnbull AV, Rivier CL (1999) Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by cytokines: actions and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev 79:1–71. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1999.79.1.1
Wimmer B, Craig BH, Pilkington JG, Pemberton JM (2004) Non-invasive assessment of parasitic nematode species diversity in wild Soay sheep using molecular markers. Int J Parasitol 34:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2003.11.022
Wrangham RW, Gittleman JL, Chapman CA (1993) Constraints on group size in primates and carnivores: population density and day-range as assays of exploitation competition. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 32:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173778
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Malagasy Ministère de l’Environnement, the Departement de Biologie Ecologie et Conservation Animale de l’Université d’Antananarivo, and the Centre National de Formation, d’Etudes et de Recherche en Environnementet Foresterie de Morondava for supporting our research in Kirindy Forest. We also thank Mamy Razafindrasamba and Tiana Andrianjanahary for their support in data collection and Dr. Roger Mundry for statistical advice. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments. The study profited greatly from discussions with members of the DFG research unit “Sociality and Health in Primates” (FOR 2136).
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), grant number Ka 1082/29-2, awarded to PMK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PMK, CF, and KR designed the study. KR and FK performed data collection. MH supervised the hormone analyses. KR conducted the lab work and analysed the data. DS helped with the analysis of the parasite data. KR drafted the manuscript and all authors contributed to writing and revising of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. Statement of ethical approval, approval of research protocols, and capture procedures was approved by a committee of the Ministry for the Environment, Water and Forests of Madagascar (MINEEF) (Permit numbers: 50/16/MEEMF/SG/DGF/DAPT/SCBT.Re, 234/16/MEEF/SG/DGF/DSAP/SCB.Re, 72/17/MEEF/SG/DGF/DSAP/SCB.Re, 250/17/MEEF/SG/DGF/DSAP/SCB.Re). All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by M. A. van Noordwijk
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Rudolph, K., Fichtel, C., Schneider, D. et al. One size fits all? Relationships among group size, health, and ecology indicate a lack of an optimal group size in a wild lemur population. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 73, 132 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-019-2746-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-019-2746-0