Abstract
Purpose
This study sought to provide preliminary results on the biodistribution and dosimetry following intra-arterial liver injection of 188Re-SSS Lipiodol on hepatocellular carcinoma patients included in the Phase I Lip-Re 1 study.
Methods
Results of the first six patients included are reported. Analysis of the 188Re-SSS Lipiodol biodistribution was based on planar scintigraphic and tomoscintigraphic (SPECT) studies performed at 1, 6, 24, 48, and 72 h post-administration. Quantification in blood, urine, and stool samples was performed. Determination of the tumour to non-tumour uptake ratio (T/NT) was calculated. Absorbed doses to target organs and tumours were evaluated using the MIRD formalism.
Results
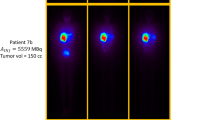
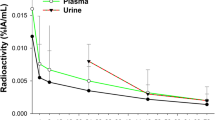
The mean injected activity of 188Re-SSS Lipiodol was 1645 ± 361 MBq. Uptakes were seen in the liver (tumour and healthy liver) and the lungs only. All these uptakes were stable over time. A mean 1.4 ± 0.7% of 188Re-SSS Lipiodol administered was detected in serum samples at 6 h, declining rapidly thereafter. On average, 1.5 ± 1.6% of administered activity was eliminated in urine and feces over 72 h. Overall, 90.7 ± 1.6% of detected activity on SPECT studies was found in the liver (74.9 ± 1.8% in tumours and 19.1 ± 1.7% in the healthy liver) and 9.3 ± 1.6% in the lungs (5.7 ± 1.1% in right and 3.7 ± 0.5% in left lungs). Mean doses absorbed were 7.9 ± 3.7Gy to the whole liver, 42.7 ± 34.0Gy to the tumours, 10.2 ± 3.7Gy to the healthy liver, and 1.5 ± 1.2Gy to the lungs. Four patients had stable disease on CT scans at 2 months. The first patient with rapidly progressive disease died at 1 month, most probably of massive tumour progression. Due to this early death and using a conservative approach, the trial independent evaluation committee decided to consider this event as a treatment-related toxicity.
Conclusion
188Re-SSS Lipiodol has a favorable biodistribution profile concerning radioembolization, with the highest in-vivo stability among all radiolabeled Lipiodol compounds reported to date. These preliminary results must be further confirmed while completing this Phase I Lip Re1 study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc J-F, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–90.
Vilgrain V, Bouattour M, Sibert A, Lebtahi R, Ronot M, Pageaux G-P, et al. SARAH: a randomised controlled trial comparing efficacy and safety of selective internal radiation therapy (with yttrium-90 microspheres) and sorafenib in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2017;66:S85–6.
Vilgrain V, Pereira H, Assenat E, Guiu B, Ilonca AD, Pageaux G-P, et al. Efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres compared with sorafenib in locally advanced and inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (SARAH): an open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1624–36.
Chow PKH, Gandhi M, Tan S-B, Khin MW, Khasbazar A, Ong J, et al. SIRveNIB: selective internal radiation therapy versus sorafenib in Asia-Pacific patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(19):1913–21. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.76.0892.
Raoul JL, Guyader D, Bretagne JF, Duvauferrier R, Bourguet P, Bekhechi D, et al. Randomized controlled trial for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis: intra-arterial iodine-131-iodized oil versus medical support. J Nucl Med. 1994;35:1782–7.
Noiret N, Garin E, Lepareur N, Ardisson V. Composition for treating liver cancer in humans based on rhenium-188 and method for preparing such a composition [Internet]. 2011 [cited 2017 Oct 11]. Available from: https://www.google.com/patents/EP2536438A1?hl=fr&cl=en
Lepareur N. Vectorisations active et passive de radiopharmaceutiques du technetium-99m et du rhénium-188 pour l’imagerie médicale et la thérapie [Internet]. Rennes 1; 2003 [cited 2017 Jul 10]. Available from: http://www.theses.fr/2003REN10110
Garin E, Noiret N, Malbert C, Lepareur N, Roucoux A, Caulet-Maugendre S, et al. Development and biodistribution of 188Re-SSS lipiodol following injection into the hepatic artery of healthy pigs. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;31:542–6.
Garin E, Noiret N, Malbert C-H, Lepareur N, Roucoux A, Dazord L, et al. Development of 99mTc labelled lipiodol: biodistribution following injection into the hepatic artery of the healthy pig. Nucl Med Commun. 2004;25:291–7.
Garin E, Denizot B, Noiret N, Lepareur N, Roux J, Moreau M, et al. 188Re-SSS lipiodol: radiolabelling and biodistribution following injection into the hepatic artery of rats bearing hepatoma. Nucl Med Commun. 2004;25:1007–13.
Garin E, Rakotonirina H, Lejeune F, Denizot B, Roux J, Noiret N, et al. Effect of a 188 re-sss lipiodol/131i-lipiodol mixture, 188 re-sss lipiodol alone or 131i-lipiodol alone on the survival of rats with hepatocellular carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27:363–9.
Lepareur N, Ardisson V, Noiret N, Boucher E, Raoul J-L, Clément B, et al. Automation of labelling of Lipiodol with high-activity generator-produced 188Re. Appl Radiat Isot. 2011;69:426–30.
Lepareur N, Ardisson V, Noiret N, Garin E. (188)re-SSS/Lipiodol: development of a potential treatment for HCC from bench to bedside. Int J Mol Imaging. 2012;2012:278306.
188RE-SSS lipiodol to treat hepatocellular carcinomas — full text view.ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2016 Jun 9]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01126463
Jaszczak RJ, Greer KL, Floyd CE Jr, Harris CC, Coleman RE. Improved SPECT quantification using compensation for scattered photons. J Nucl Med. 1984;25:893–900.
Snyder WS, Ford MR, Warner GG, Watson SB. MIRD Pamphlet #11: S, Absorbed dose per unit cumulated activity for selected radionuclides and organs. 1975 [cited 2017 Oct 10]; Available from: https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=a0909e6e-4b0b-469b-b9c7-09c8dac3fc37
Siegel JA, Thomas SR, Stubbs JB, Stabin MG, Hays MT, Koral KF, et al. MIRD pamphlet no. 16: techniques for quantitative radiopharmaceutical biodistribution data acquisition and analysis for use in human radiation dose estimates. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:37S–61S.
Zanzonico PB, Divgi C. Patient-specific radiation dosimetry for radionuclide therapy of liver tumours with intrahepatic artery rhenium-188 lipiodol. Semin Nucl Med. 2008;38:S30–9.
Sgouros G. Bone marrow dosimetry for radioimmunotherapy: theoretical considerations. J Nucl Med. 1993;34:689–94.
Lambert B, Bacher K, Defreyne L, Gemmel F, Van Vlierberghe H, Jeong JM, et al. 188Re-HDD/lipiodol therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase I clinical trial. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:60–6.
Lambert B, Bacher K, De Keukeleire K, Smeets P, Colle I, Jeong JM, et al. 188Re-HDD/lipiodol for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a feasibility study in patients with advanced cirrhosis. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1326–32.
Lambert B, Bacher K, Defreyne L, Van Vlierberghe H, Jeong JM, Wang RF, et al. (188)re-HDD/lipiodol therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: an activity escalation study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006;33:344–52.
Lambert B, Bacher K, Defreyne L. Rhenium-188 based radiopharmaceuticals for treatment of liver tumours. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;53:305–10.
Bernal P, Raoul J-L, Stare J, Sereegotov E, Sundram FX, Kumar A, et al. International Atomic Energy Agency-sponsored multination study of intra-arterial rhenium-188-labeled lipiodol in the treatment of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: results with special emphasis on prognostic value of dosimetric study. Semin Nucl Med. 2008;38:S40–5.
Bernal P, Raoul J-L, Vidmar G, Sereegotov E, Sundram FX, Kumar A, et al. Intra-arterial Rhenium-188 Lipiodol in the treatment of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma: results of an IAEA-sponsored multination study. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2007;69:1448–55.
Boschi A, Uccelli L, Duatti A, Colamussi P, Cittanti C, Filice A, et al. A kit formulation for the preparation of 188Re-lipiodol: preclinical studies and preliminary therapeutic evaluation in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun. 2004;25:691–9.
Knapp FF. Continued availability of the tungsten-188/rhenium-188 generator to enhance therapeutic utility of 188Re. Int J Nucl Med Res [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2018 Dec 7]; Available from: http://www.cosmosscholars.com/special-issues-ijnmr/46-abstracts/ijnmr/724-abstract-continued-availability-of-the-tungsten-188-rhenium-188-generator-to-enhance-therapeutic-utility-of-188re
Pillai MR, Dash A, Knapp FF. Rhenium-188: availability from the 188W/188Re generator and status of current applications. Curr Radiopharm. 2012;5:228–43.
Kan Z, Ivancev K, Hägerstrand I, Chuang VP, Lunderquist A. In vivo microscopy of the liver after injection of lipiodol into the hepatic artery and portal vein in the rat. Acta Radiol. 1989;30:419–25.
Park C, Choi SI, Kim H, Yoo HS, Lee YB. Distribution of Lipiodol in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver. 1990;10:72–8.
Celler A, Esquinas PL. Personalized dosimetry for 188 Re radionuclide therapies based on post-treatment SPECT/CT scans. 2017 [cited 2017 Aug 24]; Available from: http://cosmosscholars.com/phms/index.php/ijnmr/article/view/776
Fernández E, Luis P. Quantitative measurements of Rhenium-188 for radionuclide therapies [Internet]. University of British Columbia; 2017 [cited 2017 Aug 24]. Available from: https://open.library.ubc.ca/cIRcle/collections/ubctheses/24/items/1.0348703
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported in part by a grant from the French National Agency for Research called “Investissements d’Avenir” Labex IRON n°ANR-11-LABX-0018-01.
We are grateful to Prof Mario Marengo, from Bologna University, for his help with the calibration settings for 188Re.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
Yan Rolland, Julien Edeline, and Etienne Garin are consultants for BTG UK Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delaunay, K., Edeline, J., Rolland, Y. et al. Preliminary results of the Phase 1 Lip-Re I clinical trial: biodistribution and dosimetry assessments in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with 188Re-SSS Lipiodol radioembolization. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 46, 1506–1517 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04277-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04277-9