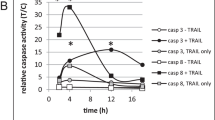
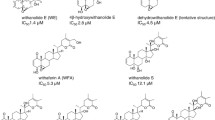
Abstract
We have developed a high-throughput screen (HTS) to search for novel molecules that can synergize with TRAIL, thus promoting apoptosis of ACHN renal tumor cells in a combinatorial fashion. The HTS detects synthetic compounds and pure natural products that can pre-sensitize the cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, yet have limited toxicity on their own. We have taken into account the individual effects of the single agents, versus the combination, and have identified hits that are synergistic, synergistic-toxic, or additive when combined with TRAIL in promoting tumor cell death. Preliminary mechanistic studies indicate that a subset of the synergistic TRAIL sensitizers act very rapidly to promote cleavage and activation of caspase-8 following TRAIL binding. Caspase-8 is an apical enzyme that initiates programmed cell death via the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Thus, these TRAIL sensitizers may potentially reduce resistance of tumor cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Two representative sensitizers were found to increase levels of p53 but did not inhibit the proteasome, suggesting that early DNA damage-sensing pathways may be involved in their mechanisms of action.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TRAIL:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- HTS:
-
High-throughput screen
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TR1/TR2/TR3/TR4:
-
TRAIL death receptors-1/-2/-3/-4
- XTT:
-
2,3-Bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-5-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-2H-tetrazolium hydroxide
- SRB:
-
Sulforhodamine B
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- DMSO:
-
Dimethylsulfoxide
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- −TRAIL:
-
In the absence of TRAIL ligand
- +TRAIL:
-
In the presence of TRAIL ligand
- %GI:
-
Percent growth inhibition
- MMP:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
References
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert A, DeForge L, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen H, Shahrokh Z, Schwall RH (1999) Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest 104(2):155–162
Brooks AD, Ramirez T, Toh U, Onksen J, Elliott PJ, Murphy WJ, Sayers TJ (2005) The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (Velcade) sensitizes some human tumor cells to Apo2L/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Ann NY Acad Sci 1059:160–167
Buchsbaum DJ, Forero-Torres A, LoBuglio AF (2007) TRAIL-receptor antibodies as a potential cancer treatment. Future Oncol 3(4):405–409
Cheng J, Hylander BL, Baer MR, Chen X, Repasky EA (2006) Multiple mechanisms underlie resistance of leukemia cells to Apo2 Ligand/TRAIL. Mol Cancer Ther 5(7):1844–1853
Choi JW (2005) Relationships between tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis- inducing ligand (TRAIL) and hematopoietic activity in healthy adults. Ann Hematol 84(11):728–733
Choi JW, Song JS, Pai SH (2004) Associations of serum TRAIL concentrations, anthropometric variables, and serum lipid parameters in healthy adults. Ann Clin Lab Sci 34(4):400–404
Degli-Esposti MA, Dougall WC, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Smith CA, Goodwin RG (1997) The novel receptor TRAIL-R4 induces NF-kappaB and protects against TRAIL- mediated apoptosis, yet retains an incomplete death domain. Immunity 7(6):813–820
Degli-Esposti MA, Smolak PJ, Walczak H, Waugh J, Huang CP, DuBose RF, Goodwin RG, Smith CA (1997) Cloning and characterization of TRAIL-R3, a novel member of the emerging TRAIL receptor family. J Exp Med 186(7):1165–1170
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Pallares J, Rue M, Comella JX, Matias-Guiu X (2005) FLIP is frequently expressed in endometrial carcinoma and has a role in resistance to TRAIL- induced apoptosis. Lab Invest 85(7):885–894
Duiker EW, Mom CH, de Jong S, Willemse PH, Gietema JA, van der Zee AG, de Vries EG (2006) The clinical trail of TRAIL. Eur J Cancer 42(14):2233–2240
Falschlehner C, Emmerich CH, Gerlach B, Walczak H (2007) TRAIL signalling: decisions between life and death. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(7–8):1462–1475
Fukumori T, Takenaka Y, Oka N, Yoshii T, Hogan V, Inohara H, Kanayama HO, Kim HR, Raz A (2004) Endogenous galectin-3 determines the routing of CD95 apoptotic signaling pathways. Cancer Res 64(10):3376–3379
Fulda S, Wick W, Weller M, Debatin KM (2002) Smac agonists sensitize for Apo2L/TRAIL- or anticancer drug-induced apoptosis and induce regression of malignant glioma in vivo. Nat Med 8(8):808–815
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Haas TL, Sykora J, Li-Weber M, Herzer K, Walczak H (2005) Proteasome inhibition sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells, but not human hepatocytes, to TRAIL. Hepatology 42(3):588–597
Georgakis GV, Li Y, Humphreys R, Andreeff M, O’Brien S, Younes M, Carbone A, Albert V, Younes A (2005) Activity of selective fully human agonistic antibodies to the TRAIL death receptors TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in primary and cultured lymphoma cells: induction of apoptosis and enhancement of doxorubicin- and bortezomib-induced cell death. Br J Haematol 130(4):501–510
Gill C, Walsh SE, Morrissey C, Fitzpatrick JM, Watson RW (2007) Resveratrol sensitizes androgen independent prostate cancer cells to death-receptor mediated apoptosis through multiple mechanisms. Prostate 67(15):1641–1653
Grossmann J, Walther K, Artinger M, Kiessling S, Scholmerich J (2001) Apoptotic signaling during initiation of detachment-induced apoptosis (“anoikis”) of primary human intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Growth Differ 12(3):147–155
Hao C, Beguinot F, Condorelli G, Trencia A, Van Meir EG, Yong VW, Parney IF, Roa WH, Petruk KC (2001) Induction and intracellular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) mediated apotosis in human malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res 61(3):1162–1170
Hayashi T, Okutomi T, Suzuki S, Okazaki H (1983) Inhibition of nucleic acid biosynthesis in procaryotic and eucaryotic cells by cyanocycline A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 36(9):1228–1235
Hill GC, Wunz TP, MacKenzie NE, Gooley PR, Remers WA (1991) Computer simulation of the binding of naphthyridinomycin and cyanocycline A to DNA. J Med Chem 34(7):2079–2088
Huang Y, Sheikh MS (2007) TRAIL death receptors and cancer therapeutics. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 224(3):284–289
Jin X, Wu XX, Abdel-Muneem Nouh MA, Kakehi Y (2007) Enhancement of death receptor 4 mediated apoptosis and cytotoxicity in renal cell carcinoma cells by subtoxic concentrations of doxorubicin. J Urol 177(5):1894–1899
Kelley SK, Harris LA, Xie D, Deforge L, Totpal K, Bussiere J, Fox JA (2001) Preclinical studies to predict the disposition of Apo2L/tumor necrosis factor-relatedapoptosis-inducing ligand in humans: characterization of in vivo efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299(1):31–38
Kim YS, Schwabe RF, Qian T, Lemasters JJ, Brenner DA (2002) TRAIL-mediated apoptosis requires NF-kappaB inhibition and the mitochondrial permeability transition in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology 36(6):1498–1508
Lacour S, Micheau O, Hammann A, Drouineaud V, Tschopp J, Solary E, Dimanche- Boitrel MT (2003) Chemotherapy enhances TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand DISC assembly in HT29 human colon cancer cells. Oncogene 22(12):1807–1816
Lavrik I, Krueger A, Schmitz I, Baumann S, Weyd H, Krammer PH, Kirchhoff S (2003) The active caspase-8 heterotetramer is formed at the CD95 DISC. Cell Death Differ 10(1):144–145
Lee TJ, Jung EM, Lee JT, Kim S, Park JW, Choi KS, Kwon TK (2006) Mithramycin A sensitizes cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by down-regulation of XIAP gene promoter through Sp1 sites. Mol Cancer Ther 5(11):2737–2746
Lombo F, Menendez N, Salas JA, Mendez C (2006) The aureolic acid family of antitumor compounds: structure, mode of action, biosynthesis, and novel derivatives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73(1):1–14
MacFarlane M, Ahmad M, Srinivasula SM, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Cohen GM, Alnemri ES (1997) Identification and molecular cloning of two novel receptors for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J Biol Chem 272(41):25417–25420
Marini P (2006) Drug evaluation: lexatumumab, an intravenous human agonistic mAb targeting TRAIL receptor 2. Curr Opin Mol Ther 8(6):539–546
Marsters SA, Sheridan JP, Pitti RM, Huang A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Yuan J, Gurney A, Goddard AD, Godowski P, Ashkenazi A (1997) A novel receptor for Apo2L/TRAIL contains a truncated death domain. Curr Biol 7(12):1003–1006
Merino D, Lalaoui N, Morizot A, Solary E, Micheau O (2007) TRAIL in cancer therapy: present and future challenges. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11(10):1299–1314
Mirandola P, Sponzilli I, Gobbi G, Marmiroli S, Rinaldi L, Binazzi R, Piccari GG, Ramazzotti G, Gaboardi GC, Cocco L, Vitale M (2006) Anticancer agents sensitize osteosarcoma cells to TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand downmodulating IAP family proteins. Int J Oncol 28(1):127–133
Mitsiades N, Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, Anderson KC, Treon SP (2002) Intracellular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells. Blood 99(6):2162–2171
Mori S, Murakami-Mori K, Nakamura S, Ashkenazi A, Bonavida B (1999) Sensitization of AIDS-Kaposi’s sarcoma cells to Apo-2 ligand-induced apoptosis by actinomycin D. J Immunol 162(9):5616–5623
Morimoto M, Fukui M, Ohkubo S, Tamaoki T, Tomita F (1982) Tetrocarcins, new antitumor antibiotics. 3. Antitumor activity of tetrocarcin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 35(8):1033–1037
Muhlethaler-Mottet A, Flahaut M, Bourloud KB, Auderset K, Meier R, Joseph JM, Gross N (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors strongly sensitise neuroblastoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a caspases-dependent increase of the pro- to anti- apoptotic proteins ratio. BMC Cancer 6:214
Nagy K, Szekely-Szuts K, Izeradjene K, Douglas L, Tillman M, Barti-Juhasz H, Dominici M, Spano C, Luca Cervo G, Conte P, Houghton JA, Mihalik R, Kopper L, Petak I (2006) Proteasome inhibitors sensitize colon carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via enhanced release of Smac/DIABLO from the mitochondria. Pathol Oncol Res 12(3):133–142
Nakajima H, Sakaguchi K, Fujiwara I, Mizuta M, Tsuruga M, Magae J, Mizuta N (2007) Apoptosis and inactivation of the PI3-kinase pathway by tetrocarcin A in breast cancers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356(1):260–265
Nakata S, Yoshida T, Horinaka M, Shiraishi T, Wakada M, Sakai T (2004) Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate death receptor 5/TRAIL-R2 and sensitize apoptosis induced by TRAIL/APO2-L in human malignant tumor cells. Oncogene 23(37):6261–6271
Ng CP, Zisman A, Bonavida B (2002) Synergy is achieved by complementation with Apo2L/TRAIL and actinomycin D in Apo2L/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of prostate cancer cells: role of XIAP in resistance. Prostate 53(4):286–299
O’Kane HF, Watson CJ, Johnston SR, Petak I, Watson RW, Williamson KE (2006) Targeting death receptors in bladder, prostate and renal cancer. J Urol 175(2):432–438
Ozoren N, El-Deiry WS (2002) Defining characteristics of Types I and II apoptotic cells in response to TRAIL. Neoplasia 4(6):551–557
Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R, Dixit VM (1997a) An antagonist decoy receptor and a death domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science 277(5327):815–818
Pan G, O’Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R, Ebner R, Ni J, Dixit VM (1997b) The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 276(5309):111–113
Petak I, Houghton JA (2001) Shared pathways: death receptors and cytotoxic drugs in cancer therapy. Pathol Oncol Res 7(2):95–106
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue CJ, Moore A, Ashkenazi A (1996) Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J Biol Chem 271(22):12687–12690
Plummer R, Attard G, Pacey S, Li L, Razak A, Perrett R, Barrett M, Judson I, Kaye S, Fox NL, Halpern W, Corey A, Calvert H, de Bono J (2007) Phase 1 and pharmacokinetic study of lexatumumab in patients with advanced cancers. Clin Cancer Res 13(20):6187–6194
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R, Alderson R, Bloom M, Sung C, Riccobene T, Johnson R, Fiscella M, Mahoney A, Carrell J, Boyd E, Yao XT, Zhang L, Zhong L, von Kerczek A, Shepard L, Vaughan T, Edwards B, Dobson C, Salcedo T, Albert V (2005) HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1 monoclonal antibody, induces cell death in multiple tumour types in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer 92(8):1430–1441
Ramakrishnan R, Antonia S, Gabrilovich DI (2008) Combined modality immunotherapy and chemotherapy: a new perspective. Cancer Immunol Immunother. doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0531-4
Reddy RM, Yeow WS, Chua A, Nguyen DM, Baras A, Ziauddin MF, Shamimi-Noori SM, Maxhimer JB, Schrump DS (2007) Rapid and profound potentiation of Apo2L/TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis in thoracic cancer cells by the histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A: the essential role of the mitochondria- mediated caspase activation cascade. Apoptosis 12(1):55–71
Riley T, Sontag E, Chen P, Levine A (2008) Transcriptional control of human p53- regulated genes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(5):402–412
Sato K, Lepage GA (1965) Metabolic effects of an antibiotic, Nsc-51954, on susceptible and resistant tumor cells. Cancer Res 25:477–483
Saulle E, Petronelli A, Pasquini L, Petrucci E, Mariani G, Biffoni M, Ferretti G, Scambia G, Benedetti-Panici P, Cognetti F, Humphreys R, Peschle C, Testa U (2007) Proteasome inhibitors sensitize ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 12(4):635–655
Sayers TJ, Brooks AD, Koh CY, Ma W, Seki N, Raziuddin A, Blazar BR, Zhang X, Elliott PJ, Murphy WJ (2003) The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 sensitizes neoplastic cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by reducing levels of c-FLIP. Blood 102(1):303–310
Schimmer AD, Thomas MP, Hurren R, Gronda M, Pellecchia M, Pond GR, Konopleva M, Gurfinkel D, Mawji IA, Brown E, Reed JC (2006) Identification of small molecules that sensitize resistant tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor-family death receptors. Cancer Res 66(4):2367–2375
Scudiero DA, Shoemaker RH, Paull KD, Monks A, Tierney S, Nofziger TH, Currens MJ, Seniff D, Boyd MR (1988) Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 48(17):4827–4833
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray CL, Baker K, Wood WI, Goddard AD, Godowski P, Ashkenazi A (1997) Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 277(5327):818–821
Singh R, Pervin S, Chaudhuri G (2002) Caspase-8-mediated BID cleavage and release of mitochondrial cytochrome c during Nomega-hydroxy-l-arginine-induced apoptosis in MDA-MB-468 cells. Antagonistic effects of l-ornithine. J Biol Chem 277(40):37630–37636
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D, Warren JT, Bokesch H, Kenney S, Boyd MR (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay foranticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 82(13):1107–1112
Smiley ST, Reers M, Mottola-Hartshorn C, Lin M, Chen A, Smith TW, Steele GD Jr, Chen LB (1991) Intracellular heterogeneity in mitochondrial membrane potentials revealed by a J-aggregate-forming lipophilic cation JC-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA A88(9):3671–3675
Song JH, Song DK, Pyrzynska B, Petruk KC, Van Meir EG, Hao C (2003) TRAIL triggers apoptosis in human malignant glioma cells through extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Brain Pathol 13(4):539–553
Tibbetts MD, Zheng L, Lenardo MJ (2003) The death effector domain protein family: regulators of cellular homeostasis. Nat Immunol 4(5):404–409
Tolcher AW, Mita M, Meropol NJ, von Mehren M, Patnaik A, Padavic K, Hill M, Mays T, McCoy T, Fox NL, Halpern W, Corey A, Cohen RB (2007) Phase I pharmacokinetic and biologic correlative study of mapatumumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody with agonist activity to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis- inducing ligand receptor-1. J Clin Oncol 25(11):1390–1395
Van Geelen CM, de Vries EG, de Jong S (2004) Lessons from TRAIL-resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer cells: paving the road to patient-tailored therapy. Drug Resist Updat 7(6):345–358
Vichai V, Kirtikara K (2006) Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat Protoc 1(3):1112–1116
Vulfovich M, Saba N (2005) Technology evaluation: mapatumumab, Human Genome Sciences/GlaxoSmithKline/Takeda. Curr Opin Mol Ther 7(5):502–510
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS, Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, Timour , Gerhart MJ, Schooley KA, Smith CA, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT (1997) TRAIL-R2: a novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for TRAIL. EMBO J 6(17):5386–5397
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, Smith C, Smolak P, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT, Schuh JC, Lynch DH (1999) Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 5(2):157–163
Wang MJ, Liu S, Liu Y, Zheng D (2007) Actinomycin D enhances TRAIL-induced caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Neurosci Res 59(1):40–46
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS, Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA et al (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3(6):673–682
Yang L, Wu S, Zhang Q, Liu F, Wu P (2007) 23, 24-Dihydrocucurbitacin B induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells (Bcap37). Cancer Lett 256(2):267–278
Zeng Y, Wu XX, Fiscella M, Shimada O, Humphreys R, Albert V, Kakehi Y (2006) Monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2 (TRAIL-R2) induces apoptosis in primary renal cell carcinoma cells in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Int J Oncol 28(2):421–430
Zhang JH, Chung TD, Oldenburg KR (1999) A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J Biomol Screen 4(2):67–73
Zhang L, Fang B (2005) Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 12(3):228–237
Zhu H, Guo W, Zhang L, Wu S, Teraishi F, Davis JJ, Dong F, Fang B (2005) Proteasome inhibitors-mediated TRAIL resensitization and Bik accumulation. Cancer Biol Ther 4(7):781–786
Zhu H, Zhang L, Huang X, Davis JJ, Jacob DA, Teraishi F, Chiao P, Fang B (2004) Overcoming acquired resistance to TRAIL by chemotherapeutic agents and calpain inhibitor I through distinct mechanisms. Mol Ther 9(5):666–673
Acknowledgments
Jennifer Wilson generously assisted with numerous XTT assays during the development of the TRAIL HTS; Heidi R. Bokesch conducted LC-MS and NMR quality control evaluations on compounds provided by the NCI Natural Products Repository; and Antony M. Wamiru and Nancy B. Shulley were instrumental in the design and trouble-shooting of Beckman 384-FX robot programs for use in the screen. The authors thank Kirk R. Gustafson for his time to read and comment on the manuscript. This project has been funded in whole or in part with federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, under contract N01-CO-12400. The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the Department of Health and Human Services, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the U.S. Government. This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, National Cancer Institute, Center for Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Booth, N.L., Sayers, T.J., Brooks, A.D. et al. A cell-based high-throughput screen to identify synergistic TRAIL sensitizers. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58, 1229–1244 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0637-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0637-8