Abstract
Introduction
Fatty degeneration of the gluteal muscles on metal artefact reduction sequence (MARS) MRI has been shown to correlate with poor functional outcomes, particularly in patients with total hip arthroplasty (THA). Standardized, reliable classification systems that permit assessment of fatty gluteal infiltration are needed for clinical decision making. This study aimed to compare the reproducibility and accuracy of commonly used MRI classification systems for fatty gluteal atrophy in THA patients.
Methods
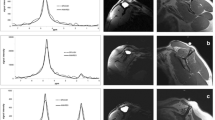
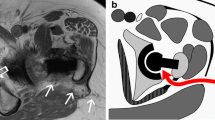
MARS magnetic resonance images of 82 patients with unilateral THA were analysed by three independent trained observers. The readers evaluated fatty degeneration of the gluteus minimus, gluteus medius, and gluteus maximus according to 3 widely used classification systems: Goutallier, Quartile, and Bal and Lowe. Interobserver and intraobserver repeatability were determined using the weighted Kappa test. Quantitative evaluation of the proportion of intramuscular fat based on MR signal intensities was obtained and represented the gold standard.
Results
Mean interobserver agreement for the Quartile classification system (0.93) was higher compared with Goutallier classification system (0.87) and the Bal and Lowe classification system (0.83; range 0.79–0.88; p = 0.04). Intraobserver repeatability was significantly higher for the Quartile classification system (weighted kappa 0.91, 0.89, 0.85) compared with the Bal and Lowe classification system (weighted kappa 0.83, 0.77, 0.75; p < 0.01) and Goutallier classification system (weighted kappa 0.83, 0.77, 0.75; p = 0.04). Agreement with the gold standard measurements was significantly higher in the Quartile classification system (0.88, 0.84, 0.81) compared with the Goutallier classification system (0.80, 0.77, 0.78; p = 0.02) and Bal and Lowe classification system (0.76, 0.74, 0.73; p < 0.01).
Discussion
This study directly compared three clinically used MRI classification systems for fatty gluteal muscle atrophy in THA patients. Our findings demonstrate that although all three classification systems demonstrate good reproducibility and accuracy, the Quartile classification system is superior to the others in terms of intraobserver reliability and accuracy to quantify fatty gluteal degeneration in THA patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurtz SM, Lau E, Ong K, Zhao K, Kelly M, Bozic KJ. Future young patient demand for primary and revision joint replacement: national projections from 2010 to 2030. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:2606–12.
Halawi MJ, Jongbloed W, Baron S, Savoy L, Williams VJ, Cote MP. Patient dissatisfaction after primary total joint arthroplasty: the patient perspective. J Arthroplast. 2019;34:1093–6.
Okafor L, Chen AF. Patient satisfaction and total hip arthroplasty: a review. Arthroplasty. 2019;1:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42836-019-0007-3.
Damm P, Zonneveld J, Brackertz S, Streitparth F, Winkler T. Gluteal muscle damage leads to higher in vivo hip joint loads 3 months after total hip arthroplasty. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0190626.
Müller M, Tohtz S, Dewey M, Springer I, Perka C. Evidence of reduced muscle trauma through a minimally invasive anterolateral approach by means of MRI. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:3192–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1378-5.
Lachiewicz PF. Abductor tendon tears of the hip: evaluation and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19:385–91.
Shellock FG, Mink JH, Curtin S, Friedman MJ. MR imaging and metallic implants for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: assessment of ferromagnetism and artifact. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1992;2:225–8.
Czervionke LF, Daniels DL, Wehrli FW, Mark LP, Hendrix LE, Strandt JA, et al. Magnetic susceptibility artifacts in gradient-recalled echo MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1988;9:1149–55.
Susa M, Oguro S, Kikuta K, Nishimoto K, Horiuchi K, Jinzaki M, et al. Novel MR imaging method--MAVRIC--for metal artifact suppression after joint replacement in musculoskeletal tumor patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:377.
Wang T, Shao L, Xu W, Chen H, Huang W. Comparison of morphological changes of gluteus medius and abductor strength for total hip arthroplasty via posterior and modified direct lateral approaches. Int Orthop. 2019;43:2467–75.
Miozzari HH, Dora C, Clark JM, Notzli HP. Late repair of abductor avulsion after the transgluteal approach for hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplast. 2010;25:450–457.e1.
Thaunat M, Clowez G, Desseaux A, Murphy CG, Sbiyaa M, Noel E, et al. Influence of muscle fatty degeneration on functional outcomes after endoscopic gluteus medius repair. Arthroscopy. 2018;34:1816–24.
Berber R, Khoo M, Cook E, Guppy A, Hua J, Miles J, et al. Muscle atrophy and metal-on-metal hip implants: a serial MRI study of 74 hips. Acta Orthop. 2015;86:351–7.
Rai S, Meng C, Wang X, Chaudhary N, Jin S, Yang S, et al. Gluteal muscle contracture: diagnosis and management options. SICOT-J. 2017;3:1.
Chi AS, Long SS, Zoga AC, Parker L, Morrison WB. Association of gluteus medius and minimus muscle atrophy and fall-related hip fracture in older individuals using computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016;40:238–42.
Goutallier D, Postel J-M, Gleyze P, Leguilloux P, Van Driessche S. Influence of cuff muscle fatty degeneration on anatomic and functional outcomes after simple suture of full-thickness tears. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2003;12:550–4.
Zanetti M, Gerber C, Hodler J. Quantitative assessment of the muscles of the rotator cuff with magnetic resonance imaging. Investig Radiol. 1998;33:163–70.
Tingart MJ, Apreleva M, Lehtinen JT, Capell B, Palmer WE, Warner JJP. Magnetic resonance imaging in quantitative analysis of rotator cuff muscle volume. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003:104–10.
Spencer EEJ, Dunn WR, Wright RW, Wolf BR, Spindler KP, McCarty E, et al. Interobserver agreement in the classification of rotator cuff tears using magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36:99–103.
Williams MD, Lädermann A, Melis B, Barthelemy R, Walch G. Fatty infiltration of the supraspinatus: a reliability study. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2009;18:581–7.
Engelken F, Wassilew GI, Kohlitz T, Brockhaus S, Hamm B, Perka C, et al. Assessment of fatty degeneration of the gluteal muscles in patients with THA using MRI: reliability and accuracy of the Goutallier and quartile classification systems. J Arthroplast. 2014;29:149–53.
Bal BS, Lowe JA. Muscle damage in minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty: MRI evidence that it is not significant. Instr Course Lect. 2008;57:223–9.
Choi S-J, Koch KM, Hargreaves BA, Stevens KJ, Gold GE. Metal artifact reduction with MAVRIC SL at 3-T MRI in patients with hip arthroplasty. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;204:140–7.
Kwon YM, Liow MHL, Dimitriou D, Tsai TY, Freiberg AA, Rubash HE. What is the natural history of “asymptomatic” pseudotumours in metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty? Minimum 4-year metal artifact reduction sequence magnetic resonance imaging longitudinal study. J Arthroplast. 2016.
Fuchs B, Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Gerber C. Fatty degeneration of the muscles of the rotator cuff: assessment by computed tomography versus magnetic resonance imaging. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 1999;8:599–605.
Kenn W, Böhm D, Gohlke F, Hümmer C, Köstler H, Hahn D. 2D SPLASH: a new method to determine the fatty infiltration of the rotator cuff muscles. Eur Radiol. 2004;14:2331–6.
Pfirrmann CWA, Schmid MR, Zanetti M, Jost B, Gerber C, Hodler J. Assessment of fat content in supraspinatus muscle with proton MR spectroscopy in asymptomatic volunteers and patients with supraspinatus tendon lesions. Radiology. 2004;232:709–15.
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979;86:420–8.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159–74.
Goldstein JM, Fehring TK, Fehring KA. Cystic adverse local tissue reactions in asymptomatic modular metal-on-metal total hips may decrease over time. J Arthroplast. 2016;31:1589–94.
Kwon YM. Evaluation of the painful dual taper modular neck stem total hip arthroplasty: do they all require revision? J Arthroplast. 2016.
Lippe J, Spang JT, Leger RR, Arciero RA, Mazzocca AD, Shea KP. Inter-rater agreement of the Goutallier, Patte, and Warner classification scores using preoperative magnetic resonance imaging in patients with rotator cuff tears. Arthrosc J Arthrosc Relat Surg. 2012;28:154–9.
Oh JH, Kim SH, Choi J-A, Kim Y, Oh CH. Reliability of the grading system for fatty degeneration of rotator cuff muscles. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:1558–64.
Bridge P, Fielding A, Rowntree P, Pullar A. Intraobserver variability: should we worry? J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2016:217–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klemt, C., Simeone, F.J., Melnic, C.M. et al. MARS MRI assessment of fatty degeneration of the gluteal muscles in patients with THA: reliability and accuracy of commonly used classification systems. Skeletal Radiol 50, 665–672 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03611-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-020-03611-9