Abstract
Purpose
To assess the role of radiomics in detection of high-risk (pT3-4) colon cancer and develop a combined model that combines both radiomics and CT staging of colon cancer.
Methods
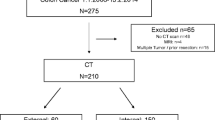
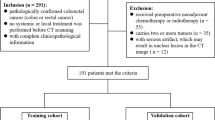
We included 292 colon cancer patients who underwent pre-operative CT and primary surgical resection within 2 months. Three-dimensional segmentations and CT staging of primary colon tumors were done. From each 3D segmentation of colon tumor, radiomic features were automatically extracted. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify associations between radiomic features and high-risk (pT3-4) colon tumors. A combined model that integrated both radiomics and CT staging was developed and their diagnostic performance was compared with that of conventional CT staging. Tenfold cross-validation was used to validate the performance of the model and CT staging.
Results
The model that combined radiomic features and CT staging demonstrated a significantly better performance in detection of high-risk colon tumors in training set (AUC = 0.799, 95% CI: 0.720–0.839 for combined model and AUC = 0.697, 95% CI = 0.538–0.756 for CT staging only, p < 0.001 for difference). Cross-validation results also demonstrated significantly better detection performance of combined model (AUC = 0.727, 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.621–0.777 for combined model and AUC = 0.628, 95% CI = 0.558–0.689 for CT staging only, Boot CI = 0.099).
Conclusion
CT radiomic features of primary colon cancer, combined with CT staging, can improve the detection of high-risk colon cancer patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foxtrot Collaborative G (2012) Feasibility of preoperative chemotherapy for locally advanced, operable colon cancer: the pilot phase of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 13 (11):1152-1160. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70348-0
Dighe S, Swift I, Magill L, Handley K, Gray R, Quirke P, Morton D, Seymour M, Warren B, Brown G (2012) Accuracy of radiological staging in identifying high-risk colon cancer patients suitable for neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a multicentre experience. Colorectal Dis 14 (4):438-444. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1318.2011.02638.x
Nerad E, Lahaye MJ, Maas M, Nelemans P, Bakers FC, Beets GL, Beets-Tan RG (2016) Diagnostic Accuracy of CT for Local Staging of Colon Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 207 (5):984-995. doi:https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.15.15785
van den Berg I, van de Weerd S, Roodhart JML, Vink GR, van den Braak R, Jimenez CR, Elias SG, van Vliet D, Koelink M, Hong E, van Grevenstein WMU, van Oijen MGH, Beets-Tan RGH, van Krieken J, JNM IJ, Medema JP, Koopman M, group CO-s (2020) Improving clinical management of colon cancer through CONNECTION, a nation-wide colon cancer registry and stratification effort (CONNECTION II trial): rationale and protocol of a single arm intervention study. BMC Cancer 20 (1):776. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-07236-y
Arredondo J, Gonzalez I, Baixauli J, Martinez P, Rodriguez J, Pastor C, Ribelles MJ, Sola JJ, Hernandez-Lizoain JL (2014) Tumor response assessment in locally advanced colon cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Gastrointest Oncol 5 (2):104-111. doi:https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2014.006
Chalabi M, Fanchi LF, Dijkstra KK, Van den Berg JG, Aalbers AG, Sikorska K, Lopez-Yurda M, Grootscholten C, Beets GL, Snaebjornsson P, Maas M, Mertz M, Veninga V, Bounova G, Broeks A, Beets-Tan RG, de Wijkerslooth TR, van Lent AU, Marsman HA, Nuijten E, Kok NF, Kuiper M, Verbeek WH, Kok M, Van Leerdam ME, Schumacher TN, Voest EE, Haanen JB (2020) Neoadjuvant immunotherapy leads to pathological responses in MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient early-stage colon cancers. Nat Med 26 (4):566-576. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0805-8
Jakobsen A, Andersen F, Fischer A, Jensen LH, Jorgensen JC, Larsen O, Lindebjerg J, Ploen J, Rafaelsen SR, Vilandt J (2015) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced colon cancer. A phase II trial. Acta Oncol 54 (10):1747-1753. doi:https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186X.2015.1037007
Yao X, Sun C, Xiong F, Zhang X, Cheng J, Wang C, Ye Y, Hong N, Wang L, Liu Z, Meng X, Wang Y, Tian J (2020) Radiomic signature-based nomogram to predict disease-free survival in stage II and III colon cancer. Eur J Radiol 131:109205. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109205
Dai W, Mo S, Han L, Xiang W, Li M, Wang R, Tong T, Cai G (2020) Prognostic and predictive value of radiomics signatures in stage I-III colon cancer. Clin Transl Med 10 (1):288-293. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.31
Huang YQ, Liang CH, He L, Tian J, Liang CS, Chen X, Ma ZL, Liu ZY (2016) Development and Validation of a Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. J Clin Oncol 34 (18):2157-2164. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.65.9128
Fan S, Li X, Cui X, Zheng L, Ren X, Ma W, Ye Z (2019) Computed Tomography-Based Radiomic Features Could Potentially Predict Microsatellite Instability Status in Stage II Colorectal Cancer: A Preliminary Study. Acad Radiol 26 (12):1633-1640. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2019.02.009
Golia Pernicka JS, Gagniere J, Chakraborty J, Yamashita R, Nardo L, Creasy JM, Petkovska I, Do RRK, Bates DDB, Paroder V, Gonen M, Weiser MR, Simpson AL, Gollub MJ (2019) Radiomics-based prediction of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer at initial computed tomography evaluation. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44 (11):3755-3763. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02117-w
Yang L, Dong D, Fang M, Zhu Y, Zang Y, Liu Z, Zhang H, Ying J, Zhao X, Tian J (2018) Can CT-based radiomics signature predict KRAS/NRAS/BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer? Eur Radiol 28 (5):2058-2067. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5146-8
Wu J, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Chen A, Li X, Wu T, Li J, Guo Y, Liu A (2019) Radiomics Analysis of Iodine-Based Material Decomposition Images With Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Imaging for Preoperatively Predicting Microsatellite Instability Status in Colorectal Cancer. Front Oncol 9:1250. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01250
Hunter C, Siddiqui M, Georgiou Delisle T, Blake H, Jeyadevan N, Abulafi M, Swift I, Toomey P, Brown G (2017) CT and 3-T MRI accurately identify T3c disease in colon cancer, which strongly predicts disease-free survival. Clin Radiol 72 (4):307-315. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2016.11.014
Traverso A, Kazmierski M, Welch ML, Weiss J, Fiset S, Foltz WD, Gladwish A, Dekker A, Jaffray D, Wee L, Han K (2020) Sensitivity of radiomic features to inter-observer variability and image pre-processing in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) maps of cervix cancer patients. Radiother Oncol 143:88-94. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.08.008
Mackin D, Fave X, Zhang L, Fried D, Yang J, Taylor B, Rodriguez-Rivera E, Dodge C, Jones AK, Court L (2015) Measuring Computed Tomography Scanner Variability of Radiomics Features. Invest Radiol 50 (11):757-765. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000180
Rizzo S, Botta F, Raimondi S, Origgi D, Fanciullo C, Morganti AG, Bellomi M (2018) Radiomics: the facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur Radiol Exp 2 (1):36. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s41747-018-0068-z
Bodalal Z, Trebeschi S, Nguyen-Kim TDL, Schats W, Beets-Tan R (2019) Radiogenomics: bridging imaging and genomics. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44 (6):1960-1984. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02028-w
Bodalal Z, Trebeschi S, Beets-Tan R (2018) Radiomics: a critical step towards integrated healthcare. Insights Imaging 9 (6):911-914. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-018-0669-3
Zanfardino M, Franzese M, Pane K, Cavaliere C, Monti S, Esposito G, Salvatore M, Aiello M (2019) Bringing radiomics into a multi-omics framework for a comprehensive genotype-phenotype characterization of oncological diseases. J Transl Med 17 (1):337. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-2073-2
Perrin T, Midya A, Yamashita R, Chakraborty J, Saidon T, Jarnagin WR, Gonen M, Simpson AL, Do RKG (2018) Short-term reproducibility of radiomic features in liver parenchyma and liver malignancies on contrast-enhanced CT imaging. Abdom Radiol (NY) 43 (12):3271-3278. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1600-6
Acknowledgements
The content of this publication was previously presented in European Congress of Radiology 2021.
Funding
No financial support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This is a retrospective study and local institutional boards from two tertiary centers approved and waived the requirement for informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, E.K., Bodalal, Z., Landolfi, F. et al. Identifying high-risk colon cancer on CT an a radiomics signature improve radiologist’s performance for T staging?. Abdom Radiol 47, 2739–2746 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03534-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03534-0