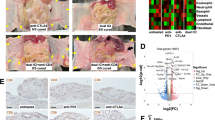
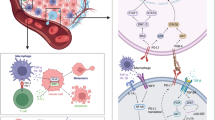
Abstract
Immunotherapy based on γδT cells has limited efficiency in solid tumors, including colon cancer (CC). The immune evasion of tumor cells may be the main cause of the difficulties of γδT cell-based treatment. In the present study, we explored whether and how B7-H3 regulates the resistance of CC cells to the cytotoxicity of Vγ9Vδ2 (Vδ2) T cells. We observed that B7-H3 overexpression promoted, while B7-H3 knockdown inhibited, CC cell resistance to the killing effect of Vδ2 T cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, we showed that B7-H3-mediated CC cell resistance to the cytotoxicity of Vδ2 T cells involved a molecular pathway comprising STAT3 activation and decreased ULBP2 expression. ULBP2 blockade or knockdown abolished the B7-H3 silencing-induced increase in the cytotoxicity of Vδ2 T cells to CC cells. Furthermore, cryptotanshinone, a STAT3 phosphorylation inhibitor, reversed the B7-H3 overexpression-induced decrease in ULBP2 expression and attenuated the killing effect of Vδ2 T cells on CC cells. Moreover, there was a negative correlation between the expression of B7-H3 and ULBP2 in the tumor tissues of CC patients. Our results suggest that the B7-H3-mediated STAT3/ULBP2 axis may be a potential candidate target for improving the efficiency of γδT cell-based immunotherapy in CC.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Tamas K, Walenkamp AM, de Vries EG, van Vugt MA, Beets-Tan RG, van Etten B, de Groot DJ, Hospers GA (2015) Rectal and colon cancer: Not just a different anatomic site. Cancer Treat Rev 41:671–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.06.007
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Fedewa SA, Butterly LF, Anderson JC, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A (2020) Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21601
Bhat SAVD (2018) Checkpoint blockade rescues the repressive effect of histone deacetylases inhibitors on γδ T cell function. Front Immunol 9:1615. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01615
Bottino CTG, Ferrini S et al (1988) Two subsets of human T lymphocytes expressing gamma/delta antigen receptor are identifiable by monoclonal antibodies directed to two distinct molecular forms of the receptor. J Exp Med 168:491–505
Pui CH, Pei D, Cheng C et al (2019) Treatment response and outcome of children with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia expressing the gamma-delta T-cell receptor. Oncoimmunology 8:1599637. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2019.1599637
Gober HJ, Kistowska M, Angman L, Jeno P, Mori L, De Libero G (2003) Human T cell receptor gammadelta cells recognize endogenous mevalonate metabolites in tumor cells. J Exp Med 197:163–168. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20021500
Z. X, (2017) Dual face of Vγ9Vδ2-T cells in tumor immunology: anti- versus pro-tumoral activities. Front Immunol 8:1041. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01041
Baker FL, Bigley AB, Agha NH, Pedlar CR, O’Connor DP, Bond RA, Bollard CM, Katsanis E, Simpson RJ (2019) Systemic beta-adrenergic receptor activation augments the ex vivo expansion and anti-tumor activity of Vgamma9Vdelta2 T-cells. Front Immunol 10:3082. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.03082
Wang ZWZ, Li S et al (2018) Decitabine enhances Vγ9Vδ2 T cell-mediated cytotoxic effects on osteosarcoma cells the NKG2DL-NKG2D Axis. Front Immunol 9:1239. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01239
Willcox BE, Willcox CR (2019) gammadelta TCR ligands: the quest to solve a 500-million-year-old mystery. Nat Immunol 20:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-018-0304-y
Li Y, Guo G, Song J, Cai Z, Yang J, Chen Z, Wang Y, Huang Y, Gao Q (2017) B7–H3 promotes the migration and invasion of human bladder cancer cells via the PI3K/Akt/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cancer 8:816–824. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.17759
Lee YH, Martin-Orozco N, Zheng P et al (2017) Inhibition of the B7–H3 immune checkpoint limits tumor growth by enhancing cytotoxic lymphocyte function. Cell Res 27:1034–1045. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.90
Liu H, Tekle C, Chen YW et al (2011) B7–H3 silencing increases paclitaxel sensitivity by abrogating Jak2/Stat3 phosphorylation. Mol Cancer Ther 10:960–971. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0072
Son Y, Kwon S-M, Cho J-Y (2019) CD276 (B7–H3) maintains proliferation and regulates differentiation in angiogenic function in late endothelial progenitor cells. Stem Cells 37:382–394. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.2944
Lemke D, Pfenning PN, Sahm F et al (2012) Costimulatory protein 4IgB7H3 drives the malignant phenotype of glioblastoma by mediating immune escape and invasiveness. Clin Cancer Res 18:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0880
Cai D, Li J, Liu D et al (2020) Tumor-expressed B7–H3 mediates the inhibition of antitumor T-cell functions in ovarian cancer insensitive to PD-1 blockade therapy. Cell Mol Immunol 17:227–236. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-019-0305-2
Lu H, Shi T, Wang M, Li X, Gu Y, Zhang X, Zhang G, Chen W (2020) B7–H3 inhibits the IFN-γ-dependent cytotoxicity of Vγ9Vδ2 T cells against colon cancer cells. OncoImmunology 9:1748991. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402x.2020.1748991
Wang R, Ma Y, Zhan S, Zhang G, Cao L, Zhang X, Shi T, Chen W (2020) B7–H3 promotes colorectal cancer angiogenesis through activating the NF-kappaB pathway to induce VEGFA expression. Cell Death Dis 11:55. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2252-3
Li X, Lu H, Gu Y, Zhang X, Zhang G, Shi T, Chen W (2020) Tim-3 suppresses the killing effect of Vgamma9Vdelta2T cells on colon cancer cells by reducing perforin and granzyme B expression. Exp Cell Res 386:111719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111719
Zhou XGY, Xiao H et al (2017) Combining Vγ9Vδ2 T cells with a lipophilic bisphosphonate efficiently kills activated hepatic stellate cells. Front Immunol 8:1381. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01381
Ma Y, Wang R, Lu H et al (2020) B7–H3 promotes the cell cycle-mediated chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells by regulating CDC25A. J Cancer 11:2158–2170. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.37255
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK, Varambally S (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 19:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
Xu L, Chen X, Shen M et al (2018) Inhibition of IL-6-JAK/Stat3 signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells enhances the NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity via alteration of PD-L1/NKG2D ligand levels. Mol Oncol 12:269–286. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12135
Lu XZZ, Jiang L et al (2015) Matrine increases NKG2D ligand ULBP2 in K562 cells via inhibiting JAK/STAT3 pathway: a potential mechanism underlying the immunotherapy of matrine in leukemia. Am J Transl Res 7:1838–1849
Park DJ, Sung PS, Kim J-H, Lee GW, Jang JW, Jung ES, Bae SH, Choi JY, Yoon SK (2020) EpCAM-high liver cancer stem cells resist natural killer cell–mediated cytotoxicity by upregulating CEACAM1. J ImmunoTher Cancer 8:e000301. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2019-000301
Terry S, Abdou A, Engelsen AST et al (2019) AXL targeting overcomes human lung cancer cell resistance to NK- and CTL-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Immunol Res 7:1789–1802. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0903
Wu J, Wang F, Liu X, Zhang T, Liu F, Ge X, Mao Y, Hua D (2018) Correlation of IDH1 and B7 H3 expression with prognosis of CRC patients. Eur J Surg Oncol 44:1254–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2018.05.005
Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Hanley SJB, Watari H (2018) B7H3 as a promoter of metastasis and promising therapeutic target. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00264
Ni L, Dong C (2017) New B7 family checkpoints in human cancers. Mol Cancer Ther 16:1203–1211. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-16-0761
Du H, Hirabayashi K, Ahn S et al (2019) Antitumor responses in the absence of toxicity in solid tumors by targeting B7–H3 via chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Cancer Cell 35:221–37.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2019.01.002
Wohler JE, Smith SS, Barnum SR (2010) Gammadelta T cells: the overlooked T-cell subset in demyelinating disease. J Neurosci Res 88:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22176
Wu YL, Ding YP, Tanaka Y, Shen LW, Wei CH, Minato N, Zhang W (2014) Gammadelta T cells and their potential for immunotherapy. Int J Biol Sci 10:119–135. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.7823
Silva-Santos B, Serre K, Norell H (2015) γδ T cells in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol 15:683–691. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3904
Riond JRS, Nicolau ML et al (2009) In vivo major histocompatibility complex class I (MHCI) expression on MHCIlow tumor cells is regulated by gammadelta T and NK cells during the early steps of tumor growth. Cancer Immunity 9:10
Zocchi MRCD, Venè R et al (2017) Zoledronate can induce colorectal cancer microenvironment expressing BTN3A1 to stimulate effector γδ T cells with antitumor activity. Oncoimmunology 6:e1278099. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2016.1278099
Li XY, Das I, Lepletier A et al (2018) CD155 loss enhances tumor suppression via combined host and tumor-intrinsic mechanisms. J Clin Invest 128:2613–2625. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI98769
Shi L, Lin H, Li G et al (2016) Cisplatin enhances NK cells immunotherapy efficacy to suppress HCC progression via altering the androgen receptor (AR)-ULBP2 signals. Cancer Lett 373:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.017
Frazao A, Colombo M, Fourmentraux-Neves E et al (2017) Shifting the balance of activating and inhibitory natural killer receptor ligands on BRAFV600E melanoma lines with vemurafenib. Cancer Immunol Res 5:582–593. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.cir-16-0380
Rothe A, Jachimowicz RD, Borchmann S et al (2014) The bispecific immunoligand ULBP2-aCEA redirects natural killer cells to tumor cells and reveals potent anti-tumor activity against colon carcinoma. Int J Cancer 134:2829–2840. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28609
Sun B, Yang D, Dai H et al (2019) Eradication of hepatocellular carcinoma by NKG2D-based CAR-T cells. Cancer Immunol Res 7:1813–1823. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.cir-19-0026
Duan S, Guo W, Xu Z et al (2019) Natural killer group 2D receptor and its ligands in cancer immune escape. Mol Cancer 18:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0956-8
Heinemann A, Zhao F, Pechlivanis S, Eberle J, Steinle A, Diederichs S, Schadendorf D, Paschen A (2012) Tumor suppressive microRNAs miR-34a/c control cancer cell expression of ULBP2, a stress-induced ligand of the natural killer cell receptor NKG2D. Cancer Res 72:460–471. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1977
Liang HX, Li YH (2020) MiR-873, as a suppressor in cervical cancer, inhibits cells proliferation, invasion and migration via negatively regulating ULBP2. Genes Genom 42:371–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00905-8
Breunig C, Pahl J, Küblbeck M et al (2017) MicroRNA-519a-3p mediates apoptosis resistance in breast cancer cells and their escape from recognition by natural killer cells. Cell Death Dis. 8:e2973-e. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.364
Textor S, Fiegler N, Arnold A, Porgador A, Hofmann TG, Cerwenka A (2011) Human NK cells are alerted to induction of p53 in cancer cells by upregulation of the NKG2D ligands ULBP1 and ULBP2. Cancer Res 71:5998–6009. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3211
Eisele G, Wischhusen J, Mittelbronn M, Meyermann R, Waldhauer I, Steinle A, Weller M, Friese MA (2006) TGF-beta and metalloproteinases differentially suppress NKG2D ligand surface expression on malignant glioma cells. Brain 129:2416–2425. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl205
Shi T, Ma Y, Cao L et al (2019) B7–H3 promotes aerobic glycolysis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer cells by regulating HK2. Cell Death Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1549-6
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the members of the department of gastroenterology, general surgery, and pathology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University for their help in collecting clinical samples.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81802843, 81672372, 81372276); Colleges and Universities Natural Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (18KJB320023, 17KJA310004); Suzhou Science & Technology plan project (SYS2019035, SYS201747, SS2019077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL, TS and WC designed the experiments; HL, YM, HW, and JL performed most of the experiments; MW and YG contributed to provide clinical samples; YM, NG, and YG assisted with experiments and analysis of the data; XZ and GZ provided administrative, technical, or material support. HL, TS, and WC wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experiments were performed under the institutional guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Soochow University. The experiments involving in tissue samples of patients with CC were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Ma, Y., Wang, M. et al. B7-H3 confers resistance to Vγ9Vδ2 T cell-mediated cytotoxicity in human colon cancer cells via the STAT3/ULBP2 axis. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70, 1213–1226 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02771-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02771-w