Abstract
Purpose
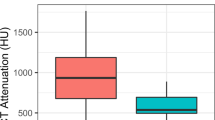
To compare noise texture and accuracy to differentiate uric acid from non-uric acid urinary stones among four different single-source and dual-source DECT approaches in an ex vivo phantom study.
Methods
Thirty-two urinary stones embedded in gelatin were mounted on a Styrofoam disk and placed into a water-filled phantom. The phantom was imaged using four different DECT approaches: (A) dual-source DECT (DS-DE); (B) 1st generation split-filter single-source DECT (SF1-TB); (C) 2nd generation split-filter single-source DECT (SF2-TB) and (D) 2nd generation split-filter single-source DECT using serial acquisitions (SF2-TS). Two different radiation doses (3 mGy and 6 mGy) were used. Noise texture was compared by assessing the average spatial frequency (fav) of the normalized noise power spectrum (nNPS). ROC curves for stone classification were computed and the accuracy for different dual-energy ratio cutoffs was derived.
Results
NNPS demonstrated comparable noise texture among A, C, and D (fav-range 0.18–0.19) but finer noise texture for B (fav = 0.27). Stone classification showed an accuracy of 96.9%, 96.9%, 93.8%, 93.8% for A, B, C, D for low-dose, respectively, and 100%, 96.9%, 96.9%, 100% for routine dose. The vendor-specified cutoff for the dual-energy ratio was optimal except for the low-dose scan in D for which the accuracy was improved from 93.8 to 100% using an optimized cutoff.
Conclusion
Accuracy to differentiate uric acid from non-uric acid stones was high among four single-source and dual-source DECT approaches for low- and routine dose DECT scans. Noise texture differed only slightly for the first-generation split-filter approach.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data and material is freely available.
Abbreviations
- SECT:
-
Single-energy computed tomography
- DECT:
-
Dual-energy computed tomography
- SF-DE:
-
Split-filter dual-energy
- DS-DE:
-
Dual source dual-energy
- SF1-TB:
-
1st generation split filter twin beam
- SF2-TB:
-
2nd generation split filter twin beam
- SF2-TS:
-
2nd generation split-filter twin spiral
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- nNPS:
-
Normalized noise power spectrum
- f av :
-
Average spatial frequency
- f peak :
-
Peak spatial frequency
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
References
C.D. Scales, A.C. Smith, J.M. Hanley, C.S. Saigal, Prevalence of Kidney Stones in the United States, Eur. Urol. 62 (2012) 160–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2012.03.052.
V.O. Edvardsson, O.S. Indridason, G. Haraldsson, O. Kjartansson, R. Palsson, Temporal trends in the incidence of kidney stone disease, Kidney Int. 83 (2013) 146–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2012.320.
P. Balthazar, G. Sadigh, D. Hughes, A.B. Rosenkrantz, T. Hanna, R. Duszak, Increasing Use, Geographic Variation, and Disparities in Emergency Department CT for Suspected Urolithiasis, J. Am. Coll. Radiol. JACR. 16 (2019) 1547–1553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2019.05.033.
A.C. Westphalen, R.Y. Hsia, J.H. Maselli, R. Wang, R. Gonzales, Radiological Imaging of Patients With Suspected Urinary Tract Stones: National Trends, Diagnoses, and Predictors, Acad. Emerg. Med. 18 (2011) 699–707. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1553-2712.2011.01103.x.
C.-W. Fwu, P.W. Eggers, P.L. Kimmel, J.W. Kusek, Z. Kirkali, Emergency department visits, use of imaging, and drugs for urolithiasis have increased in the United States, Kidney Int. 83 (2013) 479–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2012.419.
A. Lukasiewicz, M. Bhargavan-Chatfield, L. Coombs, M. Ghita, J. Weinreb, G. Gunabushanam, C.L. Moore, Radiation dose index of renal colic protocol CT studies in the United States: a report from the American College of Radiology National Radiology Data Registry, Radiology. 271 (2014) 445–451. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14131601.
K. Weisenthal, P. Karthik, M. Shaw, D. Sengupta, M. Bhargavan-Chatfield, J. Burleson, A. Mustafa, M. Kalra, C. Moore, Evaluation of Kidney Stones with Reduced-Radiation Dose CT: Progress from 2011-2012 to 2015-2016-Not There Yet, Radiology. 286 (2018) 581–589. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017170285.
M. Diamond, D. Shin, J. Wang, B. Samuelsen, C. LeBedis, Imaging of Nontraumatic Upper Urinary Tract Emergencies, Semin. Roentgenol. 55 (2020) 180–196. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ro.2019.10.009.
E. Bres–Niewada, B. Dybowski, P. Radziszewski, Predicting stone composition before treatment – can it really drive clinical decisions?, Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 67 (2014) 392–396. https://doi.org/10.5173/ceju.2014.04.art15.
A. Euler, A. Parakh, A.L. Falkowski, S. Manneck, D. Dashti, B. Krauss, Z. Szucs-Farkas, S.T. Schindera, Initial Results of a Single-Source Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Technique Using a Split-Filter: Assessment of Image Quality, Radiation Dose, and Accuracy of Dual-Energy Applications in an In Vitro and In Vivo Study, Invest. Radiol. 51 (2016) 491–498. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000257.
A. Euler, M.M. Obmann, Z. Szucs-Farkas, A. Mileto, C. Zaehringer, A.L. Falkowski, D.J. Winkel, D. Marin, B. Stieltjes, B. Krauss, S.T. Schindera, Comparison of image quality and radiation dose between split-filter dual-energy images and single-energy images in single-source abdominal CT, Eur. Radiol. 28 (2018) 3405–3412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5338-x.
M. Eichler, M. May, M. Wiesmueller, M. Saake, R. Heiss, M. Uder, W. Wuest, Single source split filter dual energy: Image quality and liver lesion detection in abdominal CT, Eur. J. Radiol. 126 (2020) 108913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108913.
O. Mm, C. A, C. J, H. V, S. B, B. Dt, Y. Bm, B. Mr, Quantitative enhancement thresholds and machine learning algorithms for the evaluation of renal lesions using single-phase split-filter dual-energy CT., Abdom. Radiol. N. Y. 45 (2020) 1922–1928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02195-w.
X. Zheng, Y. Liu, M. Li, Q. Wang, B. Song, Dual-energy computed tomography for characterizing urinary calcified calculi and uric acid calculi: A meta-analysis, Eur. J. Radiol. 85 (2016) 1843–1848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.08.013.
T.A. McGrath, R.A. Frank, N. Schieda, B. Blew, J.-P. Salameh, P.M.M. Bossuyt, M.D.F. McInnes, Diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) to differentiate uric acid from non-uric acid calculi: systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur. Radiol. 30 (2020) 2791–2801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06559-0.
E. Samei, D. Bakalyar, K.L. Boedeker, S. Brady, J. Fan, S. Leng, K.J. Myers, L.M. Popescu, J.C.R. Giraldo, F. Ranallo, J. Solomon, J. Vaishnav, J. Wang, Performance evaluation of computed tomography systems: Summary of AAPM Task Group 233, Med. Phys. 46 (2019) e735–e756. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.13763.
F. Morsbach, M.C. Wurnig, D. Müller, B. Krauss, J.G. Korporaal, H. Alkadhi, Feasibility of Single-Source Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Urinary Stone Characterization and Value of Iterative Reconstructions, Invest. Radiol. 49 (2014) 125–130. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000002.
J. Menke, Comparison of Different Body Size Parameters for Individual Dose Adaptation in Body CT of Adults, Radiology. 236 (2005) 565–571. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2362041327.
J.B. Solomon, O. Christianson, E. Samei, Quantitative comparison of noise texture across CT scanners from different manufacturers, Med. Phys. 39 (2012) 6048–6055. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4752209.
J. Solomon, J. Wilson, E. Samei, Characteristic image quality of a third generation dual-source MDCT scanner: Noise, resolution, and detectability, Med. Phys. 42 (2015) 4941–4953. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4923172.
A. Euler, J. Solomon, D. Marin, R.C. Nelson, E. Samei, A Third-Generation Adaptive Statistical Iterative Reconstruction Technique: Phantom Study of Image Noise, Spatial Resolution, Lesion Detectability, and Dose Reduction Potential, Am. J. Roentgenol. 210 (2018) 1301–1308. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.17.19102.
RStudio Team (2020), RStudio: Integrated Development for R., Boston, MA, n.d. http://www.rstudio.com/.
X. Robin, N. Turck, A. Hainard, N. Tiberti, F. Lisacek, J.-C. Sanchez, M. Müller, pROC: an open-source package for R and S + to analyze and compare ROC curves, BMC Bioinformatics. 12 (2011) 77. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-77.
M. Pansini, F. Morsbach, T. Schubert, J. Hohmann, B. Kovács, Z. Szucs-Farkas, S.T. Schindera, Feasibility of Dose Optimization in a Second-Generation Dual-Source CT Scanner for a Manufacturer-Recommended Urolithiasis Protocol for Imaging Renal Stones, AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 206 (2016) 348–354. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.15.15204.
C. Thomas, O. Patschan, D. Ketelsen, I. Tsiflikas, A. Reimann, H. Brodoefel, M. Buchgeister, U. Nagele, A. Stenzl, C. Claussen, A. Kopp, M. Heuschmid, H.-P. Schlemmer, Dual-energy CT for the characterization of urinary calculi: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a low-dose scanning protocol, Eur. Radiol. 19 (2009) 1553–1559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-009-1300-2.
M. Qu, L. Yu, D.G. Cardona, Y. Liu, X. Duan, S. Ai, S. Leng, M. Shiung, C.H. McCollough, Radiation Dose Reduction in Dual-Energy CT: Does It Affect the Accuracy of Urinary Stone Characterization?, AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 205 (2015) W172-176. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.14.12929.
A. Spek, F. Strittmatter, A. Graser, P. Kufer, C. Stief, M. Staehler, Dual energy can accurately differentiate uric acid-containing urinary calculi from calcium stones, World J. Urol. 34 (2016) 1297–1302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-015-1756-4.
G. Apfaltrer, A. Dutschke, P.A.T. Baltzer, C. Schestak, M. Özsoy, C. Seitz, J. Veser, E. Petter, T.H. Helbich, H. Ringl, P. Apfaltrer, Substantial radiation dose reduction with consistent image quality using a novel low-dose stone composition protocol, World J. Urol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03082-6.
H. Mahalingam, A. Lal, A.K. Mandal, S.K. Singh, S. Bhattacharyya, N. Khandelwal, Evaluation of low-dose dual energy computed tomography for in vivo assessment of renal/ureteric calculus composition, Korean J. Urol. 56 (2015) 587–593. https://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2015.56.8.587.
A. Franken, P.A. Gevenois, A.V. Muylem, N. Howarth, C. Keyzer, In Vivo Differentiation of Uric Acid Versus Non-Uric Acid Urinary Calculi With Third-Generation Dual-Source Dual-Energy CT at Reduced Radiation Dose, AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 210 (2018) 358–363. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.17.18091.
B. Mussmann, M. Hardy, H. Jung, M. Ding, P.J. Osther, O. Graumann, Can Dual Energy CT with Fast kV-Switching Determine Renal Stone Composition Accurately?, Acad. Radiol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2020.02.007.
J.S. Kriegshauser, A.C. Silva, R.G. Paden, M. He, M.R. Humphreys, S.I. Zell, Y. Fu, T. Wu, Ex Vivo Renal Stone Characterization with Single-Source Dual-Energy Computed Tomography: A Multiparametric Approach, Acad. Radiol. 23 (2016) 969–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2016.03.009.
R.P. Marcus, J.G. Fletcher, A. Ferrero, S. Leng, A.F. Halaweish, R. Gutjahr, T.J. Vrtiska, M.L. Wells, F.T. Enders, C.H. McCollough, Detection and Characterization of Renal Stones by Using Photon-Counting-based CT, Radiology. 289 (2018) 436–442. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018180126.
C.H. McCollough, S. Leng, L. Yu, J.G. Fletcher, Dual- and Multi-Energy CT: Principles, Technical Approaches, and Clinical Applications, Radiology. 276 (2015) 637–653. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015142631.
F.L. Coe, A. Evan, E. Worcester, Kidney stone disease, J. Clin. Invest. 115 (2005) 2598–2608. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI26662.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs. Sarah Euler for revising the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Dominik Nakhostin and André Euler. Statistical analysis was done by Thomas Sartoretti. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dominik Nakhostin and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Bernhard Krauss is an employee of Siemens Healthcare GmbH. This author had no control over the data at any point during the study. The other authors do not have any relevant disclosures.
Consent to participate
Not needed because of design as phantom study.
Consent for participation
Not needed because of design as phantom study.
Code availability
Code will be made available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Ethics approval
Not needed because of design as phantom study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakhostin, D., Sartoretti, T., Eberhard, M. et al. Low-dose dual-energy CT for stone characterization: a systematic comparison of two generations of split-filter single-source and dual-source dual-energy CT. Abdom Radiol 46, 2079–2089 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02852-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02852-5