Abstract.
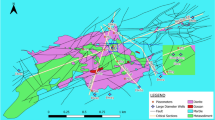
To validate the geological and piezometric subdivision of two carbonate massifs in southern Spain, and to carry out a characterisation of aquifer behaviour, 23 representative springs and wells were monitored at the end of the dry season. Temperature, pH and electrical conductivity and major ions were measured. Calcite (SIc) and dolomite (SId) saturation indexes, PCO2 and cation exchange index (CEI) were calculated with the SOLUTEQ code. Water flow and electrical conductivity were also monitored at the eight main springs. Sierra Blanca and Sierra Mijas constitute an important carbonate hydrogeological unit in southern Spain, supplying water to 250,000 people on the Costa del Sol. Hydrochemically, two basic types of aquifer behaviour can be distinguished: conduit and diffuse flow systems. The former are found in the calcareous marbles of the western Sierra Blanca. They present a calcium-bicarbonate hydrochemical facies with low mineralization, and with quick outflow and water chemistry variations in response to rainfall; hydrochemical time series present frequency distributions with several modes. The diffuse flow systems are characteristic of the dolomitic marbles of eastern Sierra Blanca and Sierra Mijas. These waters are more highly mineralised and present a calcium-magnesium bicarbonate facies. They are characterised by slight discharge fluctuations, with nearly unimodal frequency distributions. Aquifer behaviour affects groundwater exploitation in terms of the success of boreholes and the specific yield of the pumping wells, which are less in the conduit flow systems in western Sierra Blanca.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andreo, .B., Carrasco, .F., Bakalowicz, .M. et al. Use of hydrodynamic and hydrochemistry to characterise carbonate aquifers. Case study of the Blanca–Mijas unit (Málaga, southern Spain). Env Geol 43, 108–119 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0614-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0614-z