Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the clinical efficacy of celiac plexus block (CPB) combined with 125I seeds implantation (ISI) for refractory epigastric pain from abdominal malignancies.
Methods
The data of 81 patients with refractory epigastric pain [visual analog scale (VAS) score ≥ 4] from abdominal malignancies were collected in this retrospective case–control study. Group A (n = 40) was treated with CPB alone, while Group B (n = 41) underwent CPB combined with ISI. The primary study endpoints were the VAS score, quality of life (QoL), and local tumor control (LTC) rate. The secondary endpoints were complications, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
Results
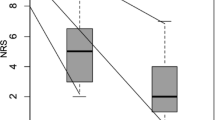
The VAS scores at week 2 (T2), week 4 (T4), week 8 (T8), and week 12 (T12) in both groups were significantly lower compared with the pretreatment values (all P < 0.01). VAS scores in Group B showed a sustained decrease, especially for “mild pain” and “moderate pain,” while the VAS scores in Group A rebounded at T8 and T12 (both P < 0.01). The QoL in Group B improved significantly from T4 until T12, which better than that at T12 in Group A (all P < 0.01). The LTC rates at T8 were 35.0% and 92.7% in Groups A and B, respectively, with a significant difference (P < 0.01). Group B had a slightly lower complication rate and a slightly longer median PFS/OS than group A, but neither was statistically different (P = 0.09 and P = 0.99, respectively).
Conclusion
CPB combined with ISI performs more sustained pain relief (up to 12 weeks) compared to CPB alone, and ultimately improves the patients’ QoL.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
In addition to the raw data in the manuscript, the datasets used are available from the corresponding author on Availability of data and materials.
References
Lohse I, Brothers SP (2020) Pathogenesis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer Related Pain. Anticancer Res 40(4):1789-1796. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.14133.
Cox-Martin E, Anderson-Mellies A, Borges V, Bradley C (2020) Chronic pain, health-related quality of life, and employment in working-age cancer survivors. J Cancer Surviv 14(2):179-187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-019-00843-0.
Huang L, Tao F, Wang Z, Wan H, Qu P, Zheng H (2014) Combined neurolytic block of celiac and superior hypogastric plexuses for incapacitating upper abdominal cancer pain. J BUON 19(3):826-830.
Vig S, Bhan S, Bhatnagar S (2021) Celiac Plexus Block - An Old Technique with New Developments. Pain Physician 24(5):379-398.
Cornman-Homonoff J, Holzwanger DJ, Lee KS, Madoff DC, Li D (2017) Celiac Plexus Block and Neurolysis in the Management of Chronic Upper Abdominal Pain. Semin Intervent Radiol 34(4):376-386. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1608861.
Ashlock K (2018) Celiac Plexus Block: Management of Abdominal Pain in Patients With Late-Stage Cancer. Clin J Oncol Nurs 22(6):663-665. https://doi.org/10.1188/18.CJON.663-665.
Osman SO, Horn S, Brady D, McMahon SJ, Yoosuf AB, Mitchell D, Crowther K, Lyons CA, Hounsell AR, Prise KM, McGarry CK, Jain S, O'Sullivan JM (2017) Prostate cancer treated with brachytherapy; an exploratory study of dose-dependent biomarkers and quality of life. Radiat Oncol 12(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-017-0792-1.
Yu W, Xie Q, Li J, Tang J, Yang W, Tao Y (2022) Salvage 125I brachytherapy for liver metastases of colorectal cancer in anatomically challenging locations after failure of systemic chemotherapy-A retrospective study. Brachytherapy 21(5):592-598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brachy.2022.05.006.
Jiao D, Ren K, Li Z, Shui S, Han X (2017) Clinical role of guidance by C-arm CT for 125I brachytherapy on pulmonary tumors. Radiol Med 122(11):829-836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-017-0791-1.
Jiao D, Xu K, Mukhiya G, Liu Y, Wu K, Li Z, Ren J, Han X (2022) Brachytherapy Drainage Catheter and Chemotherapy for Unresectable Pancreatic Carcinoma Combined with Obstructive Jaundice. Front Oncol 12:941336. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.941336.
He X, Liu M, Zhang M, Sequeiros RB, Xu Y, Wang L, Liu C, Wang Q, Zhang K, Li C (2020) A novel three-dimensional template combined with MR-guided 125I brachytherapy for recurrent glioblastoma. Radiat Oncol 15(1):146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-020-01586-4.
Swarm RA, Paice JA, Anghelescu DL, Are M, Bruce JY, Buga S, Chwistek M, Cleeland C, Craig D, Gafford E, Greenlee H, Hansen E, Kamal AH, Kamdar MM, LeGrand S, Mackey S, McDowell MR, Moryl N, Nabell LM, Nesbit S; BCPS; O'Connor N, Rabow MW, Rickerson E, Shatsky R, Sindt J, Urba SG, Youngwerth JM, Hammond LJ, Gurski LA (2019) Adult Cancer Pain, Version 3.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 17(8):977–1007. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.0038.
Filippiadis DK, Binkert C, Pellerin O, Hoffmann RT, Krajina A, Pereira PL (2017) Cirse Quality Assurance Document and Standards for Classification of Complications: The Cirse Classification System. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 40(8):1141-1146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1703-4.
Seyal AR, Gonzalez-Guindalini FD, Arslanoglu A, Harmath CB, Lewandowski RJ, Salem R, Yaghmai V (2015) Reproducibility of mRECIST in assessing response to transarterial radioembolization therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 62(4):1111-1121. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27915.
Sachdev AH, Gress FG (2018) Celiac Plexus Block and Neurolysis: A Review. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 28(4):579-586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giec.2018.06.004.
Abdel-Ghaffar ME, Ismail SA, Ismail RA, Abdelrahman MM, Abuelnaga ME (2022) Comparison Between Two Volumes of 70% Alcohol in Single Injection Ultrasound-Guided Celiac Plexus Neurolysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain Physician 25(3):293-303.
Abdelghaffar NA, El-Rahmawy GF, Elmaddawy A, El-Badrawy A (2019) Neurólise do tronco celíaco com o uso de agulha única versus agulha dupla no manejo da dor abdominal maligna: estudo randômico controlado [Single needle versus double needle celiac trunk neurolysis in abdominal malignancy pain management: a randomized controlled trial]. Braz J Anesthesiol 69(3):284-290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjan.2018.12.005.
Matsumoto T, Yoshimatsu R, Osaki M, Miyatake K, Yamanishi T, Yamagami T (2022) Computed tomography-guided single celiac plexus neurolysis analgesic efficacy and safety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Abdom Radiol (NY) 47(11):3892-3906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03670-7.
Mercadante S, Catala E, Arcuri E, Casuccio A (2003) Celiac plexus block for pancreatic cancer pain: factors influencing pain, symptoms and quality of life. J Pain Symptom Manage 26(6):1140-1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2003.04.004.
Ma JX, Jin ZD, Si PR, Liu Y, Lu Z, Wu HY, Pan X, Wang LW, Gong YF, Gao J, Zhao-shen L (2011) Continuous and low-energy 125I seed irradiation changes DNA methyltransferases expression patterns and inhibits pancreatic cancer tumor growth. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30(1):35. Published 2011 Apr 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-30-35.
Gai B, Zhang F (2018) Chinese expert consensus on radioactive 125I seeds interstitial implantation brachytherapy for pancreatic cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 14(7):1455-1462. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_96_18.
Wong GY, Schroeder DR, Carns PE, Wilson JL, Martin DP, Kinney MO, Mantilla CB, Warner DO (2004) Effect of neurolytic celiac plexus block on pain relief, quality of life, and survival in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 291(9):1092-1099. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.291.9.1092.
Urits I, Jones MR, Orhurhu V, Peck J, Corrigan D, Hubble A, Andrews M, Feng R, Manchikanti L, Kaye AD, Kaye RJ, Viswanath O (2022) A Comprehensive Review of the Celiac Plexus Block for the Management of Chronic Abdominal Pain. Curr Pain Headache Rep 24(8):42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-020-00878-4.
Funding
This study was funded by the Major science and technology projects of Henan Province in 2022 [grant numbers 221100310100].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YL, CZ, and DJ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YL and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the Ethics Committees of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Informed consent
The requirement for informed consent was waived by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University because of the retrospective nature of the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhang, C., Song, M. et al. Celiac plexus block combined with 125I seeds for refractory epigastric pain from abdominal malignancies: a retrospective case–control study. Abdom Radiol 48, 2157–2166 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03905-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03905-1