Abstract
Purpose
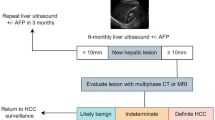
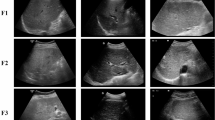
Liver biopsy was considered the gold standard for diagnosing liver fibrosis; however, with advancements in medical technology and increasing awareness of potential complications, the reliance on liver biopsy has diminished. Ultrasound is gaining popularity due to its wider availability and cost-effectiveness. This study examined the machine learning / deep learning (ML/DL) models for non-invasive liver fibrosis classification from ultrasound.
Methods
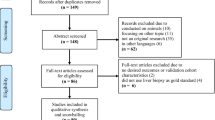
Following the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) protocol, we searched five academic databases using the query. We defined population, intervention, comparison, outcomes, and study design (PICOS) framework for the inclusion. Furthermore, Joana Briggs Institute (JBI) checklist for analytical cross-sectional studies is used for quality assessment.
Results
Among the 188 screened studies, 17 studies are selected. The methods are categorized as off-the-shelf (OTS), attention, generative, and ensemble classifiers. Most studies used OTS classifiers that combined pre-trained ML/DL methods with radiomics features to determine fibrosis staging. Although machine learning shows potential for fibrosis classification, there are limited external comparisons of interventions and prospective clinical trials, which limits their applicability.
Conclusion
With the recent success of ML/DL toward biomedical image analysis, automated solutions using ultrasound are developed for predicting liver diseases. However, their applicability is bounded by the limited and imbalanced retrospective studies having high heterogeneity. This challenge could be addressed by generating a standard protocol for study design by selecting appropriate population, interventions, outcomes, and comparison.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data sources are publicly accessible.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ACC:
-
Accuracy
- ACGAN:
-
Auxiliary classifier generative adversarial network
- AUROC:
-
Area under the receiver operating characteristic
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CNN:
-
Convolution neural network
- DL:
-
Deep learning
- HKD:
-
Homodyned k-distribution
- LSM:
-
Liver stiffness measurement
- LR:
-
Logistic regression
- ML:
-
Machine learning
- MMGN-AL:
-
Multi-modal fusion network with active learning
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- MSTNet:
-
Multi-scale texture network
- NPV:
-
Negative predictive value
- OTS:
-
Off-the-shelf
- PCFI:
-
Percentage of color fill-in
- pSWE:
-
Point shear wave elastography
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
- QUS:
-
Quantitative ultrasound
- RTE:
-
Real-time elastography
- ROI:
-
Region of Interest
- SEN:
-
Sensitivity
- SPE:
-
Specificity
- SWV:
-
Shear wave velocity
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- VGG:
-
Visual geometry group
References
Bataller, R., Brenner, D.A.: Liver fibrosis. The Journal of clinical investigation 115(2), 209–218 (2005)
Asrani, S.K., Devarbhavi, H., Eaton, J., Kamath, P.S.: Burden of liver diseases in the world. Journal of hepatology 70(1), 151–171 (2019)
Tapper, E.B., Lok, A.S.-F.: Use of liver imaging and biopsy in clinical practice. New England Journal of Medicine 377(8), 756–768 (2017)
Castera, L., Friedrich-Rust, M., Loomba, R.: Noninvasive assessment of liver disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 156(5), 1264–1281 (2019)
Mesropyan, N., Kupczyk, P., Dold, L., Weismu¨ller, T.J., Sprinkart, A.M., M¨adler: Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in autoimmune hepatitis: Diagnostic value of liver magnetic resonance parametric mapping including extracellular volume fraction. Abdominal Radiology 46(6), 2458–2466 (2021)
Wang, J., Wu, M., Linghu, R., Chang, J., Wu, M., Feng, C., Ren, X., Liu: Usefulness of new shear wave elastography technique for noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis b: a prospective multicenter study. Ultraschall in der Medizin-European Journal of Ultrasound 43(02), 1–10 (2022)
Liver, E.A., et al.: Easl-aleh clinical practice guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis. Journal of hepatology 63(1), 237–264 (2015)
Lampertico, P., Agarwal, K., Berg, T., Buti, M., Janssen, H.L., Papatheodoridis, G., Zoulim, F., Tacke, F.: Easl 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis b virus infection. Journal of hepatology 67(2), 370–398 (2017)
Li, H., Bhatt, M., Qu, Z., Zhang, S., Hartel, M.C., Khademhosseini, A., Cloutier, G.: Deep learning in ultrasound elastography imaging: A review. Medical Physics (2022)
Lee, J.H., Joo, I., Kang, T.W., Paik, Y.H., Sinn, D.H., Ha, S.Y., Kim, K., Choi, C., Lee, G., Yi, J., et al.: Deep learning with ultrasonography: automated classification of liver fibrosis using a deep convolutional neural network. European radiology 30(2), 1264–1273 (2020)
Treacher, A., Beauchamp, D., Quadri, B., Fetzer, D., Vij, A., Yokoo, T., Montillo, A.: Deep learning convolutional neural networks for the estimation of liver fibrosis severity from ultrasound texture. In: Medical Imaging 2019: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, vol. 10950, pp. 847–854 (2019). SPIE
Gotra, A., Sivakumaran, L., Chartrand, G., Vu, K.-N., Vandenbroucke-Menu, F., Kauffmann, C., Kadoury, S., Gallix, B., Guise, J.A., Tang, A.: Liver segmentation: indications, techniques and future directions. Insights into imaging 8(4), 377–392 (2017)
Anteby, R., Klang, E., Horesh, N., Nachmany, I., Shimon, O., Barash, Y., Kopylov, U., Soffer, S.: Deep learning for noninvasive liver fibrosis classification: A systematic review. Liver International 41(10), 2269–2278 (2021)
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D.G., Group, P.: Reprint—preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the prisma statement. Physical therapy 89(9), 873–880 (2009)
Covidence: Covidence systematic review software, Veritas Health Innovation, Melbourne, Australia. www.covidence.org. Online; accessed 18 October 2022 (2022)
Jiang, Z., Yamauchi, K., Yoshioka, K., Aoki, K., Kuroyanagi, S., Iwata, A., Yang, J., Wang, K.: Support vector machine-based feature selection for classification of liver fibrosis grade in chronic hepatitis c. Journal of medical systems 30, 389–394 (2006)
Alam, M.Z., Rahman, M.S., Rahman, M.S.: A random forest based predictor for medical data classification using feature ranking. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 15, 100180 (2019)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Meng, D., Zhang, L., Cao, G., Cao, W., Zhang, G., Hu, B.: Liver fibrosis classification based on transfer learning and fcnet for ultrasound images. Ieee Access 5, 5804–5810 (2017)
Zheng, M., Xu, J., Shen, Y., Tian, C., Li, J., Fei, L., Zong, M., Liu, X.: Attentionbased cnns for image classification: a survey. In: Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 2171, p. 012068 (2022). IOP Publishing
Frid-Adar, M., Diamant, I., Klang, E., Amitai, M., Goldberger, J., Greenspan, H.: Gan-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased cnn performance in liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing 321, 321–331 (2018)
Dandan, L., Huanhuan, M., Xiang, L., Yu, J., Jing, J., Yi, S.: Classification of diffuse liver diseases based on ultrasound images with multimodal features. In: 2019 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), pp. 1–5 (2019). IEEE
JBI: Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tool. https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools. Online; accessed 18 October 2022 (2022)
Xie, Y., Chen, S., Jia, D., Li, B., Zheng, Y., Yu, X.: Artificial intelligence-based feature analysis of ultrasound images of liver fibrosis. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2022 (2022)
Zhou, Z., Zhang, Z., Gao, A., Tai, D.-I., Wu, S., Tsui, P.-H.: Liver fibrosis assessment using radiomics of ultrasound homodyned-k imaging based on the artificial neural network estimator. Ultrasonic Imaging 44(5-6), 229–241 (2022)
Feng, X., Chen, X., Dong, C., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Ding, R., Huang, Q.: Multi-scale information with attention integration for classification of liver fibrosis in b-mode us image. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 215, 106598 (2022)
Duan, Y.-Y., Qin, J., Qiu, W.-Q., Li, S.-Y., Li, C., Liu, A.-S., Chen, X., Zhang, C.-X.: Performance of a generative adversarial network using ultrasound images to stage liver fibrosis and predict cirrhosis based on a deep-learning radiomics nomogram. Clinical radiology 77(10), 723–731 (2022)
Ruan, D., Shi, Y., Jin, L., Yang, Q., Yu, W., Ren, H., Zheng, W., Chen, Y., Zheng, N., Zheng, M.: An ultrasound image-based deep multi-scale texture network for liver fibrosis grading in patients with chronic hbv infection. Liver International 41(10), 2440–2454 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, D., Peng, F., Cui, S., Yang, Z.: Ultrasonic image fibrosis staging based on machine learning for chronic liver disease. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Medical Imaging Physics and Engineering (ICMIPE), pp. 1–5 (2021). IEEE
Gao, A., Wu, S., Tai, D.-I., Zhou, Z., Tsui, P.-H.: Ultrasonic evaluation of liver fibrosis using the homodyned k distribution with an artificial neural network estimator. In: 2021 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), pp. 1–4 (2021). IEEE
Gao, L., Zhou, R., Dong, C., Feng, C., Li, Z., Wan, X., Liu, L.: Multi-modal active learning for automatic liver fibrosis diagnosis based on ultrasound shear wave elastography. In: 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pp. 410–414 (2021). IEEE
Trombini, M., Borro, P., Ziola, S., Dellepiane, S.: A digital image processing approach for hepatic diseases staging based on the glisson’s capsule. In: 2020 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Control and Instrumentation Engineering (ICECIE), pp. 1–6 (2020). IEEE
Brattain, L.J., Ozturk, A., Telfer, B.A., Dhyani, M., Grajo, J.R., Samir, A.E.: Image processing pipeline for liver fibrosis classification using ultrasound shear wave elastography. Ultrasound in medicine and biology 46(10), 2667–2676 (2020)
Xue, L.-Y., Jiang, Z.-Y., Fu, T.-T., Wang, Q.-M., Zhu, Y.-L., Dai, M., Wang, W.-P., Yu, J.-H., Ding, H.: Transfer learning radiomics based on multimodal ultrasound imaging for staging liver fibrosis. European radiology 30(5), 2973–2983 (2020)
Kagadis, G.C., Drazinos, P., Gatos, I., Tsantis, S., Papadimitroulas, P., Spiliopoulos: Deep learning networks on chronic liver disease assessment with fine-tuning of shear wave elastography image sequences. Physics in Medicine & Biology 65(21), 215027 (2020)
Durot, I., Akhbardeh, A., Sagreiya, H., Loening, A.M., Rubin, D.L.: A new multimodel machine learning framework to improve hepatic fibrosis grading using ultrasound elastography systems from different vendors. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 46(1), 26–33 (2020)
Liu, J., Wang, W., Guan, T., Zhao, N., Han, X., Li, Z.: Ultrasound liver fibrosis diagnosis using multi-indicator guided deep neural networks. In: International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, pp. 230–237 (2019). Springer
Li, W., Huang, Y., Zhuang, B.-W., Liu, G.-J., Hu, H.-T., Li, X., Liang, J.-Y., Wang, Z., Huang, X.-W., Zhang, C.-Q., et al.: Multiparametric ultrasomics of significant liver fibrosis: A machine learning-based analysis. European radiology 29(3), 1496–1506 (2019)
Brattain, L.J., Telfer, B.A., Dhyani, M., Grajo, J.R., Samir, A.E.: Objective liver fibrosis estimation from shear wave elastography. In: 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 1–5 (2018). IEEE
Poynard, T., Vergniol, J., Ngo, Y., Foucher, J., Munteanu, M., Merrouche, W., Colombo, M., Thibault, V., Schiff, E., Brass, C.A., et al.: Staging chronic hepatitis c in seven categories using fibrosis biomarker (fibrotest™) and transient elastography (fibroscan®). Journal of hepatology 60(4), 706–714 (2014)
Alvarez, F., Berg, P., Bianchi, F.B., Bianchi, L., Burroughs, A., Cancado, E.L., Chapman, R., Cooksley, W., Czaja, A., Desmet, V., et al.: International autoimmune hepatitis group report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. Journal of hepatology 31(5), 929–938 (1999)
Gillies, R.J., Kinahan, P.E., Hricak, H.: Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278(2), 563–577 (2016)
Tamuly, S., Jyotsna, C., Amudha, J.: Deep learning model for image classification. In: Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing: ICCVBIC 2019, pp. 312– 320 (2020). Springer
Funding
There is no involvement of external funding source
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally in conceptualizing the research problem and preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Punn, N.S., Patel, B. & Banerjee, I. Liver fibrosis classification from ultrasound using machine learning: a systematic literature review. Abdom Radiol 49, 69–80 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-04081-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-04081-y