Abstract
Ultrasound (US)-guided musculoskeletal intervention of small joints or joints other than the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, and ankle can be technically challenging. Small joints produce a narrower landing zone for the needle and a smaller target that may be made even more inaccessible by bulky osteophytes. Sonographic (US) guidance offers important advantages including near-field visualization of the joint and soft tissues, ease of access, portability, ability to compare with the contralateral side, and lack of ionization radiation. This review article focuses on the performance of US-guided injections and aspirations involving small joints (joint capacity < 2 mL and/or typically evaluated or injected with a compact linear transducer). For each joint (temporomandibular, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, distal radioulnar, symphysis pubis, and joints of the digits of the hands and feet), a brief overview of the relevant anatomy, indications, procedural description, pearls and pitfalls will be highlighted. This article demonstrates the various approaches to diagnostic or therapeutic injection and aspiration of small joints with the aid of US images, cines and graphic illustrations, emphasizing joint positioning, anatomic landmarks, and needle trajectory for a safe and efficacious procedure. A brief review of available literature for each joint will also be provided.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oo WM, Hunter DJ. Efficacy, safety, and accuracy of intra-articular therapies for hand osteoarthritis: current evidence. Drugs Aging. 2023;40(1):1–20.
Thumboo J, O’Duffy JD. A prospective study of the safety of joint and soft tissue aspirations and injections in patients taking warfarin sodium. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41(4):736–9.
Shif Y, Kung JW, McMahon CJ, Mhuircheartaigh JN, Lin YC, Anderson ME, et al. Safety of omitting routine bleeding tests prior to image-guided musculoskeletal core needle biopsy. Skelet Radiol. 2018;47(2):215–21.
Yui JC, Preskill C, Greenlund LS. Arthrocentesis and joint injection in patients receiving direct oral anticoagulants. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017;92(8):1223–6.
Blaichman JI, Chan B, Michelin LKS. US-guided musculoskeletal interventions in the hip with MRI and US correlation. Radiographics. 2020;40(1):181–99.
Yablon CM. Ultrasound-guided interventions of the foot and ankle. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2013;17(1):60–8.
MacMahon PJ, Eustace SJ, Kavanagh EC. Injectable corticosteroid and local anesthetic preparations: a review for radiologists. Radiology. 2009;252(3):647–61.
Champs B, Corre P, Hamel A, Laffite CD, Le Goff B. US-guided temporomandibular joint injection: validation of an in-plane longitudinal approach. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;120(1):67–70.
Razek AAKA, Al Mahdy Al Belasy F, Ahmed WMS, Haggag MA. Assessment of articular disc displacement of temporomandibular joint with ultrasound. J Ultrasound. 2015;18(2):159–163.
Almeida FT, Pacheco-Pereira C, Flores-Mir C, Le LH, Jaremko JL, Major P. Diagnostic ultrasound assessment of temporomandibular joints: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2019;48(2)
Levorova J, Machon V, Hirjak D, Foltan R. Ultrasound-guided injection into the lower joint space of the temporomandibular joint. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44(4):491–2.
Parra DA, Chan M, Krishnamurthy G, Spiegel L, Amaral JG, Temple MJ, et al. Use and accuracy of US guidance for image-guided injections of the temporomandibular joints in children with arthritis. Pediatr Radiol. 2010;40(9):1498–504.
Habibi S, Ellis J, Strike H, Ramanan AV. Safety and efficacy of US-guided CS injection into temporomandibular joints in children with active JIA. Rheumatology. 2012;51(5):874–7.
Chakraborty A, Datta T, Lingegowda D, Khemka R. Ultrasound-guided temporomandibular joint injection for chronic posthemimandibulectomy Jaw Pain. A A Case Rep. 2016;7(10):203–6.
Moon SY, Chung H. Ultra-thin rigid diagnostic and therapeutic arthroscopy during arthrocentesis: development and preliminary clinical findings. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;37(1):5–9.
Gayle EA, Young SM, McKenna SJ, McNaughton CD. Septic arthritis of the temporomandibular joint: case reports and review of the literature. J Emerg Med. 2013;45(5):675–8.
Symanski JS, Gimarc D, Chan B, Stephenson J, Markhardt BK, Ross AB. Ultrasound-guided temporomandibular joint aspiration: technique and results in six cases of suspected septic arthritis. Skeletal Radiol. 2023;52(5):1033–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-022-04225-z.
Lawrence CR, East B, Rashid A, Tytherleigh-Strong GM. The prevalence of osteoarthritis of the sternoclavicular joint on computed tomography. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2017;26(1):e18–22.
Min KS, Lopez A, Powlan FJ, Pham B, Lause G. Ultrasound-guided sternoclavicular joint injection: technique and case series. JSES Rev Rep, Tech. 2021;1:393–7.
DePalma AF. Surgical anatomy of acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joints. Surg Clin North Am. 1963;43(6):1541–50.
Widman DS, Craig JG, van Holsbeeck MT. Sonographic detection, evaluation and aspiration of infected acromioclavicular joints. Skelet Radiol. 2001;30(7):388–92.
Scillia A, Issa K, Mcinerney VK. Accuracy of in vivo palpation-guided acromioclavicular joint injection assessed with contrast material and fluoroscopic evaluations. Skelet Radiol. 2015;44(8):1135–9.
Wasserman BR, Pettrone S, Jazrawi LM, Zuckerman JD, Rokito AS. Accuracy of acromioclavicular joint injections. Am J Sport Med. 2013;41(1):149–52.
Colegate-Stone T, Allom R, Singh R, Elias DA, Standring S, Sinha J. Classification of the morphology of the acromioclavicular joint using cadaveric and radiological analysis. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 2010;92(5):743–6.
Peck E, Lai JK, Pawlina W, Smith J. Accuracy of ultrasound-guided versus palpation-guided acromioclavicular joint injections: a cadaveric study. PM R. 2010;2(9):817–21.
Borbas P, Kraus T, Clement H, Grechenig S, Weinberg AM, Heidari N. The influence of ultrasound guidance in the rate of success of acromioclavicular joint injection: an experimental study on human cadavers. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2012;21(12):1694–7.
Sabeti-Aschraf M, Lemmerhofer B, Lang S, Schmidt M, Funovics PT, Ziai P, et al. Ultrasound guidance improves the accuracy of the acromioclavicular joint infiltration: a prospective randomized study. Knee Surg, Sport Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(2):292–5.
Edelson G, Saffuri H, Obid E, Lipovsky E, Ben-David D. Successful injection of the acromioclavicular joint with use of ultrasound: anatomy, technique, and follow-up. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2014;23(10):e243–50.
Rawat U, Pierce JL, Evans S, Chhabra AB, Nacey NC. High-resolution MR imaging and US anatomy of the thumb. Radiographics. 2016;36(6):1701–16.
Sonne-Holm S, Jacobsen S. Osteoarthritis of the first carpometacarpal joint: a study of radiology and clinical epidemiology. Results from the Copenhagen Osteoarthritis Study. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2006;14(5):496–500.
Khorashadi L, Ha AS, Chew FS. Radiologic guide to surgical treatment of first carpometacarpal joint osteoarthritis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;198(5):1152–60.
Maarse W, Watts AC, Bain GI. Medium-term outcome following intra-articular corticosteroid injection in first CMC joint arthritis using fluoroscopy. Hand Surg. 2009;14(2–3):99–104.
McCann PA, Wakeley CJ, Amirfeyz R. The effect of ultrasound guided steroid injection on progression to surgery in thumb CMC arthritis. Hand Sur. 2014;19(1):49–52.
To P, McClary KN, Sinclair MK, Stout BA, Foad M, Hiratzka S, et al. The accuracy of common hand injections with and without ultrasound: an anatomical study. Hand. 2017;12(6):591–6.
Umphrey GL, Brault JS, Hurdle MFB, Smith J. Ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection of the trapeziometacarpal joint: description of technique. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89(1):153–6.
De Smet L. The distal radioulnar joint in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Orthop Belg. 2006;72(4):381–6.
Cerezal L, Abascal F, García-Valtuille R, Del Piñal F. Wrist MR arthrography: how, why, when. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005;43(4):709–31.
Raza K, Lee CY, Pilling D, Heaton S, Situnayake RD, Carruthers DM, et al. Ultrasound guidance allows accurate needle placement and aspiration from small joints in patients with early inflammatory arthritis. Rheumatology. 2003;42(8):976–9.
Bashir MA, Arya A. A simple technique for injecting the small joints of the fingers and thumb using finger traps for traction. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2016;98(5):343–4.
Becker I, Woodley SJ, Stringer MD. The adult human pubic symphysis: a systematic review. J Anat. 2010;217(5):475–87.
Rennie WJ, Lloyd DM. Sportsmans groin: the inguinal ligament and the Lloyd technique. J Belg Soc Radiol. 2017;101(Suppl 2):1–4.
Morelli V, Smith V. Groin injuries in athletes. Am Fam Physician. 2001;64(8):1405–14.
Schilders E, Bismil Q, Robinson P, PJ OC, Gibbon WW, Talbot JC. Adductor-related groin pain in competitive athletes. Role of adductor enthesis, magnetic resonance imaging, and entheseal pubic cleft injections. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 2007;89(10):2173–8.
Byrne CA, Bowden DJ, Alkhayat A, Kavanagh EC, Eustace SJ. Sports-related groin pain secondary to symphysis pubis disorders: correlation between MRI findings and outcome after fluoroscopy-guided injection of steroid and local anesthetic. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209(2):380–8.
Murphy G, Foran P, Murphy D, Tobin O, Moynagh M, Eustace S. “Superior cleft sign” as a marker of rectus abdominus/adductor longus tear in patients with suspected sportsman’s hernia. Skelet Radiol. 2013;42(6):819–25.
Reilly I, Chockalingam N, Naemi R. Palpation-guided intra-articular injection of the first metatarsophalangeal joint: injection technique and safe practice for novice practitioners. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;2(3):1–7.
Wempe MK, Sellon JL, Sayeed YA, Smith J. Feasibility of first metatarsophalangeal joint injections for sesamoid disorders: a cadaveric investigation. PM R. 2012;4(8):556–60.
Hansford BG, Mills MK, Hanrahan CJ, Yablon CM. Pearls and pitfalls of fluoroscopic-guided foot and ankle injections: what the radiologist needs to know. Skelet Radiol. 2019;48(11):1661–74.
Acknowledgements
Illustrations prepared by Dr. Dyan V. Flores, Ottawa, Canada, and Ilija Visnjic, Belgrade, Serbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
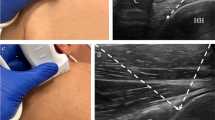
62-year-old male with chronic pain on top of the shoulder, for steroid injection. Long-axis US image of the ACJ demonstrates the in-plane approach with the transducer parallel to the joint and depiction of the entire needle (arrows) as it is inserted in a lateral to medial direction. Technique details shown in Figure 6. (MP4 2.08 mb)
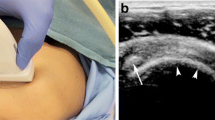
71-year-old male with longstanding SCJ OA and repeat injection for recurrent chest pain. Short-axis US image of the sternoclavicular joint shows the out-of-plane approach with the transducer perpendicular to the joint and the needle tip (arrow) within the joint space. Note the echogenic foci representing the injectate swirling around the needle tip. Technique details shown in Figure 2. (MP4 371 kb)
68-year-old female with longstanding left TMJ pain, suspected inflammatory arthritis, for steroid injection. Long-axis US image of the left TMJ shows localization of the condyle by dynamic maneuver from open to closed-mouth position, before using an in-plane approach to insert the needle (arrows) in a caudal-cranial direction. Echogenic foci representing the injectate at the target site (encircled) are also shown. (MP4 1.56 mb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Flores, D.V., Sampaio, M.L. & Agarwal, A. Ultrasound-guided injection and aspiration of small joints: techniques, pearls, and pitfalls. Skeletal Radiol 53, 195–208 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-023-04374-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-023-04374-9