Abstract
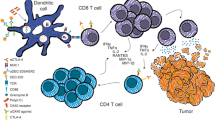
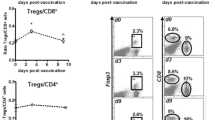
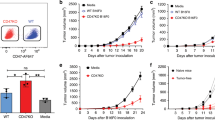
Disrupting tumor-mediated mechanisms suppressing host immunity represents a novel approach to tumor immunotherapy. Depletion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) increases endogenous anti-tumor immunity and the efficacy of active immunotherapy in experimental tumor models. HLA-A2.1/HLA-DR1 (A2.1/DR1) × BALB- neuT + (neuT +) triple transgenic mice represent an improvement over neuT + mice for evaluating vaccination regimens to overcome tolerance against HER-2/neu. We questioned whether depletion of Tregs with Denileukin diftitox (Ontak) enhances the efficacy of a therapeutic vaccine consisting of HER-2(85–94) (p85) CTL and HER-2(776–790) (p776) Th peptides against the growth of TUBO.A2 transplantable tumor in male A2.1/DR1 × neuT + Tg mice. While the therapeutic vaccine primed the tumor-reactive CD8+ CTLs and CD4+ effector T lymphocytes (Teffs) compartment, inducing activation, tumor infiltration, and tumor rejection or delay in tumor growth, treatment with Ontak 1 day prior to vaccination resulted in enhanced CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell-mediated vaccine-specific immune responses in the periphery. This was closely associated with greater infiltration and a striking change in the intratumor balance of Tregs and vaccine-specific CTLs/Teffs that directly correlated with markedly enhanced antitumor activity. The data suggest that Tregs control both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell activity within the tumor, emphasize the importance of the intratumor ratio of vaccine-specific lymphocytes to Tregs, and demonstrate significant inversion of this ratio and correlation with tumor rejection during Ontak/vaccine immunotherapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Tregs:
-
Regulatory T cells
- Tg:
-
Transgenic
- Teffs:
-
Effector T cell
- FasL:
-
Fas ligand
- PENT:
-
Pentamer
- Tm:
-
Tetramer
- TIL:
-
Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes
References
Levings MK, Sangregorio R, Roncarolo MG (2001) Human CD25(+)CD4(+) t regulatory cells suppress naïve and memory T cell proliferation and can be expanded in vitro without loss of function. J Exp Med 193:1295–1302
Shevach EM (2001) Certified professionals: CD4(+)CD25(+) Suppressor T cells. J Exp Med 193:41–46
Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Schuler G, Knop J, Enk AH (2000) Induction of interleukin10-producing, non proliferating CD4(+) Tcells with regulatory properties by repetitive stimulation with allogeneic immature human dendritic cells. J Exp Med 192:1213–1222
Read S, Powrie F (2001) CD4(+) regulatory T cells. Curr Opin Immunol 13:644–649
Terabe M, Berzofsky JA (2004) Immunoregulatory T cells in tumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 16:157–162
Ahmad M, Rees RC, Ali SA (2004) Escape from immunotherapy: possible mechanisms that influence tumor regression/progression. Cancer Immunol Immunother 53:844–854
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L et al (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10:942–949
Wolf AM, Wolf D, Steurer M, Gastl G, Gunsilius E, Grubeck-Loebenstein B (2003) Increase of regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 9:606–612
Viguier M, Lemaitre F, Verola O, Cho MS, Gorochov G, Dubertret L, Bachelez H, Kourilsky P, Ferradini L (2004) Foxp3 expressing CD4+CD25(high) regulatory T cells are overrepresented in human metastatic melanoma lymph nodes and inhibit the function of infiltrating T cells. J Immunol 173:1444–1453
Woo EY, Yeh H, Chu CS, Schlienger K, Carroll RG, Riley JL, Kaiser LR, June CH (2002) Cutting edge: regulatory T cells from lung cancer patients directly inhibit autologous T cell proliferation. J Immunol 168:4272–4276
Shevach EM (2002) CD4+CD25+suppressor T cells: more questions than answers. Nat Rev Immunol 2:389–400
Gallimore A, Sakaguchi S (2002) Regulation of tumour immunity by CD25 +T cells. Immunology 107:5–9
Steitz J, Brück J, Lenz J, Knop J, Tüting T (2001) Depletion of CD25(+) CD4(+) T cells and treatment with tyrosinase-related protein 2-transduced dendritic cells enhance the interferon alpha-induced, CD8(+) T-cell-dependent immune defense of B16 melanoma. Cancer Res 61:8643–8646
Ercolini AM, Ladle BH, Manning EA, Pfannenstiel LW, Armstrong TD, Machiels JP, Bieler JG, Emens LA, Reilly RT, Jaffee EM (2005) Recruitment of latent pools of high-avidity CD8(+) T cells to the antitumor immune response. J Exp Med 201:1591–1602
Sutmuller RP, van Duivenvoorde LM, van Elsas A, Schumacher TN, Wildenberg ME, Allison JP, Toes RE, Offringa R, Melief CJ (2001) Synergism of cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen 4 blockade and depletion of CD25(+) regulatory T cells in antitumor therapy reveals alternative pathways for suppression of autoreactive cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Exp Med 194:823–832
Pasare C, Medzhitov R (2003) Toll pathway dependent blockade of CD4+CD25+T cell mediated suppression by dendritic cells. Science 299:1033–1036
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakaguchi S (1999) Induction of tumor immunity by removing CD25+CD4+T cells: a common basis between tumor immunity and autoimmunity. J Immunol 163:5211–5218
Klages K, Mayer CT, Lahl K, Loddenkemper C, Teng MW, Ngiow SF, Smyth MJ, Hamann A, Huehn J, Sparwasser T (2010) Selective Depletion of Foxp3 + Regulatory T Cells Improves Effective Therapeutic Vaccination against Established Melanoma. Cancer Res 70:7788–7799
Eklund JW, Kuzel TM (2005) Denileukin diftitox: a concise clinical review. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 5:33–38
Knutson KL, Dang Y, Lu H, Lukas J, Almand B, Gad E, Azeke E, Disis ML (2006) IL-2 immunotoxin therapy modulates tumor-associated regulatory T cells and leads to lasting immune-mediated rejection of breast cancers in neu-transgenic mice. J Immunol 177:84–91
Morse MA, Hobeika AC, Osada T, Serra D, Niedzwiecki D, Lyerly HK, Clay TM (2008) Depletion of human regulatory T cells specifically enhances antigen-specific immune responses to cancer vaccines. Blood 112:610–618
Litzinger MT, Fernando R, Curiel TJ, Grosenbach DW, Schlom J, Palena C (2007) IL-2 immunotoxin denileukin diftitox reduces regulatory T cells and enhances vaccine-mediated T-cell immunity. Blood 110:3192–3201
Gritzapis AD, Voutsas IF, Lekka E, Papamichail M, Baxevanis CN (2010) Peptide vaccination breaks tolerance to HER-2/neu by generating vaccine-specific FasL(+) CD4(+) T cells: first evidence for intratumor apoptotic regulatory T cells. Cancer Res 70:2686–2696
Gritzapis AD, Voutsas IF, Lekka E, Tsavaris N, Missitzis I, Sotiropoulou P, Perez S, Papamichail M, Baxevanis CN (2008) Identification of a novel immunogenic HLA-A*0201-binding epitope of HER-2/neu with potent antitumor properties. J Immunol 181:146–154
Gritzapis AD, Mahaira LG, Perez SA, Cacoullos NT, Papamichail M, Baxevanis CN (2006) Vaccination with human HER-2/neu (435–443) CTL peptide induces effective antitumor immunity against HER-2/neu-expressing tumor cells in vivo. Cancer Res 66:5452–5460
Quezada SA, Peggs KS, Curran MA, Allison JP (2006) CTLA4 blockade and GM-CSF combination immunotherapy alters the intratumor balance of effector and regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest 116:1935–1945
Voutsas IF, Gritzapis AD, Mahaira LG, Salagianni M, von Hofe E, Kallinteris NL, Baxevanis CN (2007) Induction of potent CD4+ T cell-mediated antitumor responses by a helper HER-2/neu peptide linked to the Ii-Key moiety of the invariant chain. Int J Cancer 121:2031–2041
Whiteside TL (2010) Inhibiting the inhibitors: evaluating agents targeting cancer immunosuppression. Expert Opin Biol Ther 10:1019–1035
Ko K, Yamazaki S, Nakamura K, Nishioka T, Hirota K, Yamaguchi T, Shimizu J, Nomura T, Chiba T, Sakaguchi S (2005) Treatment of advanced tumors with agonistic anti-GITR mAb and its effects on tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 202:885–891
Labarrière N, Pandolfino MC, Gervois N, Khammari A, Tessier MH, Dréno B, Jotereau F (2002) Therapeutic efficacy of melanoma-reactive TIL injected in stage III melanoma patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 51:532–538
Salama P, Phillips M, Grieu F, Morris M, Zeps N, Joseph D, Platell C, Iacopetta B (2009) Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3 + T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:186–192
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S (2006) Prevalence of FOXP3 + regulatoryT cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res 12:5423–5434
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, Ojima H, Kanai Y, Kosuge T, Nakajima A, Hirohashi S (2007) FOXP3 + regulatory T cells affect the development and progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res 13:902–911
Lee AM, Clear AJ, Calaminici M, Davies AJ, Jordan S, MacDougall F, Matthews J, Norton AJ, Gribben JG, Lister TA, Goff LK (2006) Number of CD4+ cells and location of forkhead box protein P3-positive cells in diagnostic follicular lymphoma tissue microarrays correlates with outcome. J Clin Oncol 24:5052–5059
Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J, Peyrard S, Klein C, Agueznay Nel H, Mosseri V, Laccourreye O, Bruneval P, Fridman WH et al (2006) Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res 12:465–472
Strauss L, Bergmann C, Gooding W, Johnson JT, Whiteside TL (2007) The frequency and suppressor function of CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells in the circulation of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res 13:6301–6311
Petersen RP, Campa MJ, Sperlazza J, Conlon D, Joshi MB, Harpole DH Jr, Patz EF Jr (2006) Tumor infiltrating Foxp3 + regulatory T-cells are associated with recurrence in pathologic stage I NSCLC patients. Cancer 107:2866–2872
Leffers N, Gooden MJ, de Jong RA, Hoogeboom BN, ten Hoor KA, Hollema H, Boezen HM, van der Zee AG, Daemen T, Nijman HW (2009) Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes in primary and metastatic lesions of advanced stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58:449–459
Strauss L, Whiteside TL, Knights A, Bergmann C, Knuth A, Zippelius A (2007) Selective survival of naturally occurring human CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells cultured with rapamycin. J Immunol 178:320–329
Prince HM, Duvic M, Martin A, Sterry W, Assaf C, Sun Y, Straus D, Acosta M, Negro-Vilar A (2010) Phase III placebo-controlled trial of denileukin diftitox for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 28:1870–1877
Kadin EM, Vonderheid EC (2010) Targeted therapies: Denileukin diftitox—a step towards a ‘magic bullet’ for CTCL. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7:430–432
Rasku MA, Clem AL, Telang S, Taft B, Gettings K, Gragg H, Cramer D, Lear SC, McMasters KM, Miller DM, Chesney J (2008) Transient T cell depletion causes regression of melanoma metastases. J Transl Med 6:12. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-6-12
Chesney J, Rasku MA, Klarer AC, Miller DM, Telang S (2011) Effect of denileukin diftitox on serum GM-CSF and clinical responses in stage IV melanoma. ASCO Annual Meeting J Clin Oncol 29:2011 (suppl; abstr 2507)
Dannull J, Su Z, Rizzieri D, Yang BK, Coleman D, Yancey D, Zhang A, Dahm P, Chao N, Gilboa E, Vieweg J (2005) Enhancement of vaccine-mediated antitumor immunity in cancer patients after depletion of regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest 115:3623–3633
Taieb J, Chaput N, Schartz N, Roux S, Novault S, Ménard C, Ghiringhelli F, Terme M, Carpentier AF, Darrasse-Jèze G et al (2006) Chemoimmunotherapy of tumors: cyclophosphamide synergizes with exosome based vaccines. J Immunol 176:2722–2729
Rech AJ, Vonderheide RH (2009) Clinical use of anti-CD25 antibody daclizumab to enhance immune responses to tumor antigen vaccination by targeting regulatory T cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1174:99–106
Martorelli D, Muraro E, Merlo A, Turrini R, Rosato A, Dolcetti R (2009) Role of CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the control of viral diseases and cancer. Int Rev Immunol 29:371–402
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gritzapis, A.D., Voutsas, I.F. & Baxevanis, C.N. Ontak reduces the immunosuppressive tumor environment and enhances successful therapeutic vaccination in HER-2/neu-tolerant mice. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61, 397–407 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-011-1113-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-011-1113-4