Abstract
Purpose
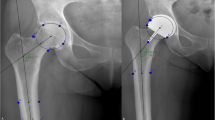
The positioning of the femoral cup in hip resurfacing is essential for the survival of the implant. We described a technique in 2005 to position the femoral cup guided by fluoroscopy independent of the approach performed. The main objectives were to study the positioning of the femoral components of the implant and the accuracy of the technique.
Methods
Between 2003 and 2011 we conducted a prospective study of 160 consecutive hip resurfacings all operated with this fluoroscopic-guided technique. Three independent observers performed a radiographic analysis at the pre-operative planning stage and on postoperative radiographs using OsiriX software. The statistical analysis was based on comparison of two groups by Student’s t test.
Results
The entire implant was positioned in valgus, with an average of 7.816° valgus (p <0.001). All implants were positioned in neutral or anteverted with a mean of 1.98° (p <0.001). The risk of malpositioning on the antero-posterior plane was less than 1.41° with p <0.019. The risk of profile positioning error was lower than 0.80° with p <0.047.
Conclusion
This study validates a technique of femoral implant positioning for resurfacing. It is simple, precise and independent of the approach performed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Haan R, Campbell PA, Su EP, De Smet KA (2008) Revision of metal-on-metal resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip: the influence of malpositioning of the components. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(9):1158–1163
Kim PR, Beaulé PE, Laflamme GY, Dunbar M (2008) Causes of early failure in a multicenter clinical trial of hip resurfacing. J Arthroplast 23(6 Suppl 1):44–49
Pailhé R, Sharma A, Reina N, Cavaignac E, Chiron P, Laffosse J-M (2012) Hip resurfacing: a systematic review of literature. Int Orthop 36(12):2399–2410
Chiron P (2005) Use of a guide wire in hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Osteologie 14(suppl 2):65–67
Cavaignac E, Chiron P, Espié A, Reina N, Lepage B, Laffosse J-M (2012) Experimental study of an original radiographic view for diagnosis of cam-type anterior femoroacetabular impingement. Int Orthop 36(9):1783–1788
Rosset A, Spadola L, Ratib O (2004) OsiriX: an open-source software for navigating in multidimensional DICOM images. J Digit Imaging 17(3):205–216
Tannast M, Zheng G, Anderegg C, Burckhardt K, Langlotz F, Ganz R, Siebenrock KA (2005) Tilt and rotation correction of acetabular version on pelvic radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res 438:182–190
Sayed-Noor ASA, Hugo AA, Sjödén GOG, Wretenberg PP (2009) Leg length discrepancy in total hip arthroplasty: comparison of two methods of measurement. CORD Conf Proc 33(5):1189–1193
Royston P (1991) Estimating departure from normality. Stat Med 10(8):1283–1293
Won S, Morris N, Lu Q, Elston RC (2009) Choosing an optimal method to combine P-values. Stat Med 28(11):1537–1553
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174
Hurst JM, Millett PJ (2010) A simple and reliable technique for placing the femoral neck guide pin in hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 25(5):832–834
Olsen M, Gamble P, Chiu M, Tumia N, Boyle RA, Schemitsch EH (2010) Assessment of accuracy and reliability in preoperative templating for hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 25(3):445–449
Beaulé PE, Lee JL, Le Duff MJ, Amstutz HC, Ebramzadeh E (2004) Orientation of the femoral component in surface arthroplasty of the hip. A biomechanical and clinical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(9):2015–2021
Richards CJ, Giannitsios D, Huk OL, Zukor DJ, Steffen T, Antoniou J (2008) Risk of periprosthetic femoral neck fracture after hip resurfacing arthroplasty: valgus compared with anatomic alignment. A biomechanical and clinical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Supplement 3):96–101
Freeman MA (1978) Some anatomical and mechanical considerations relevant to the surface replacement of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res 134:19–24
Long JP, Bartel DL (2006) Surgical variables affect the mechanics of a hip resurfacing system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 453:115–122
Laffosse JM, Aubin K, Lavigne M, Roy A, Vendittoli PA (2011) Radiographic changes of the femoral neck after total hip resurfacing. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97(3):229–240
Steffen R-T, Foguet PR, Krikler SJ, Gundle R, Beard DJ, Murray DW (2009) Femoral neck fractures after hip resurfacing. J Arthroplast 24(4):614–619
Witjes S, Smolders JMH, Beaulé PE, Pasker P, van Susante JLC (2009) Learning from the learning curve in total hip resurfacing: a radiographic analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129(10):1293–1299
Seyler TM, Lai LP, Sprinkle DI, Ward WG, Jinnah RH (2008) Does computer-assisted surgery improve accuracy and decrease the Learning curve in hip resurfacing? A radiographic analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Supplement 3):71–80
Ganapathi M, Vendittoli P-A, Lavigne M, Günther K-P (2009) Femoral component positioning in hip resurfacing with and without navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(5):1341–1347
Myers GJC, Morgan D, Mcbryde CW, O’Dwyer K (2009) Does surgical approach influence component positioning with Birmingham hip resurfacing? Int Orthop 33(1):59–63
McBryde CW, Revell MP, Thomas AM, Treacy RB, Pynsent PB (2008) The influence of surgical approach on outcome in Birmingham hip resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(4):920–926
Hananouchi T, Nishii T, Lee SB, Ohzono K, Yoshikawa H, Sugano N (2009) The vascular network in the femoral head and neck after hip resurfacing. J Arthroplast 25(1):146–151
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiron, P., Pailhé, R., Reina, N. et al. Radiological validation of a fluoroscopic guided technique for femoral implant positioning during hip resurfacing. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 37, 361–368 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-1777-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-013-1777-9