Abstract
Objective. To assess a three-dimensional computed tomography (3DCT) technique for measurement of acetabular coverage in adults.
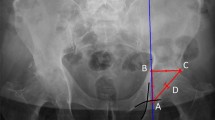
Design. We used 3DCT to define the geometric centre of the femoral head and to measure centre-edge angles (CEAs) at 10° rotational increments around the acetabular rim. The means, ranges, standard deviations and 95% confidence intervals for the CEAs at the various rotational increments were determined. Inter- and intra-observer variability was measured. The normal values are compared with two example cases of acetabular dysplasia.
Patients. The normal hips of 15 subjects aged 19–49 years (mean 34.2 years) were measured.
Results. The 3DCT measurements are reproducible (mean difference inter-observer, 1.7°–7.9°; mean difference intra-observer, 0.6°–6.9°). Mean normal CEA at the lateral rim was 33° with a 95% confidence interval of 23°–43°. Mean normal CEAs at 10° rotational increments from anterior to posterior rim were determined, and graphed as a ’normal curve’.
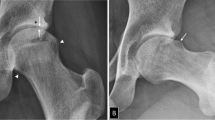
Conclusion. This new 3DCT method of assessing acetabular dysplasia is simple, reproducible, and applicable to diagnosis, quantification and surgical planning for adult acetabular dysplasia patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janzen, D., Aippersbach, S., Munk, P. et al. Three-dimensional CT measurement of adult acetabular dysplasia: technique, preliminary results in normal subjects, and potential applications. Skeletal Radiol 27, 352–358 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002560050397
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002560050397