Abstract
Objective
In the evolving landscape of medical research and radiology, effective communication of intricate ideas is imperative, with visualizations playing a crucial role. This study explores the transformative potential of ChatGPT4, a powerful Large Language Model (LLM), in automating the creation of schematics and figures for radiology research papers, specifically focusing on its implications for musculoskeletal studies.
Materials and methods
Deploying ChatGPT4, the study aimed to assess the model’s ability to generate anatomical images of six large joints—shoulder, elbow, wrist, hip, knee, and ankle. Four variations of a text prompt were utilized, to generate a coronal illustration with annotations for each joint. Evaluation parameters included anatomical correctness, correctness of annotations, aesthetic nature of illustrations, usability of figures in research papers, and cost-effectiveness. Four panellists performed the assessment using a 5-point Likert Scale.
Results
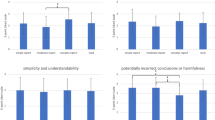
Overall analysis of the 24 illustrations encompassing the six joints of interest (4 of each) revealed significant limitations in ChatGPT4’s performance. The anatomical design ranged from poor to good, all of the illustrations received a below-average rating for annotation, with the majority assessed as poor. All of them ranked below average for usability in research papers. There was good agreement between raters across all domains (ICC = 0.61).
Conclusion
While LLMs like ChatGPT4 present promising prospects for rapid figure generation, their current capabilities fall short of meeting the rigorous standards demanded by musculoskeletal radiology research. Future developments should focus on iterative refinement processes to enhance the realism of LLM-generated musculoskeletal schematics.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The images were generated using the open access software “Chat GPT-4v”, with the specific prompts we have already provided in the article. Users can generate similar images using the prompts we have provided.
References
Divecha C, Tullu M, Karande S. Utilizing tables, figures, charts and graphs to enhance the readability of a research paper. Medknow; 2023. p. 125–31.
Singhal K, Azizi S, Tu T, Mahdavi SS, Wei J, Chung HW, et al. Large language models encode clinical knowledge. Nature. 2023;620(7972):172–80.
Clusmann J, Kolbinger FR, Muti HS, Carrero ZI, Eckardt JN, Laleh NG, et al. The future landscape of large language models in medicine. Commun Med (Lond). 2023;3(1):141.
Naveed H, Khan AU, Qiu S, Saqib M, Anwar S, Usman M, et al. A comprehensive overview of large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:230706435.2023.
Ariyaratne S, Iyengar KP, Botchu R. Will collaborative publishing with ChatGPT drive academic writing in the future? Br J Surg. 2023;110(9):1213–4.
Botchu R, Iyengar KP. Will ChatGPT drive radiology in the future? Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2023;33(4):436–7.
Sullivan GM, Artino AR Jr. Analyzing and interpreting data from Likert-type scales. J Grad Med Educ. 2013;5(4):541–2.
Corl FM, Garland MR, Fishman EK. Role of computer technology in medical illustration. Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175(6):1519–24.
Stokel-Walker C, Van Noorden R. What ChatGPT and generative AI mean for science. Nature. 2023;614(7947):214–6.
Sallam M. ChatGPT utility in healthcare education, research, and practice: systematic review on the promising perspectives and valid concerns. Healthcare 2023;11(6):887. MDPI.
Liebrenz M, Schleifer R, Buadze A, Bhugra D, Smith A. Generating scholarly content with ChatGPT: ethical challenges for medical publishing. Lancet Digital Health. 2023;5(3):e105–6.
Li H, Moon JT, Purkayastha S, Celi LA, Trivedi H, Gichoya JW. Ethics of large language models in medicine and medical research. Lancet Digital Health. 2023;5(6):e333–5.
https://www.theverge.com/2023/11/6/23948386/chatgpt-active-user-count-openai-developer-conference (accessed: 26th December 2023, at 6:00 PM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ajmera, P., Nischal, N., Ariyaratne, S. et al. Validity of ChatGPT-generated musculoskeletal images. Skeletal Radiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-024-04638-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-024-04638-y