Abstract
Purpose
Cross-linked polyethylene (PE) has been used with great clinical success in total hip arthroplasty (THA) since its debut in the late 1990’s. However, reports regarding this bearing couple near the end of its second decade of service are still scant. The aim of this study was to first determine the long term clinical and radiological results and second Investigate what factors affect wear rates using a metal-on-crosslinked PE bearing articulation.
Methods
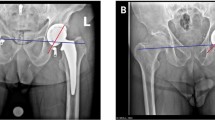
55 THAs using a single brand of cross-linked liner, cementless cup and 28 mm hip ball were performed in 44 patients. Age, sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) and need for revision surgery were recorded. Linear and volumetric wear was determined using the Martell method.
Results
Mean age at operation was 51.2 (29–73 ± 12.1) years. Mean duration of follow-up was 16.9 years (range 15.0–20.1 ± 1.1 years). Osteolysis was not present in the latest follow-up radiographs.
Median linear and volumetric wear rate was 0.038 mm/year (95% CI 0.032–0.047) and 7.115mm3/year (95% CI 6.92–17.25) respectively. Acetabular component position was not found to be related to both linear and volumetric wear. No significant difference was found in the linear and volumetric wear rates of thinner and thicker liners (8 mm or below and > 8 mm) (p = 0.849 and p = 0.64 respectively).
Conclusion
Metal-on-crosslinked PE is associated with low linear and volumetric wear rates which has virtually obviated osteolysis and has translated to excellent survivorship even at long term follow up. In-vivo oxidation does not appear to be of clinical concern at this point.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Research data is not available publicly to protect patient privacy.
Code availability
N/A
References
Maloney WJ, Galante JO, Anderson M, Goldberg V, Harris WH, Jacobs J, Kraay M, Lachiewicz P, Rubash HE, Schutzer S, Woolson ST (1999) Fixation, polyethylene wear, and pelvic osteolysis in primary total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 369:157–64. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-199912000-00016
Oparaugo PC, Clarke IC, Malchau H, Herberts P (2001) Correlation of wear debris-induced osteolysis and revision with volumetric wear-rates of polyethylene: A survey of 8 reports in the literature. Acta Orthop Scand 72:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/000164701753606644
Broomfield JA, Malak TT, Thomas GE, Palmer AJ, Taylor A, Glyn-Jones S (2017) The Relationship Between Polyethylene Wear and Periprosthetic Osteolysis in Total Hip Arthroplasty at 12 Years in a Randomized Controlled Trial Cohort. J Arthroplasty 32:1186–1191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2016.10.037
Kurtz S, Manley M (2009) CHAPTER 61 - Cross-Linked Polyethylene. In: Hozack WJ, Parvizi J, Bender B (eds) Surgical Treatment of Hip Arthritis. Saunders, Philadelphia, W.B., pp 456–467
Shia DS, Clohisy JC, Schinsky MF, Martell JM, Maloney WJ (2009) THA with highly cross-linked polyethylene in patients 50 years or younger. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:2059–2065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0697-2
Cheung A, Yan CH, Fu H, Cheung MH, Chan PK, Chiu KY (2019) Ten- to Sixteen-Year Follow-Up of Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Total Hip Arthroplasty: What Factors Affect Wear? J Arthroplasty 34:2016–2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.04.041
Hopper RH Jr, Ho H, Sritulanondha S, Williams AC, Engh CA Jr (2018) Otto Aufranc Award: Crosslinking Reduces THA Wear, Osteolysis, and Revision Rates at 15-year Followup Compared With Noncrosslinked Polyethylene. Clin Orthop Relat Res 476:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999.0000000000000036
Moon NH, Shin WC, Do MU, Kang SW, Lee SM, Suh KT (2021) Wear and osteolysis outcomes for highly cross-linked polyethylene in primary total hip arthroplasty compared with conventional polyethylene: a 15- to 18-year single-centre follow-up study. Hip Int 31:526–532. https://doi.org/10.1177/1120700019896970
Rames RD, Stambough JB, Pashos GE, Maloney WJ, Martell JM, Clohisy JC (2019) Fifteen-Year Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cobalt-Chromium Femoral Heads on Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Patients 50 Years and Less. J Arthroplasty 34:1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.01.071
Roedel GG, Kildow BJ, Sveom DS, Garvin KL (2021) Total hip arthroplasty using highly cross-linked polyethylene in patients aged 50 years and younger : minimum 15-year follow-up. Bone Joint J 103-b:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.103b7.Bjj-2020-2443.R1
Bryan AJ, Calkins TE, Karas V, Culvern C, Nam D, Della Valle CJ (2019) Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients Less Than 50 Years of Age at a Mean of 16 Years: Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene Significantly Reduces the Risk of Revision. J Arthroplasty 34:S238-s241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.02.025
Shin WC, Moon NH, Jeon SB, Suh KT (2020) Comparison of Surgical Outcomes Between Standard and Elevated-Rim Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene Acetabular Liners in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty With Minimum 15-Year Follow-Up: Single-Center, Retrospective Cohort Study. J Arthroplasty 35:1290–1296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2019.12.026
Kurtz SM UHMWPE Biomaterials Handbook - Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene in Total Joint Replacement and Medical Devices (3rd Edition). In. Elsevier
Dumbleton JH, D’Antonio JA, Manley MT, Capello WN, Wang A (2006) The basis for a second-generation highly cross-linked UHMWPE. Clin Orthop Relat Res 453:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.blo.0000238856.61862.7d
Akagi M, Asano T, Clarke IC, Niiyama N, Kyomoto M, Nakamura T, Hamanishi C (2006) Wear and toughness of crosslinked polyethylene for total knee replacements: a study using a simulator and small-punch testing. J Orthop Res 24:2021–2027. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.20223
Currier BH, Currier JH, Mayor MB, Lyford KA, Collier JP, Van Citters DW (2007) Evaluation of oxidation and fatigue damage of retrieved crossfire polyethylene acetabular cups. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:2023–2029. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.F.00336
Gallo J, Havranek V, Zapletalova J (2010) Risk factors for accelerated polyethylene wear and osteolysis in ABG I total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 34:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0731-3
Patil S, Bergula A, Chen PC, Colwell CW, Jr., D'Lima DD (2003) Polyethylene wear and acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A Suppl 4:56–63. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200300004-00007
Wan Z, Boutary M, Dorr LD (2008) The influence of acetabular component position on wear in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 23:51–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2007.06.008
Goyal P, Howard JL, Yuan X, Teeter MG, Lanting BA (2017) Effect of Acetabular Position on Polyethylene Liner Wear Measured Using Simultaneous Biplanar Acquisition. J Arthroplasty 32:1670–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2016.11.057
Teeter MG, Goyal P, Yuan X, Howard JL, Lanting BA (2018) Change in Acetabular Cup Orientation From Supine to Standing Position and Its Effect on Wear of Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene. J Arthroplasty 33:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.08.016
Haw JG, Battenberg AK, Huang DT, Schmalzried TP (2017) Wear Rates of Larger-Diameter Cross-Linked Polyethylene at 5 to 13 Years: Does Liner Thickness or Component Position Matter? J Arthroplasty 32:1381–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2016.11.022
Chua W, Roy S, Sng J, Liang S, De SD (2014) Total hip replacement using a highly crosslinked polyethylene liner in Asians with small acetabulum. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 22:342–346. https://doi.org/10.1177/230949901402200315
Lee JH, Lee BW, Lee BJ, Kim SY (2011) Midterm results of primary total hip arthroplasty using highly cross-linked polyethylene: minimum 7-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty 26:1014–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.03.015
Kim MY, Chung YY, Park JH, Lee JH (2015) Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner. Hip Pelvis 27:216–222. https://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.216
Baghdadi J, Alkhateeb S, Roth A, Jäger M (2023) Cup positioning and its effect on polyethylene wear of vitamin E- and non-vitamin E-supplemented liners in total hip arthroplasty: radiographic outcome at 5-year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 143:1679–1688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04424-2
Nielson T, Owens G, Miller B, Meneghini E, Deckard ER, Meneghini RM (2022) Large Femoral Heads in Total Hip Arthroplasty With Vitamin E Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene: Head Penetration Rates Compared to Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene. J Arthroplasty 37:S685-s691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2022.01.075
Bartel DL, Bicknell VL, Wright TM (1986) The effect of conformity, thickness, and material on stresses in ultra-high molecular weight components for total joint replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 68:1041–1051
Devane PA, Horne JG, Ashmore A, Mutimer J, Kim W, Stanley J (2017) Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene Reduces Wear and Revision Rates in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A 10-Year Double-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 99:1703–1714. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.16.00878
Fransen BL, Bengoa FJ, Neufeld ME, Sheridan GA, Garbuz DS, Howard LC (2023) Thin highly cross-linked polyethylene liners combined with large femoral heads in primary total hip arthroplasty show excellent survival and low wear rates at a mean follow-up of 12.8 years. Bone Joint J 105-b:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.105b1.Bjj-2022-0812.R1
Baker CE, Bukowski BR, Abdel MP, Trousdale RT (2021) The Lawrence D. Dorr Surgical Techniques & Technologies Award: Using Big Heads and Small Acetabular Components With Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Total Hip Arthroplasty: Is It Safe? J Arthroplasty 36:S11-s17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2021.01.067
Lachiewicz PF, Soileau ES, Martell JM (2016) Wear and Osteolysis of Highly Crosslinked Polyethylene at 10 to 14 Years: The Effect of Femoral Head Size. Clin Orthop Relat Res 474:365–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4319-5
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Dr. Thomas Tang and Mr. Lison Fung for their assistance in data collection.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Amy Cheung. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Amy Cheung and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study has been approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong / Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster (UW 21–745).
Consent for publication
Consent for publication from participants was not needed owing to the retrospective nature of this study and this has been approved by the local Institutional Review Board.
Informed consent
Informed consent from participants was not needed owing to the retrospective nature of this study and this has been approved by the local Institutional Review Board.
Conflict of interest
Dr. PK Chan is a paid speaker for Stryker, Depuy Johnson and Johnson, Zimmer Biomet and Smith and Nephew.
Dr. Fu is a paid speaker for Stryker, Depuy Johnson and Johnson, Zimmer Biomet and Smith and Nephew. He also receives research support from Smith and Nephew as a principal investigator.
Dr. MH Cheung is a paid consultant for Zimmer Biomet.
Professor Chiu is a paid consultant for Depuy Johnson and Johnson, Smith and Nephew, Stryker Mako and Zimmer Biomet.
Dr. A Cheung, VWK Chan and MH Luk have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheung, A., Chan, P.K., Fu, H. et al. Metal-on-crosslinked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty – an excellent combination at fifteen to twenty years of follow-up. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 2547–2552 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05844-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05844-4