Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility of administering increasing activities of 188Re-4-hexadecyl-1-2,9,9-tetramethyl-4,7-diaza-1,10-decanethiol/lipiodol (188Re-HDD/lipiodol) for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with well-compensated cirrhosis.
Methods
The activity levels were increased by 1.1 GBq/step after a 6-week interval without unacceptable adverse events in at least five consecutive patients. Absorbed doses to the various organs were calculated according to the MIRD formalism, based on three gamma-scintigraphic studies. Response was assessed by means of MRI and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) monitoring.
Results
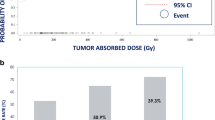
Thirty-five treatments were carried out in 28 patients. Activities from 4.8 to 7.0 GBq 188Re-HDD/lipiodol were administered via a transfemoral catheter. The mean absorbed dose to the liver (including tumour) was 7.6±2.2, 9.8±4.9 and 15.2±4.9 Gy for the 4.8-, 5.9- and 7.0-GBq groups, respectively. Treatment was well tolerated at all activity levels. Further escalation of the administered activity was not feasible owing to limitations related to the radiolabelling procedure. Response assessment on MRI showed partial response, stable disease and disease progression in 1, 28 and 2 assessable treatments, respectively. In 8 of 17 treatment sessions with an initially elevated AFP, a reduction ranging from 19% to 97% was observed 6 weeks later.
Conclusion
Following the intra-arterial administration of 4.8–7.0 GBq 188Re-HDD/lipiodol in patients with HCC and well-compensated liver cirrhosis, no severe adverse events occurred. Further escalation was not feasible owing to limitations in the radiolabelling procedure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin MD, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: globocan 2000. Int J Cancer 2001;94:153–6
El-Serag HB, Masson AC. Rising incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Eng J Med 1999;340:745–50
El-Serag HB, Davila JA, Petersen NJ, McGlynn KA. The continuing increase in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: an update. Ann Intern Med 2003;139:817–23
Schafer DF, Sorrell MF. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 1999;353:1253–7
Giovannini M, Elias D, Monges G, Raoul JL, Rougier P. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer 2001;84:74–7
Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, Beaugrand M, Lencioni R, Burroughs AK, et al. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol 2001;35:421–30
Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology 2003;37:429–42
Raoul JL, Guyader D, Bretagne JF, Heautot JF, Duvauferrier R, Bourguet P, et al. Prospective randomized trial of chemoembolization versus intra-arterial injection of 131-I-iodized oil in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1997;26:1156–61
Leung WT, Lau WY, Ho S, Chan M, Leung N, Lin J, et al. Selective internal radiation therapy with intra-arterial iodine-131-lipiodol in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Nucl Med 1994;35:1313–8
Risse JH, Grünwald F, Kersjes W, Strunk H, Caselmann WH, Palmedo H, et al. Intra arterial HCC therapy with 131I-lipiodol. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2000;15:65–70
Knapp FF. Rhenium-188—a generator-derived radioisotope for cancer therapy. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 1998;13:337–49
Sundram FX, Jeong JM, Zanzonico P, et al. Trans-arterial rhenium-188 lipiodol in the treatment of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. An IAEA sponsored multi-centre phase 1 study. World J Nucl Med 2002;1:5–11
Sundram F, Chau TC, Onkhuudai P, Bernal P, Padhy AK. Preliminary results of transarterial rhenium-188 HDD lipiodol in the treatment of inoperable primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;31:250–7
Lambert B, Bacher K, Defreyne L, Gemmel F, Van Vlierberghe H, Jeong JM, et al. 188Re-HDD/lipiodol therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase I clinical trial. J Nucl Med 2005;46:60–6
Jeong JM, Kim YJ, Lee YS, Ko JI, Son M, Lee DS, et al. Lipiodol solution of a lipophilic agent, 188-Re-TDD, for the treatment of liver cancer. Nucl Med Biol 2001;28:197–204
Lee YS, Jeong JM, Kim YJ, Chung JW, Park JH, Suh YG, et al. Synthesis of 188Re-labelled long chain alkyl diaminedithiol for therapy of liver cancer. Nucl Med Commun 2002;23:237–42
Guhlke S, Beets AL, Oetjen K, Mirzadeh S, Biersack HJ, Knapp FF Jr. Simple new method for effective concentration of Re-188 solutions from alumina-based W-188–Re-188 generator. J Nucl Med 2000;4:1271–8
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 1973;60:646–9
Loevinger R, Budinger TF, Watson EE. MIRD primer for absorbed dose calculations. New York: The Society of Nuclear Medicine, 1991
Stabin MG. MIRDOSE: personal computer software for internal dose assessment in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med 1996;37:538–46
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 2000;92:205–16
Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H, Tomimatsu M, Okazaki N, Hasegawa H, et al. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Cancer 1985;56:918–28
The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients. Hepatology 1998;28:751–5
Brans B, Bacher K, Vandevyver V, Vanlangenhove P, Smeets P, Thierens H, et al. Intra-arterial radionuclide therapy for liver tumours: effect of selectivity of catheterization and 131I-lipiodol delivery on tumour uptake and response. Nucl Med Commun 2003;24:391–6
Raoul JL, Bourguet P, Bretagne JF, Duvauferrier R, Coornaert S, Darnault P, et al. Hepatic artery injection of I-131-labeled lipiodol. Biodistribution study results in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases. Radiology 1988;168:541–5
Nakajo M, Kobayashi H, Shimabukuro K, Shirono K, Sakata H, Taguchi M, et al. Biodistribution and in vivo kinetics of iodine-131 lipiodol infused via the hepatic artery of patients with hepatic cancer. J Nucl Med 1988;29:1066–77
Lambert B, Praet M, Vanlangenhove P, Troisi R, de Hemptinne B, Gemmel F, et al. Radiolabelled lipiodol therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients awaiting liver transplantation: pathology of the explant livers and clinical outcome. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2005:20:209–14
Boschi A, Uccelli L, Duatti A, Colamussi P, Cittanti C, Filice A, et al. A kit formulation for the preparation of 188Re-lipiodol: preclinical studies and preliminary therapeutic evaluation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun 2004; 25:691–9
Garin E, Noiret N, Malbert C, Lepareur N, Roucoux A, Caulet-Maugendre S, et al. Development and biodistribution of 188Re-SSS lipiodol following injection into the hepatic artery of healthy pigs. Eur J of Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;31:542–6
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the IRE (Institut des Radio-Eléments, Fleurus, Belgium) for their technical assistance. The work was supported by a grant of the Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds (Ghent University, No 011D9501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambert, B., Bacher, K., Defreyne, L. et al. 188Re-HDD/lipiodol therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: an activity escalation study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33, 344–352 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1954-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-005-1954-1