Abstract
Purpose
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) has demonstrated excellent results in elderly patients, however, the indications, outcomes, and long-term results in adolescent patients are less understood. This study aims to assess the outcomes of THA in patients under 21, providing insights for clinical decision-making in this exceptional population.
Methods
A systematic review in PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Embase database was performed. We included studies reporting clinical, radiological, and functional outcomes of THA in patients younger than 21 years, for any cause, with a with a minimum follow-up of one year. The ten year survivorship estimate was pooled using a meta-analysis methodology and each study was weighted according to its standard error, calculated from published confidence intervals.
Results
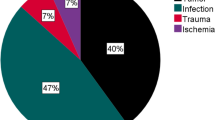
We included 25 studies involving 1166 hips. Median age was 17 years old, 60% were females, and the average follow-up was 8.1 years. Juvenile inflammatory arthritis was the main indication for total hip arthroplasty (THA). The all-cause revision rate was 14.4% and aseptic loosening was the most common cause. Only eight studies reported ten year survival rates and form the pooled analysis an 84.91% survival rate (95% CI 70.56 – 99.27) was obtained. An average score of 88.08 in the Harris Hip Score (HHS) was observed. We found a 3.43% complication rate.
Conclusions
Hip arthroplasty is an acceptable option for adolescents with end-stage arthritis. However, the altered hip anatomy, the elevated revision rate, and the long-term implant survival must be considered before performing a THA in adolescent patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials. Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the authors.
References
Sedrakyan A, Romero L, Graves S, Davidson D, de Steiger R, Lewis P et al (2014) Survivorship of hip and knee implants in pediatric and young adult populations: analysis of registry and published data. J Bone Joint Surg A 96:73–78. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.N.00541
Metcalfe D, Peterson N, Wilkinson JM, Perry DC (2018) Temporal trends and survivorship of total hip arthroplasty in very young patients: a study using the National Joint Registry data set. Bone Joint J 100-B:1320–9. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.100B10.BJJ-2017-1441.R2
Novais EN (2021) Treatment options for end-stage hip disease in adolescents: to replace, fuse, or reconstruct? J Pediatr Orthop 41(Suppl 1):S47–S52. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000001780
Bayliss LE, Culliford D, Monk AP, Glyn-Jones S, Prieto-Alhambra D, Judge A et al (2017) The effect of patient age at intervention on risk of implant revision after total replacement of the hip or knee: a population-based cohort study. The Lancet 389:1424–1430. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30059-4
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M et al (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ 349:g7647–g7647. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647
Roach JW, Paradies LH (1984) Total hip arthroplasty performed during adolescence. J Pediatr Orthop 4:418–421. https://doi.org/10.1097/01241398-198408000-00005
Ruddlesdin C, Ansell B, Arden G, Swann M (1986) Total hip replacement in children with juvenile chronic arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 68-B:218–22. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.68B2.3958006
Maric Z, Haynes RJ (1993) Total hip arthroplasty in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 290:197–9
Daurka JS, Malik AK, Robin DA, Witt JD (2012) The results of uncemented total hip replacement in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis at ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 94-B:1618–24. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.94B12.29124
Rainer W, Shirley MB, Trousdale RT, Shaughnessy WJ (2021) The Open triradiate cartilage: how young is too young for total hip arthroplasty? J Pediatr Orthop 41(9):e793–e799. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000001940
Singsen BH, Isaacson AS, Bernstein BH, Patzakis MJ, Kornreich HK, King KK et al (1978) Total hip replacement in children with arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 21:401–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780210401
Torchia ME, Klassen RA, Bianco AJ (1996) Total hip arthroplasty with cement in patients less than twenty years old. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78(7):995–1003. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-199607000-00003
Wroblewski BM, Purbach B, Siney PD, Fleming PA (2010) Charnley low-friction arthroplasty in teenage patients: the ultimate challenge. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92-B:486–8. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.92B4.23477
Restrepo C, Lettich T, Roberts N, Parvizi J, Hozack WJ (2008) Uncemented total hip arthroplasty in patients less than twenty-years. Acta Orthop Belg 74(5):615–622
D’Ambrosi R, Marciandi L, Frediani PV, Facchini RM (2016) Uncemented total hip arthroplasty in patients younger than 20 years. J Orthop Sci 21:500–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2016.03.009
Van de Velde SK, Loh B, Donnan L (2017) Total hip arthroplasty in patients 16 years of age or younger. J Child Orthop 11:428–433. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.11.170085
Buddhdev PK, Vanhegan IS, Khan T, Hashemi-Nejad A (2020) Early to medium-term outcomes of uncemented ceramic-bearing total hip arthroplasty in teenagers for paediatric hip conditions. Bone Joint J 102-B:1491–6. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.102B11.BJJ-2020-0668.R1
Luceri F, Morelli I, Sinicato CM, Della Grazia A, Verdoni F, Maffulli N et al (2020) Medium-term outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in juvenile patients. J Orthop Surg Res 15:476. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01990-2
Trisolino G, Stallone S, Castagnini F, Bordini B, Cosentino M, Lucchini S et al (2021) Cementless Ceramic-on-ceramic total hip replacement in children and adolescents. Children 8:858. https://doi.org/10.3390/children8100858
Chapot A, Zambelli P-Y, Merckaert SR (2023) Functional and patient-related outcomes of total hip arthroplasty in patients younger than 20 years. Arthroplasty Today 20:101100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artd.2023.101100
Finkbone PR, Severson EP, Cabanela ME, Trousdale RT (2012) Ceramic-on-ceramic total hip arthroplasty in patients younger than 20 years. J Arthroplasty 27:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.05.022
Hannouche D, Devriese F, Delambre J, Zadegan F, Tourabaly I, Sedel L et al (2016) Ceramic-on-ceramic THA implants in patients younger than 20 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res 474:520–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4546-9
Bessette BJ, Fassier F, Tanzer M, Brooks CE (2003) Total hip arthroplasty in patients younger than 21 years: a minimum 10-year follow-up. Can J Surg 46(4):257–262
Tsukanaka M, Halvorsen V, Nordsletten L, EngesæTer IØ et al (2016) Implant survival and radiographic outcome of total hip replacement in patients less than 20 years old. Acta Orthop 87:479–484. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453674.2016.1212180
Pallante GD, Statz JM, Milbrandt TA, Trousdale RT (2020) Primary total hip arthroplasty in patients 20 years old and younger. J Bone Joint Surg Am 102:519–525. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.19.00699
Bose VC, Kalaivanan K, Manohar M, Kumar A, Patil S, Suryanarayan P (2021) Is the revision rate higher after hip arthroplasty in teenage patients? a prospective study with long-term follow-up of more than 10 years. Indian J Orthop 55:993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-021-00370-0
Kamath AF, Sheth NP, Hosalkar HH, Babatunde OM, Lee G-C, Nelson CL (2012) Modern total hip arthroplasty in patients younger than 21 years. J Arthroplasty 27:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.04.042
Patel NK, Luff T, Whittingham-Jones P, Gooding CR, Hashemi-Nejad A (2012) Total hip arthroplasty in teenagers: an alternative to hip arthrodesis. HIP Int 22:621–627. https://doi.org/10.5301/HIP.2012.10352
Fernandez-Fernandez R, Moraleda-Novo L, De Armas JN, Cruz-Pardos A (2022) Outcome measures and survivorship following total hip arthroplasty in adolescent population. Int Orthop 46:2785–2791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05536-5
Ringold S, Angeles-Han ST, Beukelman T, Lovell D, Cuello CA, Becker ML et al (2019) 2019 American college of rheumatology/arthritis foundation guideline for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: therapeutic approaches for non-systemic polyarthritis, sacroiliitis, and enthesitis. Arthritis Care Res 71:717–734. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.23870
Engesæter IØ, Lie SA, Lehmann TG et al (2008) Neonatal hip instability and risk of total hip replacement in young adulthood. Acta Orthop 79:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453670710015201
Kuitunen I, Uimonen MM, Haapanen M et al (2022) Incidence of neonatal developmental dysplasia of the hip and late detection rates based on screening strategy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 5:e2227638. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.27638
Crnogaca K, Sulje Z, Delimar D (2022) Previous corrective osteotomies of femur and pelvis are a risk factor for complications following total hip arthroplasty in hip dysplasia. J Orthop 33:100–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2022.07.008
Yacovelli S, Abdelaal M, Fillingham Y, Sutton R, Madding R, Parvizi J (2021) Prior pelvic osteotomy affects the outcome of subsequent total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 36:600–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2020.07.080
Shapira J, Annin S, Rosinsky PJ, Maldonado DR, Lall AC, Domb BG (2021) Total hip arthroplasty after pelvic osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia: A systematic review. J Orthop 25:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jor.2021.04.001
Halvorsen V, Fenstad AM, Engesæter LB, Nordsletten L, Overgaard S, Pedersen AB et al (2019) Outcome of 881 total hip arthroplasties in 747 patients 21 years or younger: data from the Nordic Arthroplasty Register Association (NARA) 1995–2016. Acta Orthop 90:331–337. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453674.2019.1615263
Deere K, Whitehouse MR, Kunutsor SK, Sayers A, Mason J, Blom AW (2022) How long do revised and multiply revised hip replacements last? A retrospective observational study of the National Joint Registry. Lancet Rheumatol 4:e468–e479. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(22)00097-2
Stambough JB, Pashos G, Bohnenkamp FC, Maloney WJ, Martell JM, Clohisy JC (2016) Long- term results of total hip arthroplasty with 28-millimeter cobalt-chromium femoral heads on highly cross-linked polyethylene in patients 50 years and less. J Arthroplasty 31:162–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2015.07.025
Prock-Gibbs H, Pumilia CA, Meckmongkol T, Lovejoy J, Mumith A, Coathup M (2021) Incidence of osteolysis and aseptic loosening following metal-on-highly cross-linked polyethylene hip arthroplasty: a systematic review of studies with up to 15-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 103:728–740. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.20.01086
Cash DJW, Khanduja V (2014) The case for ceramic-on-polyethylene as the preferred bearing for a young adult hip replacement. Hip Int 24:421–427. https://doi.org/10.5301/hipint.5000138
Wamper KE, Sierevelt IN, Poolman RW, Bhandari M, Haverkamp D (2010) The Harris hip score: Do ceiling effects limit its usefulness in orthopedics?: A systematic review. Acta Orthop 81:703–707. https://doi.org/10.3109/17453674.2010.537808
Kahlenberg CA, Garvey MD, Blevins JL, Sculco TP, Sculco PK, Figgie MP (2021) High satisfaction and activity levels after total hip arthroplasty in patients under age 21. J Arthroplasty 36:3485–3489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2021.05.020
Funding
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Elina Huerfano, Maria Bautista and Manuel Huerfano. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Elina Huerfano and Maria Bautista and Juan M. Nossa all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study is a meta-analysis that integrates data from previously published research, without direct involvement or interaction with human or animal subjects. In accordance with the guidelines and standards for meta-analyses, this type of study does not require ethical approval.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huerfano, E., Bautista, M., Huerfano, M. et al. Total hip arthroplasty in adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-024-06175-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-024-06175-8