Abstract
Purpose
The primary purpose of this study was to compare bone tracer uptake (BTU) on SPECT/CT in symptomatic and asymptomatic total hip arthroplasty (THA) and identify a possible relationship between BTU patterns and patient’s symptoms. The secondary purpose was to investigate if the fixation methods (cemented versus uncemented) lead to different BTU patterns.
Methods
A total of 58 THAs, 31 symptomatic (group S) and 27 asymptomatic (group AS), were prospectively collected and retrospectively analyzed. All symptomatic patients underwent standardized detailed history, clinical examination, radiographs and 99mTc-HDP SPECT/CT. BTU in SPECT/CT was quantified in three dimensions and anatomically localized in a scheme of quadrants and levels using a customized previously validated software. T tests were used on both quadrants and levels inside and between groups. A Pearson correlation was performed for BTU within the quadrants. An area under receiver operating characteristic curves was drawn in order to find a BTU value that could differentiate the two groups. Within the groups, patients with cemented and uncemented stems were compared for influences on BTU intensity.
Results
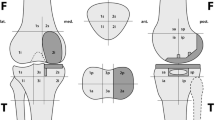
The causes of pain were identified in 61% of the patients. The most common problem was aseptic loosening (n = 12). In group AS, levels 1, 2 and 5 had similar BTUs. BTUs in these levels were significantly higher than in level 3, 4 and 6. In group S, no significant differences were seen in terms of BTU in level 1–5. However, BTU here was significantly higher than at level 6 (p < 0.001). In both groups, level 1, the superior, had a significantly higher BTU than level 2 (group AS p < 0.01, group S p < 0.05). Comparing the BTU of the two groups among levels, significant differences were found for level 4, level 5 and the entire stem areas (p < 0.05). The ROC curve calculated on the whole stem allowed identification of a BTU ratio of 3.1 that separated the 92.6% patients of group AS with BTU < 3.1 from the 54.8% of patients of group S with a BTU ≥ 3.1. With regards to the fixation technique, only the BTU at the level 6 in group S presented a significant difference between cemented and uncemented stems (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Higher BTU levels significantly correlated with symptoms, but a normal BTU could not exclude a specific pathology after THA. A threshold of BTU in SPECT/CT was identified to distinguish between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients after THA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anakwe RE, Jenkins PJ, Moran M. Predicting dissatisfaction after total hip arthroplasty: a study of 850 patients. J Arthroplast. 2011;26:209–13.
Bourne RB, Chesworth BM, Davis AM, Mahomed NN, Charron KD. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: who is satisfied and who is not? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:57–63.
Rolfson O, Kärrholm J, Dahlberg LE, Garellick G. Patient-reported outcomes in the Swedish hip Arthroplasty register: results of a nationwide prospective observational study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93:867–75.
Mancuso CA, Salvati EA, Johanson NA, Peterson MG, Charlson ME. Patients' Expectations and satisfaction with total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplast. 1997;12:387–96.
Spinarelli A, Patella V, Petrera M, Abate A, Pesce V, Patella S. Heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty: our experience. Musculoskelet Surg. 2011;95:1–5.
Pluot E, Davis ET, Revell M, Davies AM, S.L.J. J. Hip arthroplasty. Part 2: normal and abnormal radiographic findings. Clin Radiol. 2009;64:961–71.
Vanquickenborne B, Maes A, Nuyts J, Van Acker F, Stuyck J, Mulier M, et al. The value of 18FDG-PET for the detection of infected hip prosthesis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:705–15.
Tam H, Bhaludin B, Rahman F, Weller A, Ejindu V, Parthipun A. SPECT-CT in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Radiol. 2014;69:82–95.
Kaisidis A, Megas P, Apostolopoulos D, Spiridonidis T, Koumoundourou D, Zouboulis P, et al. Diagnose septischer Hüftprothesenlockerung via LeukoScan. Orthopade. 2005;34:462–9.
Awengen R, Rasch H, Amsler F, Hirschmann MT. Symptomatic versus asymptomatic knees after bilateral total knee arthroplasty: what is the difference in SPECT/CT? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:762–72.
Forrer F, Hirschmann MT, Rasch HF. Painful knee prosthesis: is there a role for bone SPECT/CT? Nucl Med Commun. 2014;35:782.
Hirschmann A, Hirschmann MT. Chronic knee pain: clinical value of MRI versus SPECT/CT. Seminars Muscul Radiol. 2016;20:3–11.
Hirschmann M, Mathis D, Rasch H, Amsler F, Friederich N, Arnold M. SPECT/CT tracer uptake is influenced by tunnel orientation and position of the femoral and tibial ACL graft insertion site. Int Orthop. 2013;37:301–9.
Hirschmann MT, Adler T, Rasch H, Hügli RW, Friederich NF, Arnold MP. Painful knee joint after ACL reconstruction using biodegradable interference screws- SPECT/CT a valuable diagnostic tool? A case report. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. 2010;2(24).
Hirschmann MT, Davda K, Iranpour F, Rasch H, Friederich NF. Combined single photon emission computerised tomography and conventional computerised tomography (SPECT/CT) in patellofemoral disorders: a clinical review. Int Orthop. 2011;35:675–80.
Hirschmann MT, Davda K, Rasch H, Arnold MP, Friederich NF. Clinical value of combined single photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computer tomography (SPECT/CT) in sports medicine. Sports Med Arthrosc. 2011;19:174–81.
Hirschmann MT, Iranpour F, Davda K, Rasch H, Hügli R, Friederich NF. Combined single-photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computerized tomography (SPECT/CT): clinical value for the knee surgeons? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:341–5.
Hirschmann MT, Iranpour F, Konala P, Kerner A, Rasch H, Cobb JP, et al. A novel standardized algorithm for evaluating patients with painful total knee arthroplasty using combined single photon emission tomography and conventional computerized tomography. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:939–44.
Hirschmann MT, Johann H, Helmut R. SPECT/CT in patients with painful knee arthroplasty - what is the evidence? Skelet Radiol. 2013;42:1201–7.
Hirschmann MT, Konala P, Iranpour F, Kerner A, Rasch H, Friederich NF. Clinical value of SPECT/CT for evaluation of patients with painful knees after total knee arthroplasty--a new dimension of diagnostics?. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12(36).
Hirschmann MT, Mathis D, Afifi FK, Rasch H, Henckel J, Amsler F, et al. Single photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computerized tomography (SPECT/CT) for evaluation of patients after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a novel standardized algorithm combining mechanical and metabolic information. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21:965–74.
Hirschmann MT, Schmid R, Dhawan R, Skarvan J, Rasch H, Friederich NF, et al. Combined single photon emission computerized tomography and conventional computerized tomography: clinical value for the shoulder surgeons? Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011;5:72–6.
Hirschmann MT, Schön S, Afifi FK, Amsler F, Rasch H, Friederich NK, et al. Assessment of loading history of compartments in the knee using bone SPECT/CT: a study combining alignment and 99mTc-HDP tracer uptake/distribution patterns. J Orthop Res. 2012;31:268–74.
Hirschmann MT, Wagner CR, Rasch H, Henckel J. Standardized volumetric 3D–analysis of SPECT/CT imaging in orthopaedics: overcoming the limitations of qualitative 2D analysis. BMC Med Imaging. 12(5).
Konala P, Iranpour F, Kerner A, Rasch H, Friederich NF, Hirschmann MT. Clinical benefit of SPECT/CT for follow-up of surgical treatment of osteochondritis dissecans. Ann Nucl Med. 2010;24:621–4.
Hirschmann MT, Amsler F, Rasch H. Clinical value of SPECT/CT in the painful total knee arthroplasty (TKA): a prospective study in a consecutive series of 100 TKA. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:1869–82.
Mathis DT, Rasch H, Hirschmann MT. In vivo bone tunnel remodeling in symptomatic patients after ACL reconstruction: a retrospective comparison of articular and extra-articular fixation. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2015;5:316–24.
Milos Dordevic M, Hirschmann MT, Rechsteiner J, Falkowski A, Testa E, Hirschmann A. Do Chondral lesions of the knee correlate with bone tracer uptake by using SPECT/CT? Radiology. 2016;278:223–31.
Mucha A, Dordevic M, Hirschmann A, Rasch H, Amsler F, Arnold MP, et al. Effect of high tibial osteotomy on joint loading in symptomatic patients with varus aligned knees: a study using SPECT/CT. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23:2315–23.
Mucha A, Dordevic M, Testa EA, Rasch H, Hirschmann MT. Assessment of the loading history of patients after high tibial osteotomy using SPECT/CT-a new diagnostic tool and algorithm. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8(46).
Rasch H, Falkowski AL, Forrer F, Henckel J, Hirschmann MT. 4D-SPECT/CT in orthopaedics: a new method of combined quantitative volumetric 3D analysis of SPECT/CT tracer uptake and component position measurements in patients after total knee arthroplasty. Skelet Radiol. 2013;42:1215–23.
Rieger B, Friederich NF, Rasch H, Hirschmann MT. Non-dislocated osteoporotic insufficiency fracture of the medial femoral neck. SPECT/CT makes the diagnostic difference. Unfallchirurgie. 2014;117:369–73.
Schön SN, Afifi FK, Rasch H, Amsler F, Friederich NF, Arnold MP, et al. Assessment of in vivo loading history of the patellofemoral joint: a study combining patellar position, tilt, alignment and bone SPECT/CT. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22:3039–46.
Suter B, Testa E, Stämpfli P, Konala P, Rasch H, Friederich NF et al. A novel standardized algorithm using SPECT/CT evaluating unhappy patients after unicondylar knee arthroplasty-a combined analysis of tracer uptake distribution and component position. BMC Med Imaging. 2015;15(11).
Testa EA, Haeni DL, Behrens G, Hirschmann MT. Unexplained proximal tibiofibular joint pain after high tibial osteotomy. Indian J Orthop. 2014;48:335–8.
Arıcan P, Okudan TB, Şefizade R, Naldöken S, Baştuğ A, Özkurt B. The role of bone SPECT/CT in the evaluation of painful joint prostheses. Nucl Med Commun. 2015;36:931–40.
Chew CG, Lewis P, Middleton F, Van den Wijngaard R, Deshaies A. Radionuclide arthrogram with SPECT/CT for the evaluation of mechanical loosening of hip and knee prostheses. Ann Nucl Med. 2010;24:735–43.
Dobrindt O, Amthauer H, Krueger A, Ruf J, Wissel H, Grosser OS et al. Hybrid SPECT/CT for the assessment of a painful hip after uncemented total hip arthroplasty. BMC Med Imaging. 2015;15(18).
Yue B, Tang T. The use of nuclear imaging for the diagnosis of periprosthetic infection after knee and hip arthroplasties. Nucl Med Commun. 2015;36:305–11.
Tavakol M, Dennick R. Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. Int J Med Educ. 2011;2:53–5.
Synder M, Krajewski K, Sibinski M, Drobniewski M. Periprosthetic bone remodeling around short stem. Orthopedics. 2015;38(3 Suppl):S40–5.
Zeh A, Pankow F, Röllinhoff M, Delank S, Wohlrab D. A prospective dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry study of bone remodeling after implantation of the Nanos short-stemmed prosthesis. Acta Orthop Belg. 2013;79:174–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Studies involving human participants
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schweizer, T., Schiapparelli, FF., Rotigliano, N. et al. Patterns of bone tracer uptake on SPECT-CT in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with primary total hip arthroplasty. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45, 283–291 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3827-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-017-3827-9