Abstract
Purpose
We conducted a systematic review of the literature in order to take stock of hip resurfacing according to the principle of “evidence based medicine”. Our main objective was to compare the rate of revision of resurfacing implants with survival limits set by the National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE).
Methods
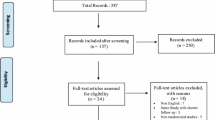
A systematic review was undertaken of all published (Medline, Cochrane, EMBASE) literature research databases up to July 2012 as recommended by the PRISMA statement. Data extraction focused on functional outcomes, complications and survival rates. The survival rates of implants were analysed according to the mean of the series in comparison to the NICE criteria.
Results
Fifty-three studies were identified and included 26,456 cases with an average of 499.17 ± 856.7 (range, 38–5000) cases per study. The median survival was 95.57 % ± 3.7 % (range, 84–100). The percentage of studies which satisfied the criteria set by NICE was 69.8 %. In terms of cumulative revision rates pondered by the number of implants, BHR®, Conserve Plus® and Cormet® showed the best results. The mean postoperative score was 91.2 ± 7.72 (range, 68.3–98.6). There was no statistically significant difference between implants in terms of functional outcomes.
Conclusion
On the basis of the current evidence base, this review of the literature emphasises the importance of certain parameters that can improve the results of resurfacing. The type of implant seems to play an important role as does patient selection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prosser GH, Yates PJ, Wood DJ, Graves SE, de Steiger RN, Miller LN (2010) Outcome of primary resurfacing hip replacement: evaluation of risk factors for early revision. Acta Orthop 81(1):66–71
Delaunay C, Petit I, Learmonth ID, Oger P, Vendittoli PA (2010) Metal-on-metal bearings total hip arthroplasty: the cobalt and chromium ions release concern. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 96(8):894–904
National Institute of Clinical Excellence (2000) Guidance on the selection of prostheses for primary total hip replacement (Technology appraisal guidance). NICE, London
Cullum N, Sheldon T, Watt I, West P, Wright J (2004) Assessment of NICE guidance. Lancet 364(9429):136, author reply 137
Roberts VI, Esler CN, Harper WM (2007) What impact have NICE guidelines had on the trends of hip arthroplasty since their publication? The results from the Trent Regional Arthroplasty Study between 1990 and 2005. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(7):864–867
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Vist GE, Falck-Ytter Y, Schünemann HJ, Group GW (2008) What is “quality of evidence” and why is it important to clinicians? BMJ 336(7651):995–998
Baker RP, Pollard TCB, Eastaugh-Waring SJ, Bannister GC (2011) A medium-term comparison of hybrid hip replacement and Birmingham hip resurfacing in active young patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(2):158–163
Australian Orthopaedic Association (2011) Five-year results of the ASR XL Acetabular System and the ASR Hip Resurfacing System: an analysis from the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. J Bone Joint Surg 93(24):2287–2293
Amstutz HC, Wisk LE, Le Duff MJ (2011) Sex as a patient selection criterion for metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 26(2):198–208
Aulakh TS, Rao C, Kuiper J-H, Richardson JB (2010) Hip resurfacing and osteonecrosis: results from an independent hip resurfacing register. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130(7):841–845
Beaulé PE, Shim P, Banga K (2009) Clinical experience of Ganz surgical dislocation approach for metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. J Arthroplasty 24(6 Suppl):127–131
Bergeron SG, Desy NM, Nikolaou VS, Debiparshad K, Antoniou J (2009) The early results of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing—a prospective study at a minimum two-year follow-up. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 67(2):132–134
Bose VC, Baruah BD (2010) Resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip for avascular necrosis of the femoral head: a minimum follow-up of four years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(7):922–928
Carrothers AD, Gilbert RE, Richardson JB (2011) Birmingham hip resurfacing in patients who are seventy years of age or older. Hip Int 21(2):217–224
Costa CR, Johnson AJ, Naziri Q, Mont MA (2011) Review of total hip resurfacing and total hip arthroplasty in young patients who had Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Orthop Clin North Am 42(3):419–422, viii
Daniel J, Pynsent PB, McMinn DJW (2004) Metal-on-metal resurfacing of the hip in patients under the age of 55 years with osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(2):177–184
Daniel J, Ziaee H, Kamali A, Pradhan C, Band T, McMinn DJW (2010) Ten-year results of a double heat treated metal on metal hip resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(1):20–27
De Smet KA (2005) Belgium experience with metal-on-metal surface arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 36(2):203–213, ix
Valle Della CJ, Nunley RM, Raterman SJ, Barrack RL (2009) Initial American experience with hip resurfacing following FDA approval. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(1):72–78
Delport HP, De Schepper J, Smith EJ, Nichols M, Bellemans J (2011) Resurfacing hip arthroplasty. A 3 to 5-year matched pair study of two different implant designs. Acta Orthop Belg 77(5):609–615
Fowble VA, dela Rosa MA, Schmalzried TP (2009) A comparison of total hip resurfacing and total hip arthroplasty—patients and outcomes. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 67(2):108–112
Giannini S, Cadossi M, Chiarello E, Faldini C, Moroni A, Romagnoli M (2011) Hip resurfacing arthroplasty: a series of 140 consecutive hips with a minimum five year follow-up. A clinical, radiological and histological analysis. Hip Int 21(1):52–58
Gravius S, Mumme T, Weber O, Berdel P, Wirtz DC (2009) Surgical principles and clinical experiences with the DUROM hip resurfacing system using a lateral approach. Oper Orthop Traumatol 21(6):586–601
Gross TP, Liu F (2011) The first 100 fully porous-coated femoral components in hip resurfacing. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 69(Suppl 1):S30–S35
Heilpern GNA, Shah NN, Fordyce MJF (2008) Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty: a series of 110 consecutive hips with a minimum five-year clinical and radiological follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(9):1137–1142
Hing CB, Back DL, Bailey M, Young DA, Dalziel RE, Shimmin AJ (2007) The results of primary Birmingham hip resurfacings at a mean of five years. An independent prospective review of the first 230 hips. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(11):1431–1438
Hulst JB, Ball ST, Wu G, Le Duff MJ, Woon RP, Amstutz HC (2011) Survivorship of Conserve® Plus monoblock metal-on-metal hip resurfacing sockets: radiographic midterm results of 580 patients. Orthop Clin North Am 42(2):153–159, vii
Jameson SS, Langton DJ, Nargol AVF (2010) Articular surface replacement of the hip: a prospective single-surgeon series. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(1):28–37
Khan M, Kuiper J-H, Edwards D, Robinson E, Richardson JB (2009) Birmingham hip arthroplasty: five to eight years of prospective multicenter results. J Arthroplasty 24(7):1044–1050
Killampalli VV, Hayes A, Parsons N, Costa ML, Prakash U (2009) Hip resurfacing using the trochanteric flip osteotomy. Hip Int 19(2):131–135
Kim PR, Beaulé PE, Laflamme GY, Dunbar M (2008) Causes of early failure in a multicenter clinical trial of hip resurfacing. J Arthroplasty 23(6 Suppl 1):44–49
Klein M, Scherger B, Bernd H, Ostermann PA (2008) Complications after hip resurfacing using the ASR prosthesis in patients with osteoarthritis. Z Orthop Unfall 146(2):179–184
Langton DJ, Jameson SS, Joyce TJ, Hallab NJ, Natu S, Nargol AVF (2010) Early failure of metal-on-metal bearings in hip resurfacing and large-diameter total hip replacement: A consequence of excess wear. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(1):38–46
Larbpaiboonpong V, Turajane T, Pragtong P (2009) The early outcome of Birmingham hip resurfacing: an independent Thai surgeon experiences. J Med Assoc Thai 92(Suppl 6):S134–S140
Lei M, Yang S, Xu W, Ye S, Ze R, Fan L (2010) Metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing arthroplasty for treatment of advanced osteonecrosis of femoral head in young and middle-aged patients. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi 24(3):262–265
Alberta Hip Improvement Project; MacKenzie JR, O’Connor GJ et al (2012) Functional outcomes for 2 years comparing hip resurfacing and total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 27(5):750–7.e2
Madadi F, Eajazi A, Kazemi SM, Aalami Harandi A, Madadi F, Sharifzadeh SR (2011) Total hip arthroplasty in advanced osteonecrosis: the short-term results by metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. Med Sci Monit 17(2):CR78–CR82
Madhu TS, Akula MR, Raman RN, Sharma HK, Johnson VG (2011) The Birmingham hip resurfacing prosthesis: an independent single surgeon’s experience at 7-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty 26(1):1–8
Malhotra R, Kannan A, Kumar V, Nagaraj C, Marimuthu K, Khatri D (2012) Hip resurfacing arthroplasty in inflammatory arthritis a 3- to 5-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty 27(1):15–20
Marker DR, Zywiel MG, Johnson AJ, Seyler TM, Mont MA (2010) Are component positioning and prosthesis size associated with hip resurfacing failure? BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:227
Marulanda GA, Wilson MS, Edwards P, Raterman S (2008) Early clinical experience with the use of the Birmingham hip resurfacing system. Orthopedics 31(12 Suppl 2)
McAndrew AR, Khaleel A, Bloomfield MD, Aweid A (2007) A district general hospital’s experience of hip resurfacing. Hip Int 17(1):1–3
McBryde CW, Theivendran K, Thomas AMC, Treacy RBC, Pynsent PB (2010) The influence of head size and sex on the outcome of Birmingham hip resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(1):105–112
McMinn DJW, Daniel J, Ziaee H, Pradhan C (2011) Indications and results of hip resurfacing. Int Orthop 35(2):231–237
Mont MA, Marker DR, Smith JM, Ulrich SD, McGrath MS (2009) Resurfacing is comparable to total hip arthroplasty at short-term follow-up. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(1):66–71
Mont MA, Seyler TM, Ulrich SD et al (2007) Effect of changing indications and techniques on total hip resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 465:63–70
Naal FD, Pilz R, Munzinger U, Hersche O, Leunig M (2011) High revision rate at 5 years after hip resurfacing with the Durom implant. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(9):2598–2604
Ollivere B, Duckett S, August A, Porteous M (2010) The Birmingham Hip Resurfacing: 5-year clinical and radiographic results from a District General Hospital. Int Orthop 34(5):631–634
Sandiford NA, Muirhead-Allwood SK, Skinner JA, Hua J (2010) Metal on metal hip resurfacing versus uncemented custom total hip replacement—early results. J Orthop Surg Res 5:8
Siebel T, Maubach S, Morlock MM (2006) Lessons learned from early clinical experience and results of 300 ASR hip resurfacing implantations. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 220(2):345–353
Smolders JMH, Hol A, Rijnberg WJ, van Susante JLC (2011) Metal ion levels and functional results after either resurfacing hip arthroplasty or conventional metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop 82(5):559–566
Steffen RT, Pandit HP, Palan J, Beard DJ, Gundle R, McLardy-Smith P, Murray DW, Gill HS (2008) The five-year results of the Birmingham Hip Resurfacing arthroplasty: an independent series. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(4):436–441
Stulberg BN, Trier KK, Naughton M, Zadzilka JD (2008) Results and lessons learned from a United States hip resurfacing investigational device exemption trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Suppl 3):21–26
Swank ML, Alkire MR (2009) Minimally invasive hip resurfacing compared to minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 67(2):113–115
Takamura KM, Yoon J, Ebramzadeh E, Campbell PA, Amstutz HC (2011) Incidence and significance of femoral neck narrowing in the first 500 Conserve® Plus series of hip resurfacing cases: a clinical and histologic study. Orthop Clin North Am 42(2):181–193, viii
Treacy RBC, Mcbryde CW, Shears E, Pynsent PB (2011) Birmingham hip resurfacing: a minimum follow-up of ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(1):27–33
Vendittoli P-A, Ganapathi M, Roy AG, Lusignan D, Lavigne M (2010) A comparison of clinical results of hip resurfacing arthroplasty and 28 mm metal on metal total hip arthroplasty: a randomised trial with 3–6 years follow-up. Hip Int 20(1):1–13
Wang Q, Zhang XL, Chen YS, Shen H, Shao JJ (2012) Resurfacing arthroplasty for hip dysplasia: a prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 94(6):768–773
Witzleb W-C, Arnold M, Krummenauer F, Knecht A, Ranisch H, Günther K-P (2008) Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty: short-term clinical and radiographic outcome. Eur J Med Res 13(1):39–46
Johanson P-E, Fenstad AM, Furnes O, Garellick G, Havelin LI, Overgaard S, Pedersen AB, Kärrholm J (2010) Inferior outcome after hip resurfacing arthroplasty than after conventional arthroplasty. Evidence from the Nordic Arthroplasty Register Association (NARA) database, 1995 to 2007. Acta Orthop 81(5):535–541
Buergi ML, Walter WL (2007) Hip resurfacing arthroplasty: the Australian experience. J Arthroplasty 22(7 Suppl 3):61–65
McMinn DJW, Snell KIE, Daniel J, Treacy RBC, Pynsent PB, Riley RD (2012) Mortality and implant revision rates of hip arthroplasty in patients with osteoarthritis: registry based cohort study. BMJ 344:e3319
Corten K, Macdonald SJ (2010) Hip resurfacing data from national joint registries: what do they tell us? What do they not tell us? Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(2):351–357
Goodfellow JW, O’Connor JJ, Murray DW (2010) A critique of revision rate as an outcome measure: re-interpretation of knee joint registry data. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(12):1628–1631
Witjes S, Smolders JMH, Beaulé PE, Pasker P, van Susante JLC (2009) Learning from the learning curve in total hip resurfacing: a radiographic analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 129(10):1293–1299
Berend KR, Lombardi AV, Adams JB, Sneller MA (2011) Unsatisfactory surgical learning curve with hip resurfacing. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93(Suppl 2):89–92
De Haan R, Pattyn C, Gill HS, Murray DW, Campbell PA, De Smet K (2008) Correlation between inclination of the acetabular component and metal ion levels in metal-on-metal hip resurfacing replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(10):1291–1297
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pailhé, R., Sharma, A., Reina, N. et al. Hip resurfacing: a systematic review of literature. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 2399–2410 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1686-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1686-3