Abstract
Purpose
To explore the preponderant diagnostic performances of IVIM and DKI in predicting the Gleason score (GS) of prostate cancer.
Methods
Diffusion-weighted imaging data were postprocessed using monoexponential, lVIM and DK models to quantitate the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), molecular diffusion coefficient (D), perfusion-related diffusion coefficient (Dstar), perfusion fraction (F), apparent diffusion for Gaussian distribution (Dapp), and apparent kurtosis coefficient (Kapp). Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was used to explore the relationship between those parameters and the GS, Kruskal–Wallis test, and Mann–Whitney U test were performed to compare the above parameters between the different groups, and a receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the differential diagnosis ability. The interpretation of the results is in view of histopathologic tumor tissue composition.
Results
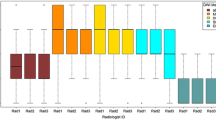
The area under the ROC curves (AUCs) of ADC, F, D, Dapp, and Kapp in differentiating GS ≤ 3 + 4 and GS > 3 + 4 PCa were 0.744 (95% CI 0.581–0.868), 0.726 (95% CI 0.563–0.855), 0.732 (95% CI 0.569–0.860), and 0.752 (95% CI 0.590–0.875), 0.766 (95% CI 0.606–0.885), respectively, and those in differentiating GS ≤ 7 and GS > 7 PCa were 0.755 (95% CI 0.594–0.877), 0.734 (95% CI 0.571–0.861), 0.724 (95% CI0.560–0.853), and 0.716 (95% CI 0.552–0.847), 0.828 (95% CI 0.676–0.929), respectively. All the P values were less than 0.05. There was no significant difference in the AUC for the detection of different GS groups by using those parameters.
Conclusion
Both the IVIM and DKI models are beneficial to predict GS of PCa and indirectly predict its aggressiveness, and they have a comparable diagnostic performance with each other as well as ADC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P.(2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin;55:74-108.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D.(2011) Global cancer statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians;61:69-90.
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A.(2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin;65:87-108.
Epstein JI, Egevad L, Amin MB, Delahunt B, Srigley JR, Humphrey PA.(2016) The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am J Surg Pathol;40:244-252.
Anwar SSM, Anwar Khan Z, Shoaib Hamid R, Haroon F, Sayani R, Beg M, Khattak YJ.(2014) Assessment of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values as Predictor of Aggressiveness in Peripheral Zone Prostate Cancer: Comparison with Gleason Score. ISRN Radiology;2014:1-7.
Boesen L, Chabanova E, Løgager V, Balslev I, Thomsen HS.(2015) Apparent diffusion coefficient ratio correlates significantly with prostate cancer gleason score at final pathology. J Magn Reson Imaging;42:446-453.
Kamel MH, Khalil MI, Alobuia WM, Su J, Davis R.(2018) Incidence of metastasis and prostate-specific antigen levels at diagnosis in Gleason 3 + 4 versus 4 + 3 prostate cancer. Urol Ann;10:203-208.
Morash C, Tey R, Agbassi C, Klotz L, McGowan T, Srigley J, Evans A.(2015) Active surveillance for the management of localized prostate cancer: Guideline recommendations. Can Urol Assoc J;9:171-178.
Ahmed HU, El-Shater BA, Brown LC, Gabe R, Kaplan R, Parmar MK, Collaco-Moraes Y, et al.(2017) Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet;389:815-822.
Rosenkrantz AB, Taneja SS.(2015) Prostate MRI Can Reduce Overdiagnosis and Overtreatment of Prostate Cancer. Acad Radiol;22:1000-1006.
Jie C, Rongbo L, Ping T.(2014) The value of diffusion-weighted imaging in the detection of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol;24:1929-1941.
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Lavaljeantet M.(1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology;168:497-505.
Shinmoto H, Tamura C, Soga S, Shiomi E, Yoshihara N, Kaji T, Mulkern RV.(2012) An intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging study of prostate cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol;199:W496-W500.
Liu X, Zhou L, Peng W, Wang C, Wang H.(2013) Differentiation of central gland prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia using monoexponential and biexponential diffusion-weighted imaging. Magn Reson Imaging;31:1318-1324.
Kuru TH, Roethke MC, Stieltjes B, Maier-Hein K, Schlemmer HP, Hadaschik BA, Fenchel M.(2014) Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion imaging in prostate cancer - what does it add? J Comput Assist Tomogr;38:558-564.
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Wu C, Wang X, Zhang J, Liu H, Liu X, et al.(2015) The Histogram Analysis of Diffusion-Weighted Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Imaging for Differentiating the Gleason grade of Prostate Cancer. Eur Radiol;25:994-1004.
Valerio M, Zini C, Fierro D, Giura F, Colarieti A, Giuliani A, Laghi A, et al.(2016) 3T multiparametric MRI of the prostate: Does intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion imaging have a role in the detection and stratification of prostate cancer in the peripheral zone? Eur J Radiol;85:790-794.
Yang DM, Kim HC, Kim SW, Jahng GH, Won KY, Lim SJ, Oh JH.(2016) Prostate cancer: correlation of intravoxel incoherent motion MR parameters with Gleason score. Clin Imaging;40:445-450.
Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K.(2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med;53:1432-1440.
Suo S, Chen X, Wu L, Zhang X, Yao Q, Fan Y, Wang H, et al.(2014) Non-Gaussian water diffusion kurtosis imaging of prostate cancer. Magn Reson Imaging;32:421-427.
Tamura C, Shinmoto H, Soga S, Okamura T, Sato H, Okuaki T, Pang Y, et al.(2014) Diffusion kurtosis imaging study of prostate cancer: Preliminary findings. J Magn Reson Imaging;40:723-729.
Quentin M, Pentang G, Schimmöller L, Kott O, Müller-Lutz A, Blondin D, Arsov C, et al.(2014) Feasibility of diffusional kurtosis tensor imaging in prostate MRI for the assessment of prostate cancer: Preliminary results. Magn Reson Imaging;32:880-885.
Wang Q, Li H, Yan X, Wu C, Liu X, Shi H, Zhang Y.(2015) Histogram analysis of diffusion kurtosis magnetic resonance imaging in differentiation of pathologic Gleason grade of prostate cancer. Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations;33:315-337.
Wu CJ, Zhang YD, Bao ML, Li H, Wang XN, Liu XS, Shi HB.(2017) Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Helps to Predict Upgrading in Biopsy-Proven Prostate Cancer With a Gleason Score of 6. AJR Am J Roentgenol;209:1081-1087.
Tamada T, Prabhu V, Li J, Babb JS, Taneja SS, Rosenkrantz AB.(2017) Prostate Cancer: Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging for Detection and Assessment of Aggressiveness-Comparison between Conventional and Kurtosis Models. Radiology;284:100-108.
Epstein JI, Feng Z, Trock BJ, Pierorazio PM.(2012) Upgrading and Downgrading of Prostate Cancer from Biopsy to Radical Prostatectomy: Incidence and Predictive Factors Using the Modified Gleason Grading System and Factoring in Tertiary Grades. Eur Urol;61:1019-1024.
Weinreb JC, Barentsz JO, Choyke PL, Cornud F, Haider MA, Macura KJ, Margolis D, et al.(2016) PI-RADS Prostate Imaging – Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. Eur Urol;69:16-40.
Jung SI, Jeon HJ, Park HS, Yu MH, Kim YJ, Lee SE, Lim SD.(2018) Multiparametric MR imaging of peripheral zone prostate cancer: effect of postbiopsy hemorrhage on cancer detection according to Gleason score and tumour volume. The British journal of radiology;91:20180001.
Rosenkrantz AB, Padhani AR, Chenevert TL, Koh D, De Keyzer F, Taouli B, Le Bihan D.(2015) Body diffusion kurtosis imaging: Basic principles, applications, and considerations for clinical practice. J Magn Reson Imaging;42:1190-1202.
Yang M, Yan Y, Wang H.(2019) IMAge/enGINE: a freely available software for rapid computation of high-dimensional quantification. Quant Imag Med Surg;9:210-218.
Cicchetti DV.(1994) Guidelines, Criteria, and Rules of Thumb for Evaluating Normed and Standardized Assessment Instruments in Psychology. Psychol Assessment;6:284-290.
Yang L, Rao S, Wang W, Chen C, Ding Y, Yang C, Grimm R, et al.(2018) Staging liver fibrosis with DWI: is there an added value for diffusion kurtosis imaging? Eur Radiol;28:3041-3049.
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL.(1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics;44:837-845.
Humphrey PA.(2004) Gleason grading and prognostic factors in carcinoma of the prostate. Modern Pathol;17:292-306.
Epstein JI, Allsbrook WC, Amin MB, Egevad LL, Bastacky S, Beltran AL, Berner A, et al.(2005) The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol;29:1228-1242.
Chatterjee A, Watson G, Myint E, Sved P, McEntee M, Bourne R.(2015) Changes in Epithelium, Stroma, and Lumen Space Correlate More Strongly with Gleason Pattern and Are Stronger Predictors of Prostate ADC Changes than Cellularity Metrics. Radiology;277:751-762.
Boesen L, Chabanova E, Løgager V, Balslev I, Thomsen HS.(2015) Apparent diffusion coefficient ratio correlates significantly with prostate cancer gleason score at final pathology. J Magn Reson Imaging;42:446-453.
De Cobelli F, Ravelli S, Esposito A, Giganti F, Gallina A, Montorsi F, Del Maschio A.(2015) Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Value and Ratio as Noninvasive Potential Biomarkers to Predict Prostate Cancer Grading: Comparison With Prostate Biopsy and Radical Prostatectomy Specimen. Am J Roentgenol;204:550-557.
Doo KW, Sung DJ, Park BJ, Kim MJ, Cho SB, Oh YW, Ko YH, et al.(2012) Detectability of low and intermediate or high risk prostate cancer with combined T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted MRI. Eur Radiol;22:1812-1819.
Hambrock T, Somford DM, Huisman HJ, van Oort IM, Witjes JA, Hulsbergen-van DKC, Scheenen T, et al.(2011) Relationship between apparent diffusion coefficients at 3.0-T MR imaging and Gleason grade in peripheral zone prostate cancer. Radiology;259:453-461.
Anwar SS, Anwar KZ, Shoaib HR, Haroon F, Sayani R, Beg M, Khattak YJ.(2014) Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient values as predictor of aggressiveness in peripheral zone prostate cancer: comparison with Gleason score. ISRN Radiol;2014:263417.
Gilani N, Malcolm P, Johnson G.(2017) A model describing diffusion in prostate cancer. Magn Reson Med;78:316-326.
Koh D, Collins DJ, Orton MR.(2011) Intravoxel incoherent motion in body diffusion-weighted MRI: reality and challenges. AJR. American journal of roentgenology;196:1351.
Pang Y, Turkbey B, Bernardo M, Kruecker J, Kadoury S, Merino MJ, Wood BJ, et al.(2013) Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging for prostate cancer: An evaluation of perfusion fraction and diffusion coefficient derived from different b-value combinations. Magn Reson Med;69:553-562.
Le Bihan D.(2007) The ‘wet mind’: water and functional neuroimaging. Phys Med Biol;52:R57-R90.
Merisaari H, Toivonen J, Pesola M, Taimen P, Boström PJ, Pahikkala T, Aronen HJ, et al.(2015) Diffusion-weighted imaging of prostate cancer: effect of b-value distribution on repeatability and cancer characterization. Magn Reson Imaging;33:1212-1218.
Barbieri S, Brönnimann M, Boxler S, Vermathen P, Thoeny HC.(2017) Differentiation of prostate cancer lesions with high and with low Gleason score by diffusion-weighted MRI. Eur Radiol;27:1547-1555.
Pesapane F, Patella F, Fumarola EM, Panella S, Ierardi AM, Pompili GG, Franceschelli G, et al.(2017) Intravoxel Incoherent Motion (IVIM) Diffusion Weighted Imaging (DWI) in the Periferic Prostate Cancer Detection and Stratification. Med Oncol;34:35.
Patel J, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H, Oei M, Babb JS, Taouli B.(2010) Diagnosis of cirrhosis with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion MRI and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI alone and in combination: Preliminary experience. J Magn Reson Imaging;31:589-600.
Hectors SJ, Semaan S, Song C, Lewis S, Haines GK, Tewari A, Rastinehad AR, et al.(2018) Advanced Diffusion-weighted Imaging Modeling for Prostate Cancer Characterization: Correlation with Quantitative Histopathologic Tumor Tissue Composition-A Hypothesis-generating Study. Radiology;286:938-948.
Lawrence EM, Warren AY, Priest AN, Barrett T, Goldman DA, Gill AB, Gnanapragasam VJ, et al.(2016) Evaluating Prostate Cancer Using Fractional Tissue Composition of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens and Pre-Operative Diffusional Kurtosis Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Plos One;11:e159652.
Le Bihan D.(2013) Apparent diffusion coefficient and beyond: what diffusion MR imaging can tell us about tissue structure. Radiology;268:318-322.
Li C, Chen M, Wan B, Yu J, Liu M, Zhang W, Wang J.(2018) A comparative study of Gaussian and non-Gaussian diffusion models for differential diagnosis of prostate cancer with in-bore transrectal MR-guided biopsy as a pathological reference. Acta Radiol;59:1395-1402.
Rosenkrantz AB, Sigmund EE, Johnson G, Babb JS, Mussi TC, Melamed J, Taneja SS, et al.(2012) Prostate Cancer: Feasibility and Preliminary Experience of a Diffusional Kurtosis Model for Detection and Assessment of Aggressiveness of Peripheral Zone Cancer. Radiology;264:126-135.
Purysko AS, Rosenkrantz AB, Barentsz JO, Weinreb JC, Macura KJ.(2016) PI-RADS Version 2: A Pictorial Update. Radiographics;36:1354-1372.
Acknowledgements
The authors of this manuscript state that this work has not received any funding. Thanks are due to the radiologists of GE 750 scanner for their understanding and support of our research work, and to urologist Zhu Yanjun, Long Qilai, and Xulei et al. for their assistance in our research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, Y., Chen, X., Liu, K. et al. Prostate cancer aggressive prediction: preponderant diagnostic performances of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) imaging and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) beyond ADC at 3.0 T scanner with gleason score at final pathology. Abdom Radiol 44, 3441–3452 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02075-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02075-3