Abstract
Background
Given the contrapositive link between the posterior tibial plateau and the femoral condyle and the similar injury cause, the fracture type should be the same as the well-known Hoffa fracture of the femoral condyle. This study aims to report a case series with Hoffa-like tibial plateau fractures to improve understanding.
Methods
We analysed six consecutive patients presented with Hoffa-like tibial plateau fractures in our hospital between October 2014 and December 2020, a period in which 1924 tibial plateau fractures were treated. Patients’ data on demographics, radiographs, surgical therapy, and assessment at a 12-month follow-up were retrieved.
Results
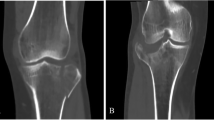
The incidence of Hoffa-like tibial plateau fractures was 0.31% (6/1924). This study included three men and three women, with a mean age of 45.8 years. The injury mechanism was either a fall from a great height or a vehicle accident. On average, 7.5 days after the injury, patients were surgically treated with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) with place/screws via a lateral or posteromedial approach. At 10 to 15 weeks, all instances had osseous union on radiography. At 12-month follow-up, the HSS score of the operated knee ranged from 93 to 98 points (mean: 94.8), and Rasmussen radiograph score was from 15 to 18 (mean: 15.8). There were no intra-operative or post-operative problems.
Conclusion
This Hoffa-like fracture of the tibial plateau is a rare condition; however, it can occur. Orthopaedic surgeons should pay attention to this neglected but actually familiar fracture type.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data will be available upon motivated request to the corresponding author of the present paper.
References
Zhang Y (2016) Clinical epidemiology of orthopaedic trauma Second Edition. THIEME, Stuttgart, New York, Delhi, Rio
Gavaskar AS, Tummala NC, Krishnamurthy M (2011) Operative management of Hoffa fractures–a prospective review of 18 patients. Injury 42(12):1495–1498
Zhou Y, Pan Y, Wang Q, Hou Z, Chen W (2019) Hoffa fracture of the femoral condyle: injury mechanism, classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(8):e14633
Bartoníček J, Rammelt S (2015) History of femoral head fracture and coronal fracture of the femoral condyles. Int Orthop 39(6):1245–1250
Arastu MH, Kokke MC, Duffy PJ, Korley RE, Buckley RE (2013) Coronal plane partial articular fractures of the distal femoral condyle: current concepts in management. Bone Joint J 95-b(9):1165–71
White EA, Matcuk GR, Schein A, Skalski M, Marecek GS, Forrester DM, Patel DB (2015) Coronal plane fracture of the femoral condyles: anatomy, injury patterns, and approach to management of the Hoffa fragment. Skeletal Radiol 44(1):37–43
Nork SE, Segina DN, Aflatoon K, Barei DP, Henley MB, Holt S, Benirschke SK (2005) The association between supracondylar-intercondylar distal femoral fractures and coronal plane fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(3):564–569
Kumar P, Agarwal S, Kumar D, Rajnish RK, Jindal K (2019) Rim plating for a rare variant of posteromedial tibial condyle fracture; partial coronal split, akin to Hoffa’s fracture, associated with multi-ligament injuries and central depression. Trauma Case Rep 20:100174
Chang SM, Zheng HP, Li HF, Jia YW, Huang YG, Wang X, Yu GR (2009) Treatment of isolated posterior coronal fracture of the lateral tibial plateau through posterolateral approach for direct exposure and buttress plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129(7):955–962
Postel M, Mazas F, de la Caffinière JY (1974) Posterior fracture-separation of the tibial plateaux. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 60(Suppl 2 (0)):317–23
Zhu Y, Chen W, Ding K, Wang H, Li JY, Yu TB, Li Q, Wang T, Zheng Z, Hou Z, Zhang Y (2020) A study on injury Mechanism of tibial plateau Hoffa fracture. Chin J Orthop Trauma 22(10):897–890
Chen W, Zhu Y, Li J, Yu T, Li Q, Wang T, Zheng Z, Hou Z, Zhang Y (2020) Preliminary study on injury characteristics and classification of tibial plateau Hoffa fracture. Chin J Trauma 36(9):827–830
Moore TM (1981) Fracture–dislocation of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 156:128–140
Martínez-Rondanelli A, Escobar-González SS, Henao-Alzate A, Martínez-Cano JP (2017) Reliability of a four-column classification for tibial plateau fractures. Int Orthop 41(9):1881–1886
Chan KK, Resnick D, Goodwin D, Seeger LL (1999) Posteromedial tibial plateau injury including avulsion fracture of the semimembranous tendon insertion site: ancillary sign of anterior cruciate ligament tear at MR imaging. Radiology 211(3):754–758
Caggiari G, Ciurlia E, Ortu S, Sirianni R, Bonini L, Pisanu F, Doria C, Manca M (2020) Osteochondral avulsion fracture of the posteromedial tibial plateau. Trauma Case Rep 25:100281
John R, Chouhan DK, Dhillon MS (2018) Neglected, semimembranosus osteochondral avulsion fracture of the posteromedial tibial plateau. Trauma Case Rep 15:16–22
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to J. Z. and H. M. of the Department of Orthopaedics for their kind assistance.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 82102551).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. Zhang conceived the idea and designed the study. Y. Zhu. J. L, and W. C. retrieved the data. K. Z. and J. Z. prepared the figures and tables. All authors contributed to the preparation of the manuscript. Y. Zhu and J. L. wrote the manuscript and contributed equally.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University (No. G2021-024–1).
Consent to participate
Informed consent to participate in this study was obtained from each included patient.
Consent for publication
Informed consent to publish the relevant data was obtained from each included patient.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Li, J., Zhao, K. et al. The Hoffa-like fracture of the tibial plateau: a clinical study. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 46, 1387–1393 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05345-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05345-w