Abstract
Background
Coronal malalignment of the lower extremity is closely related to the onset and progression of osteoarthritis. Restoring satisfactory alignment after tibial osteotomy improves the long-term success of this conservative surgery. The purpose of our study was to determine (1) if there is a difference between two-dimensional (2D) and 3D measurements of the hip-knee-ankle (HKA) angle between the mechanical axes of the femur and the tibia, (2) which parameter most affects 2D–3D HKA measurement, and (3) the percentage of patients who are at risk of error in HKA measurement.
Methods
We reviewed imaging studies of the consecutive patients referred to us for hip or knee pain between June and October 2013. Patients with previous pelvis or lower extremity surgery were excluded.
Results
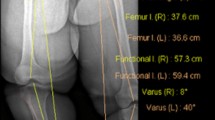
In 51 % (95/186) of lower extremities examined, the 3D method showed more valgus than the 2D method, and in 49 % (91/186), the 3D method showed more varus. In 12 % of extremities (23/186), the knee varus or valgus alignment was completely opposite in 3D images compared to 2D images. Having more than 7° of flexum/recurvatum alignment increased error in 2D HKA measurement by 5.7°. This was calculated to be 0.15° per 1° increase in femoral torsion and 0.05° per 1° increase in tibial torsion. Approximately 20 % of patients might be at risk of error in HKA angle measurement in 2D imaging studies.
Conclusions
Orthopaedic surgeons should assess lower extremity alignment in standing position, with enough exposure of the extremity to find severe alignment or rotational deformities, and consider advanced 3D images of those patients who have them. Otherwise, HKA angle can be measured with good accuracy with 2D techniques.
Level of Evidence
Level-III diagnostic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brouwer GM, van Tol AW, Bergink AP, Belo JN, Bernsen RM, Reijman M, Pols HA, Bierma-Zeinstra SM (2007) Association between valgus and varus alignment and the development and progression of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum 56:1204–1211. doi:10.1002/art.22515
Cerejo R, Dunlop DD, Cahue S, Channin D, Song J, Sharma L (2002) The influence of alignment on risk of knee osteoarthritis progression according to baseline stage of disease. Arthritis Rheum 46:2632–2636. doi:10.1002/art.10530
Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, Cahue S, Shamiyeh E, Dunlop DD (2001) The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA 286:188–195
Mullaji AB, Padmanabhan V, Jindal G (2005) Total knee arthroplasty for profound varus deformity: technique and radiological results in 173 knees with varus of more than 20 degrees. J Arthroplasty 20:550–561. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2005.04.009
Suero EM, Sabbagh Y, Westphal R, Hawi N, Citak M, Wahl FM, Krettek C, Liodakis E (2015) Effect of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy on intraarticular knee and ankle contact pressures. J Orthop Res 33:598–604. doi:10.1002/jor.22793
Williot A, Rosset P, Favard L, Brilhault J, Burdin P (2010) Total knee arthroplasty in valgus knee. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 96:S37–S42. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2010.03.009
Gaillard R, Cerciello S, Lustig S, Servien E, Neyret P (2016) Risk factors for tibial implant malpositioning in total knee arthrosplasty-consecutive series of one thousand, four hundred and seventeen cases. Int Orthop. doi:10.1007/s00264-016-3307-z
Jenny JY, Tavan A, Jenny G, Kehr P (1998) Long-term survival rate of tibial osteotomies for valgus gonarthrosis. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 84:350–357
Longstaff LM, Sloan K, Stamp N, Scaddan M, Beaver R (2009) Good alignment after total knee arthroplasty leads to faster rehabilitation and better function. J Arthroplasty 24:570–578. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2008.03.002
Matsuda S, Kawahara S, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Iwamoto Y (2013) Postoperative alignment and ROM affect patient satisfaction after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:127–133. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2533-y
Sorrells RB, Murphy JA, Sheridan KC, Wasielewski RC (2007) The effect of varus and valgus deformity on results of cementless mobile bearing TKA. Knee 14:284–288. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.004
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD (2009) Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 24:560–569. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2008.02.018
Fang D, Ritter MA (2009) Malalignment: forewarned is forearmed. Orthopedics 32(9). doi: 10.3928/01477447-20090728-29.
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 24:39–43. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.04.034
Gromov K, Korchi M, Thomsen MG, Husted H, Troelsen A (2014) What is the optimal alignment of the tibial and femoral components in knee arthroplasty? Acta Orthop 85:480–487. doi:10.3109/17453674.2014.940573
Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS, Park SD (2014) The relationship between the survival of total knee arthroplasty and postoperative coronal, sagittal and rotational alignment of knee prosthesis. Int Orthop 38:379–385. doi:10.1007/s00264-013-2097-9
Lustig S, Scholes CJ, Stegeman TJ, Oussedik S, Coolican MR, Parker DA (2012) Sagittal placement of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty predicts knee flexion contracture at one-year follow-up. Int Orthop 36:1835–1839. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1580-z
Sailer J, Scharitzer M, Peloschek P, Giurea A, Imhof H, Grampp S (2005) Quantification of axial alignment of the lower extremity on conventional and digital total leg radiographs. Eur Radiol 15:170–173. doi:10.1007/s00330-004-2436-8
Radtke K, Becher C, Noll Y, Ostermeier S (2010) Effect of limb rotation on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:451–457. doi:10.1007/s00402-009-0999-1
Thelen P, Delin C, Folinais D, Radier C (2012) Evaluation of a new low-dose biplanar system to assess lower-limb alignment in 3D: a phantom study. Skelet Radiol 41:1287–1293. doi:10.1007/s00256-012-1438-x
Meijer MF, Boerboom AL, Stevens M, Bulstra SK, Reininga IH (2014) Assessment of prosthesis alignment after revision total knee arthroplasty using EOS 2D and 3D imaging: a reliability study. PLoS ONE 9, e104613. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104613
Chaibi Y, Cresson T, Aubert B, Hausselle J, Neyret P, Hauger O, de Guise JA, Skalli W (2012) Fast 3D reconstruction of the lower limb using a parametric model and statistical inferences and clinical measurements calculation from biplanar X-rays. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 15:457–466. doi:10.1080/10255842.2010.540758
Than P, Szuper K, Somoskeoy S, Warta V, Illes T (2012) Geometrical values of the normal and arthritic hip and knee detected with the EOS imaging system. Int Orthop 36:1291–1297. doi:10.1007/s00264-011-1403-7
Cooke TD, Sled EA, Scudamore RA (2007) Frontal plane knee alignment: a call for standardized measurement. J Rheumatol 34:1796–1801
Guenoun B, Zadegan F, Aim F, Hannouche D, Nizard R (2012) Reliability of a new method for lower-extremity measurements based on stereoradiographic three-dimensional reconstruction. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 98:506–513. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2012.03.014
Quijano S, Serrurier A, Aubert B, Laporte S, Thoreux P, Skalli W (2013) Three-dimensional reconstruction of the lower limb from biplanar calibrated radiographs. Med Eng Phys 35:1703–1712. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2013.07.002
Kanungo T, Mount DM, Netanyahu NS, Piako CD, Silverman R, Wu A (2000) The analysis of a simple k-means clustering algorithm. In: ACM Symposium on Computational Geometry, 2000. ACM Press, pp 100–109
Swanson KE, Stocks GW, Warren PD, Hazel MR, Janssen HF (2000) Does axial limb rotation affect the alignment measurements in deformed limbs? Clin Orthop Relat Res 246–252
Zampogna B, Vasta S, Amendola A, Uribe-Echevarria Marbach B, Gao Y, Papalia R, Denaro V (2015) Assessing lower limb alignment: comparison of standard knee xray vs long leg view. Iowa Orthop J 35:49–54
Obeid I, Hauger O, Aunoble S, Bourghli A, Pellet N, Vital JM (2011) Global analysis of sagittal spinal alignment in major deformities: correlation between lack of lumbar lordosis and flexion of the knee. Eur Spine J 20(Suppl 5):681–685. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1936-x
Sugama R, Minoda Y, Kobayashi A, Iwaki H, Ikebuchi M, Hashimoto Y, Takaoka K, Nakamura H (2011) Sagittal alignment of the lower extremity while standing in female. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:74–79. doi:10.1007/s00167-010-1137-x
Brouwer RW, Jakma TS, Brouwer KH, Verhaar JA (2007) Pitfalls in determining knee alignment: a radiographic cadaver study. J Knee Surg 20:210–215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
There is no funding source.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazennec, J.Y., Chometon, Q., Folinais, D. et al. Are advanced three-dimensional imaging studies always needed to measure the coronal knee alignment of the lower extremity?. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 41, 917–924 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3340-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3340-y