Abstract
Objective
To describe the CT and MR imaging findings after microwave ablation of clinical stage 1 renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods
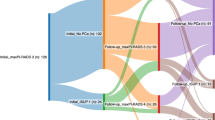
This single-center retrospective study was performed under a waiver of informed consent. 49 patients (38 M/11F, mean age 66 ± 9.0) with 52 cT1a RCC and 19 patients (10M/9F, mean age 67 ± 9.7) with 19 cT1b RCC were treated with percutaneous microwave ablation between January 2012 and June 2014. The size and volume of the RCC and ablation zone were measured and the kidney, ablation zones and retroperitoneum were assessed at immediate post-procedure CT and surveillance CT and MRI.
Results
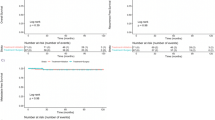
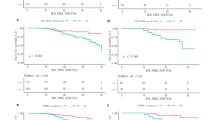
Median imaging follow-up was 18 months (IQR 12–28). Ablation zones were heterogeneously hyperintense on T1W and hypointense on T2W MRI and hyperdense at CT. Thin peripheral, but no internal enhancement after contrast administration signified successful ablation zones. Ablation zones decreased in size, but did not resolve during surveillance. Immediate post-procedure subcapsular gas and hematoma (5/71, 7%) resolved prior to first follow-up. Focal, enhancing soft tissue within the ablation zone, invariably along the renal margin, signified local recurrence. Local recurrence rates were higher for T1b (2/19, 11%) compared to T1a (1/52, 2%). Urinomas (4/71, 6%) decreased in size and resolved during surveillance. Retroperitoneal fat necrosis (6/71, 9%), with opposed-phase loss of T1W MRI signal, was confirmed at histology after percutaneous biopsy.
Conclusion
CT and MR imaging features after microwave ablation of renal cell carcinoma are predictable and reliably demonstrate treatment success, early and delayed complications, and local recurrences that can guide patient management.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell S, Uzzo RG, Allaf ME, Bass EB, Cadeddu JA, Chang A, Clark PE, Pierorazio PM, Davis BJ, Derweesh IH, Giambarresi L, Gervais DA, Hu SL, Lane BR, Leibovich BC (2017) Renal Mass and Localized Renal Cancer: AUA Guideline. J Urol. 198:520-529.
Finelli A, Ismaila N, Bro B, Durack J, Eggener S, Evans A, Gill I, Graham D, Huang W, Jewett MAS, Latcha S, Lowrance W, Rosner M, Shayegan B, Houston Thompson R, Uzzo R, Russo P (2017) Management of small renal masses: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol 35:668-680.
Brace CL (2010) Microwave tissue ablation: biophysics, technology, and applications. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 38:65-78.
McClure TD, Chow DS, Tan N, Sayre JA, Pantuck AJ, Raman SS (2014) Intermediate outcomes and predictors of efficacy in the radiofrequency ablation of 100 pathologically proven renal cell carcinomas. J Vasc Interv Radiol 25:1682-1688.
Maciolek KA, Abel EJ, Posielski NM, Hinshaw JL, Lubner MG, Lee FT Jr, Ziemlewicz TJ, Wells SA (2019) Tumor location does not impact oncologic outcomes for percutaneous microwave ablation of clinical T1a renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 29:6319-6329.
Wells SA, Wheeler KM, Mithqal A, Patel MS, Brace CL, Schenkman NS (2016) Percutaneous microwave ablation of T1a and T1b renal cell carcinoma: short-term efficacy and complications with emphasis on tumor complexity and single session treatment. Abdom Radiol 41:1203-1211.
Choueiri TK, Schutz FA, Hevelone ND, Nguyen PL, Lipsitz SR, Williams SB, Silverman SG, Hu JC (2011) Thermal ablation vs surgery for localized kidney cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database analysis. Urology 78:93-98.
Davenport MS, Caoili EM, Cohan RH, Ellis JH, Higgins EJ, Willatt J, Fox GA (2009) MRI and CT characteristics of successfully ablated renal masses: imaging surveillance after radiofrequency ablation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:1571-1578.
Wile GE, Leyendecker JR, Krehbiel KA, Dyer RB, Zagoria RJ (2007) CT and MR imaging after imaging-guided thermal ablation of renal neoplasms. Radiographics 27:325-339.
Iannuccilli JD, Grand DJ, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW (2014) Percutaneous ablation for small renal mass-imaging follow-up. Semin Intervent Radiol 31:50-63.
Schirmang TC, Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE, Beland MD, Grand DJ (2009) Kidney neoplasms: renal halo sign after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation—incidence and clinical importance in 101 consecutive patients. Radiology 253:263-269.
Wells SA, Wong VK, Wittmann TA, et al (2017) Renal mass biopsy and thermal ablation: should biopsy be performed before or during the ablation procedure? Abdom Radiol (NY) 42(6):1773–1780
Klapperich ME, Abel EJ, Ziemlewicz TJ, et al. (2017) Effect of tumor complexity and technique on efficacy and complications after percutaneous microwave ablation of stage T1a renal cell carcinoma: a single-center, retrospective study. Radiology 284(1):272–280
Maciolek KA, Abel EJ, Posielski NM, et al. (2019) Tumor location does not impact oncologic outcomes for percutaneous microwave ablation of clinical T1a renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 29(11):6319–6329
Al-Hakim RA, Abtin FG, Genshaft SJ, Kutay E, Suh RD (2016) Defining new metrics in microwave ablation of pulmonary tumors: ablation work and ablation resistance score. J Vasc Interv Radiol 27:1380-1386.
Kutikov A, Uzzo RG (2009) The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urol 182:844-853.
Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL, et al (2014) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria–a 10-year update. Radiology 273:241-260.
Samaratunga H, Gianduzzo T, Delahunt B (2014) The ISUP system of staging, grading and classification of renal cell neoplasia. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 126–39(10000):10000
Liu D, Brace CL (2017) Numerical simulation of microwave ablation incorporating tissue contraction based on thermal dose. Phys Med Biol 62:2070-2086.
Liu D, Brace CL (2019) Evaluation of tissue deformation during radiofrequency and microwave ablation procedures: influence of output energy delivery. Med Phys 46:4127-4134.
Psutka SP, Feldman AS, McDougal WS, McGovern FJ, Mueller P, Gervais DA (2013) Long-term oncologic outcomes after radiofrequency ablation for T1 renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 63:486-492.
Breen DJ, King AJ, Lockyer R, Hayes M (2018) Image-guided cryoablation for sporadic renal cell carcinoma: three- and 5-year outcomes in 220 patients with biopsy-proven renal cell carcinoma. Radiology 289:554-561.
Yu J, Zhang G, Liang P, Yu XL, Cheng ZG, Han ZY, Zhang X, Dong J, Li QY, Mu MJ, Li X (2015) Midterm results of percutaneous microwave ablation under ultrasound guidance versus retroperitoneal laparoscopic radial nephrectomy for small renal cell carcinoma. Abdom Imaging 40:3248-3256.
Lam JS, Shvarts O, Leppert JT, Pantuck AJ, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS (2005) Postoperative surveillance protocol for patients with localized and locally advanced renal cell carcinoma based on a validated prognostic nomogram and risk group stratification system. J Urol 174:466-472.
Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Frank I, Kwon ED, Weaver AL, Parker AS, Zincke H (2003) Prediction of progression after radical nephrectomy for patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a stratification tool for prospective clinical trials. Cancer 97:1663-1671.
Sorbellini M, Kattan MW, Snyder ME, Reuter V, Motzer R, Goetzl M, McKiernan J, Russo P (2005) A postoperative prognostic nomogram predicting recurrence for patients with conventional clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 173:48-51.
Dreyfuss LD, Wells SA, Best SL, Hedican SP, Ziemlewicz TJ, Lubner MG, Hinshaw JL, Lee FT Jr, Nakada SY, Abel EJ (2019) Development of a risk-stratified approach for follow-up imaging after percutaneous thermal ablation of sporadic stage one renal cell carcinoma. Urology 134:148-153.
Patel HD, Johnson MH, Pierorazio PM, Sozio SM, Sharma R, Iyoha E, Bass EB, Allaf ME (2016) Diagnostic accuracy and risks of biopsy in the diagnosis of a renal mass suspicious for localized renal cell carcinoma: systematic review of the literature. J Urol 195:1340-1347.
Bhindi B, Thompson RH, Lohse CM, Mason RJ, Frank I, Costello BA, Potretzke AM, Hartman RP, Potretzke TA, Boorjian SA, Cheville JC, Leibovich BC (2018) The probability of aggressive versus indolent histology based on renal tumor size: implications for surveillance and treatment. Eur Urol 74:489-497.
Atwell TD, Vlaminck JJ, Boorjian SA, Kurup AN, Callstrom MR, Weisbrod AJ, Lohse CM, Hartman WR, Stockland AH, Leibovich BC, Schmit GD, Thompson RH (2015) Percutaneous cryoablation of stage T1b renal cell carcinoma: technique considerations, safety, and local tumor control. J Vasc Interv Radiol 26:792-299.
Lokken RP, Gervais DA, Arellano RS, Tuncali K, Morrison PR, Tatli S, Mueller PR, Silverman SG (2007) Inflammatory nodules mimic applicator track seeding after percutaneous ablation of renal tumors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:845-848.
Durack JC, Richioud B, Lyon J, Solomon SB (2014) Late emergence of contrast-enhancing fat necrosis mimicking tumor seeding after renal cryoablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol 25:133-137.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclosures
CLB and SAW—Consultants, Ethicon Inc.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wetley, K.A., Abel, E.J., Dreyfuss, L.D. et al. CT and MR imaging surveillance of stage 1 renal cell carcinoma after microwave ablation. Abdom Radiol 45, 2810–2824 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02662-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02662-9